Are the GenAI Agents Taking Over? Navigating the Future of Work and Society
Artificial IntelligenceAre the GenAI Agents Taking Over? Navigating the Future of Work and Society
Table of Contents
- Are the GenAI Agents Taking Over? Navigating the Future of Work and Society
- Chapter 1: The Evolution of GenAI
- Chapter 2: Human-AI Collaboration
- Chapter 3: Ethical Considerations
- Chapter 4: The Future Job Landscape
- Chapter 5: Strategies for Adaptation
- Conclusion: Embracing the Future with GenAI
- Practical Resources
- Specialized Applications
Chapter 1: The Evolution of GenAI
Historical Context
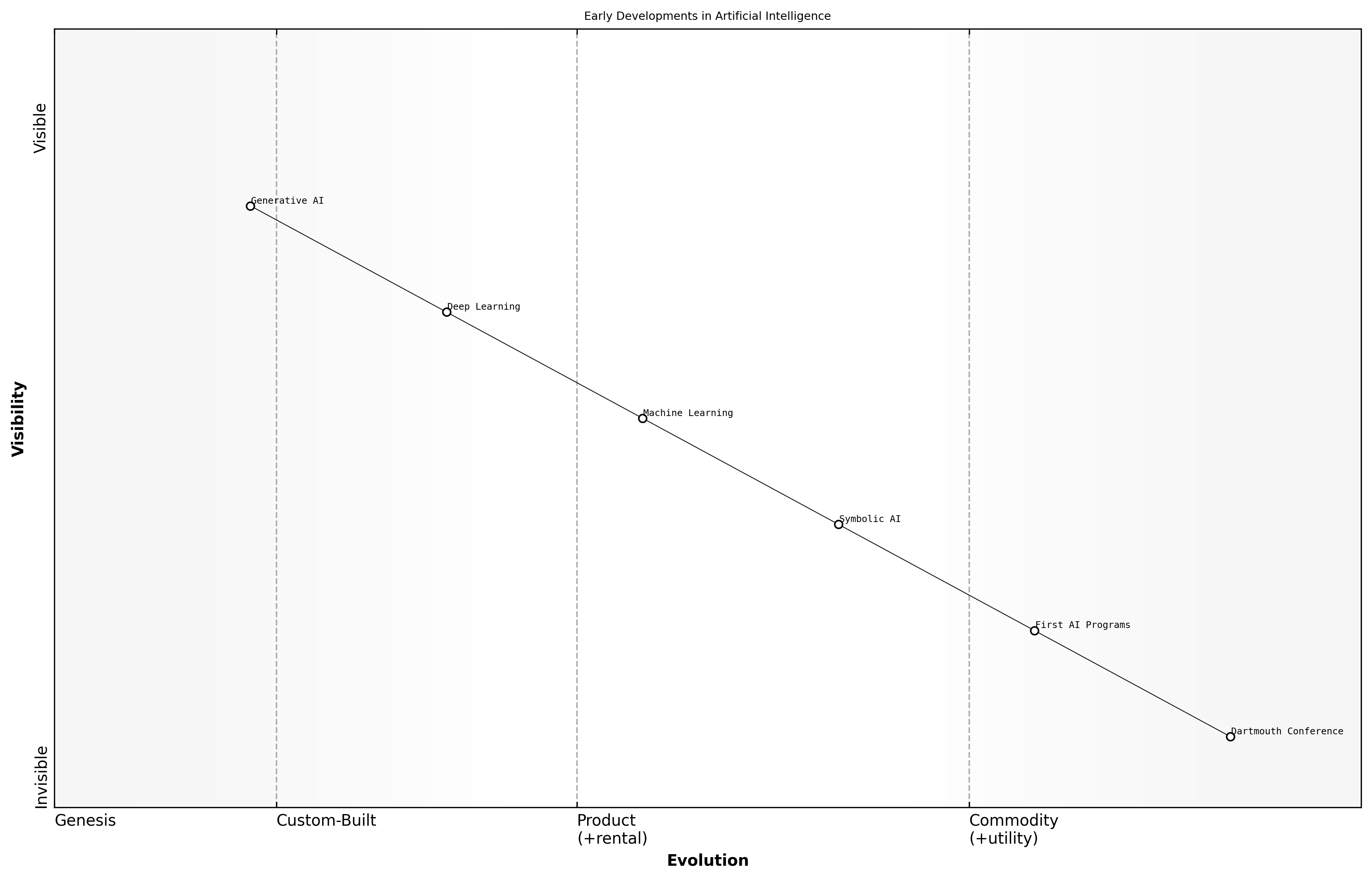
Early Developments in Artificial Intelligence
The early developments in artificial intelligence (AI) set the foundation for the transformative technologies we see today. From the initial conceptual frameworks to the first practical applications, these advancements were pivotal in shaping the trajectory of AI research and implementation. Understanding this historical context is crucial for appreciating the evolution of generative AI (GenAI) and its implications for society.
- The Dartmouth Conference of 1956, which is widely regarded as the birth of AI as a field of study.
- The development of the first AI programs, such as the Logic Theorist and the General Problem Solver, which demonstrated the potential of machines to perform tasks that required human-like reasoning.
- The introduction of symbolic AI, which focused on manipulating symbols and rules to simulate human cognition.
The early days of AI were marked by optimism and groundbreaking discoveries, says a leading expert in the field.
These early milestones laid the groundwork for subsequent innovations in AI, including the rise of machine learning and deep learning techniques. The foundational theories and methodologies developed during this period continue to influence contemporary AI research and applications, making it essential to reflect on these historical contexts as we navigate the future of GenAI.
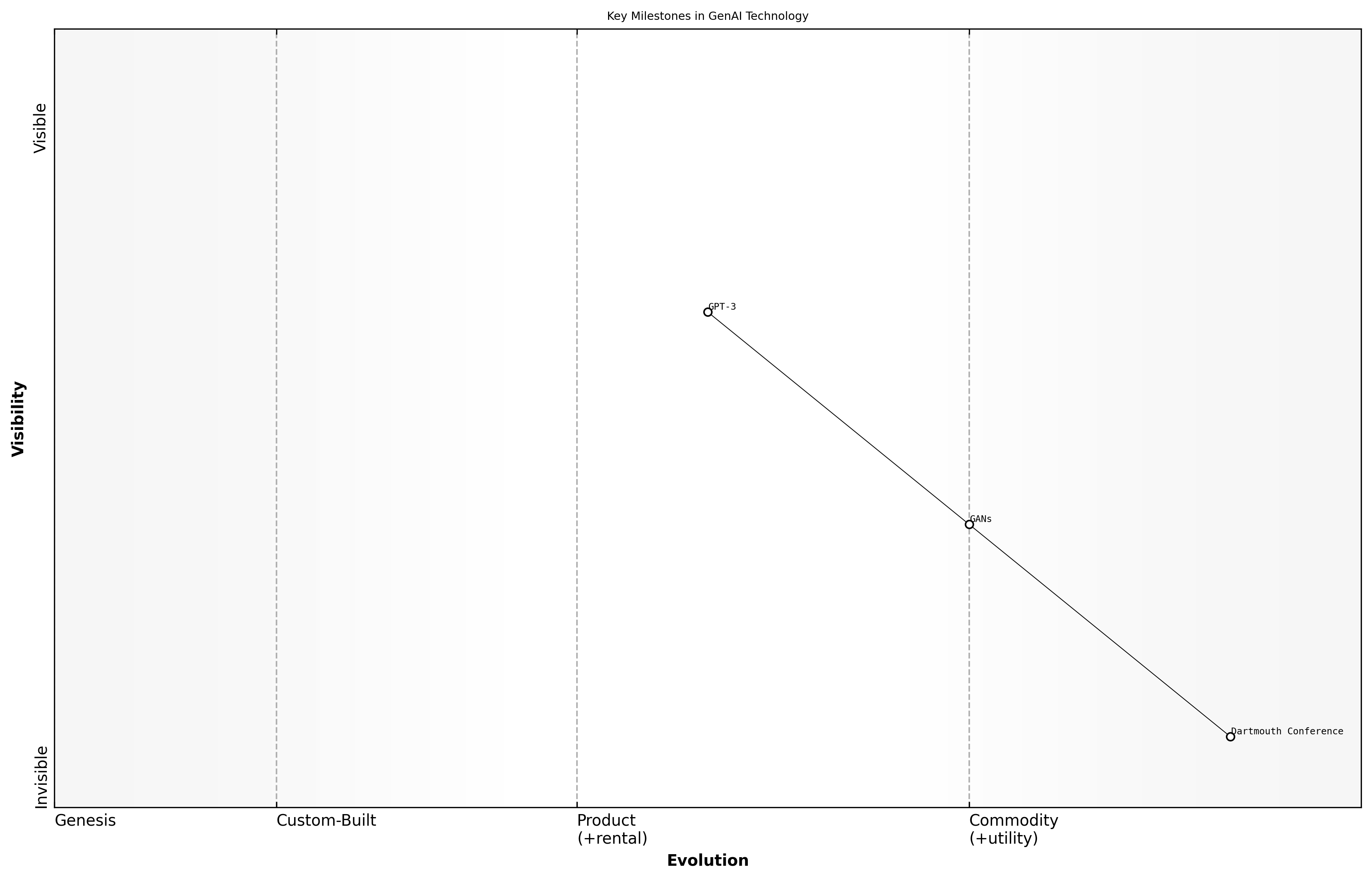
Key Milestones in GenAI Technology
The evolution of Generative AI (GenAI) technology has been marked by several key milestones that have significantly shaped its development and application across various sectors. Understanding these milestones is crucial for grasping the current landscape of GenAI and its potential future trajectory.
- 1956: The Dartmouth Conference, where the term 'artificial intelligence' was coined, laying the groundwork for future AI research.
- 2014: The introduction of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) by Ian Goodfellow, which revolutionised the way machines generate new data.
- 2020: The release of OpenAI's GPT-3, showcasing the capabilities of large language models in generating human-like text.
These milestones not only highlight technological advancements but also reflect the growing interest and investment in AI research and applications. Each breakthrough has contributed to the capabilities of GenAI agents, enabling them to perform increasingly complex tasks.
The rapid progression of GenAI technology is a testament to the collaborative efforts of researchers and practitioners across disciplines, says a leading expert in the field.
As we explore these milestones, it becomes evident that the journey of GenAI is not just about technological prowess but also about the ethical and societal implications that accompany such advancements. This context is essential for understanding how GenAI agents are poised to take on more significant roles in various sectors.
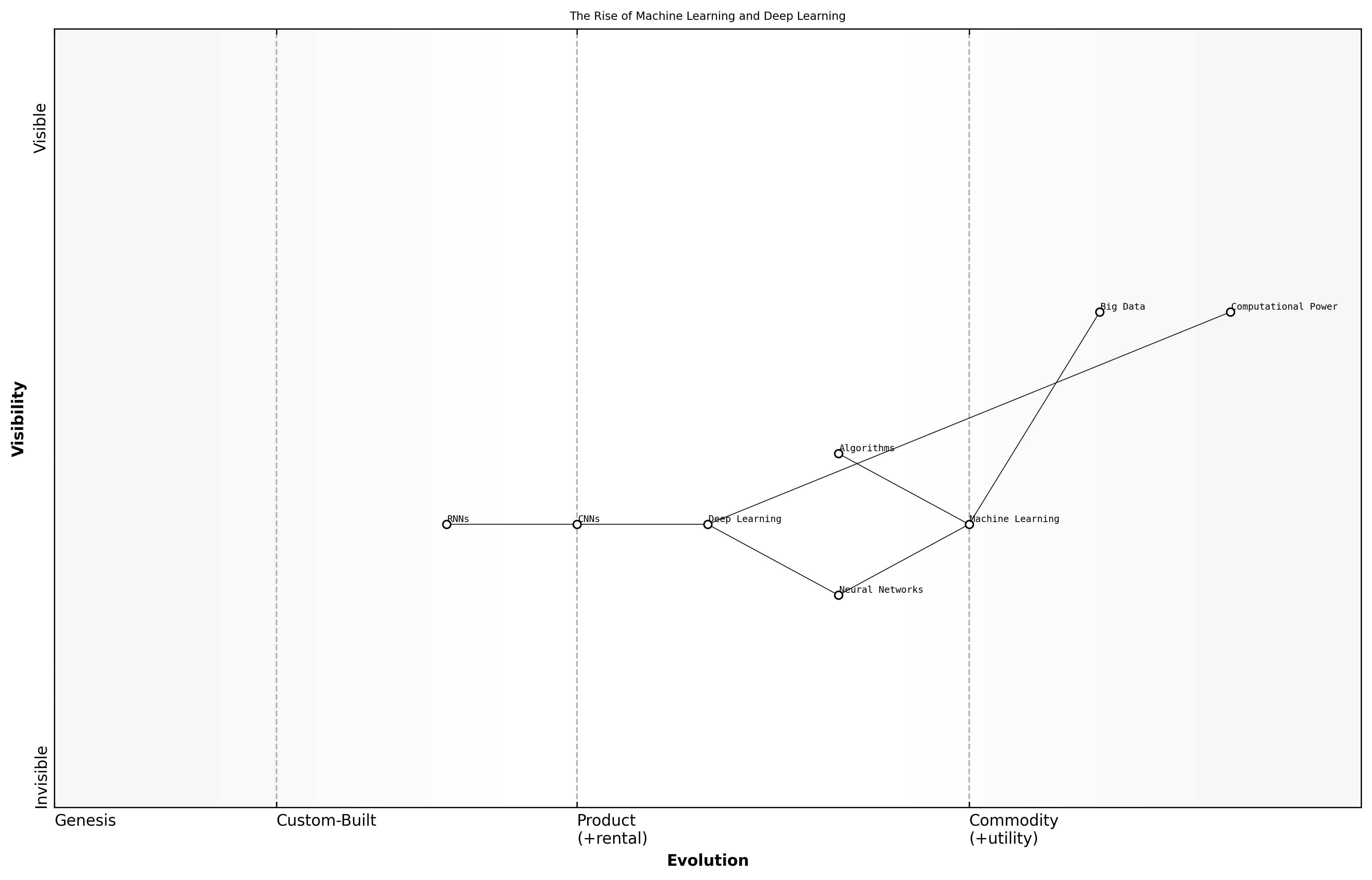
The Rise of Machine Learning and Deep Learning
The rise of machine learning and deep learning represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies have transformed the landscape of data processing and analysis, enabling systems to learn from data and improve over time without explicit programming. Understanding the historical context of these advancements is crucial for grasping their significance in the broader narrative of GenAI.
- The inception of machine learning can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with early algorithms designed to mimic human learning processes.
- The introduction of neural networks in the 1980s marked a significant milestone, laying the groundwork for deep learning by enabling more complex data representations.
- The explosion of big data in the 21st century provided the necessary fuel for machine learning and deep learning models, allowing them to thrive and evolve.
By the late 2000s, advancements in computational power and the availability of vast datasets catalysed the resurgence of deep learning. This period saw the development of sophisticated architectures such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), which have since become foundational in various applications, including image and speech recognition.
The convergence of increased computational power, large datasets, and innovative algorithms has propelled machine learning and deep learning into the forefront of technological advancement, says a leading expert in the field.
The implications of these technologies extend beyond mere technical achievements; they are reshaping industries, influencing decision-making processes, and redefining the relationship between humans and machines. As we delve deeper into the evolution of GenAI, it is essential to appreciate how the historical context of machine learning and deep learning informs our current understanding and future trajectories.
Technological Advancements
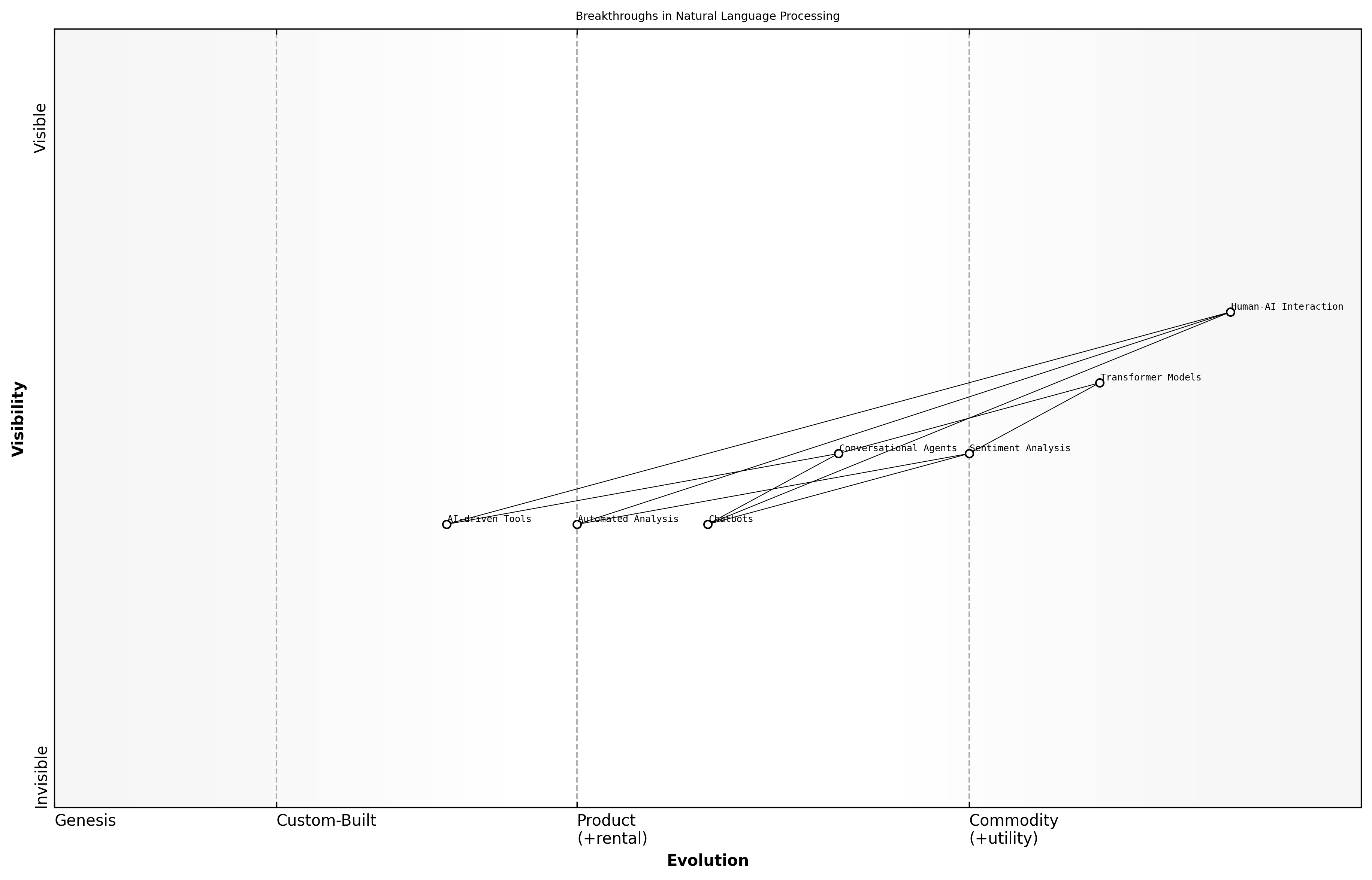
Breakthroughs in Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has undergone significant breakthroughs in recent years, fundamentally transforming the way machines understand and generate human language. These advancements are crucial in the context of GenAI, as they enable more sophisticated interactions between humans and AI systems, enhancing communication, accessibility, and efficiency across various sectors.
- Development of transformer models, such as BERT and GPT, which have revolutionised contextual understanding.
- Improvements in sentiment analysis, allowing for nuanced interpretation of emotions in text.
- Advancements in conversational agents, enabling more natural and human-like interactions.
The introduction of transformer architectures has been a game changer in NLP. Unlike previous models that processed language sequentially, transformers can consider the entire context of a sentence simultaneously. This capability has led to significant improvements in tasks such as translation, summarisation, and question-answering, making AI systems far more effective in understanding human language.
The ability of AI to comprehend and generate language at a human-like level is not just a technological feat; it is a fundamental shift in how we interact with machines, says a leading expert in the field.
Moreover, breakthroughs in NLP have practical applications in government and public sector contexts. For instance, automated systems can now assist in processing citizen inquiries, analysing public sentiment on policy issues, and even drafting reports, thereby streamlining operations and improving service delivery.
- Chatbots for citizen engagement and support services.
- Automated analysis of social media for public sentiment tracking.
- AI-driven tools for drafting and reviewing policy documents.
As we look to the future, the continuous evolution of NLP technologies will likely lead to even more innovative applications. The integration of these advancements into government operations not only promises enhanced efficiency but also raises important questions about ethics, accountability, and the role of human oversight in AI-driven processes.
Advancements in Computer Vision
The field of computer vision has witnessed remarkable advancements over the past decade, significantly enhancing the capabilities of GenAI systems. These advancements are not only transforming industries but also reshaping the way we interact with technology. As a leading expert in the field notes, the integration of deep learning techniques has propelled computer vision into new realms of accuracy and efficiency.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: The introduction of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has revolutionised image recognition tasks, allowing machines to achieve human-level performance in various applications.
- Real-Time Processing: Advances in hardware, such as GPUs and TPUs, have enabled real-time image and video processing, which is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles and surveillance systems.
- 3D Vision and Augmented Reality: The development of algorithms that can interpret 3D data has paved the way for augmented reality applications, enhancing user experiences in sectors like gaming and retail.
These advancements align closely with the overarching theme of GenAI agents taking over specific tasks traditionally performed by humans. By automating complex visual recognition processes, organisations can improve efficiency and reduce human error.
The future of computer vision lies in its ability to learn from vast amounts of data, enabling machines to not only see but also understand the context of what they observe, says a senior government official.
Practical applications of these advancements are evident in various sectors. For instance, in healthcare, computer vision is being used to analyse medical images for early detection of diseases, while in agriculture, it aids in monitoring crop health through aerial imagery.
The Role of Big Data in GenAI Development
Big Data plays a pivotal role in the development of Generative AI (GenAI) by providing the vast amounts of information necessary for training complex models. The integration of Big Data into GenAI not only enhances the accuracy and efficiency of AI systems but also enables the creation of more sophisticated and nuanced outputs. As the volume of data continues to grow exponentially, the potential for GenAI applications expands, influencing various sectors including healthcare, finance, and public administration.
- Data Diversity: Big Data encompasses a wide range of data types, including structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data, which enriches the training datasets for GenAI.
- Enhanced Learning: The availability of large datasets allows for more robust machine learning algorithms, improving the model's ability to generalise from training data.
- Real-Time Insights: Big Data technologies facilitate real-time data processing, enabling GenAI systems to adapt and learn from new information continuously.
The synergy between Big Data and GenAI is particularly evident in the context of natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision, where large datasets are essential for training models that can understand and generate human-like text or interpret visual information accurately. This relationship underscores the importance of data governance and ethical considerations in the collection and use of Big Data, ensuring that the information used to train GenAI systems is both representative and free from bias.
The effectiveness of GenAI systems is directly proportional to the quality and quantity of data they are trained on, highlighting the indispensable role of Big Data in this technological evolution, says a leading expert in the field.
Chapter 2: Human-AI Collaboration
Case Studies in Various Industries
Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care
The integration of Generative AI (GenAI) in healthcare has transformed patient care by enhancing diagnosis, personalising treatment plans, and improving operational efficiencies. This subsection explores various case studies that illustrate the successful application of GenAI technologies in healthcare settings, demonstrating how these innovations are reshaping the patient experience and outcomes.
- Case Study 1: AI-Driven Diagnostic Tools in Radiology
- Case Study 2: Virtual Health Assistants for Chronic Disease Management
- Case Study 3: Predictive Analytics for Patient Readmission Prevention
In the first case study, AI-driven diagnostic tools have been implemented in radiology departments, significantly reducing the time taken to analyse medical images. By leveraging deep learning algorithms, these tools can identify anomalies with high accuracy, allowing radiologists to focus on complex cases and improving overall diagnostic efficiency.
The second case study highlights the use of virtual health assistants that support patients with chronic diseases. These AI-powered platforms provide patients with tailored health advice, medication reminders, and symptom tracking, leading to improved adherence to treatment plans and better health outcomes.
Lastly, predictive analytics has been utilised to prevent patient readmissions. By analysing historical patient data, healthcare providers can identify at-risk patients and implement proactive measures, such as follow-up appointments or targeted interventions, ultimately reducing hospital readmission rates.
The application of GenAI in healthcare not only enhances patient care but also optimises resource allocation, allowing healthcare professionals to deliver more effective services, says a leading expert in the field.
Finance: Risk Assessment and Fraud Detection
The integration of GenAI in the finance sector has revolutionised risk assessment and fraud detection, enabling institutions to analyse vast amounts of data with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This subsection explores various case studies that illustrate the successful application of AI technologies in these critical areas.
- Case Study 1: A leading bank implemented an AI-driven risk assessment model that reduced loan default rates by 30% through enhanced predictive analytics.
- Case Study 2: An investment firm utilised machine learning algorithms to detect fraudulent trading patterns, resulting in a 50% increase in detection rates compared to traditional methods.
- Case Study 3: A fintech startup developed a real-time fraud detection system using natural language processing to analyse customer interactions, leading to a significant decrease in false positives.
These case studies not only highlight the efficacy of GenAI in mitigating risks and identifying fraudulent activities but also underscore the importance of human oversight in the decision-making process. As one senior financial analyst noted, the combination of AI's analytical power and human intuition creates a robust framework for risk management.
The future of finance lies in harnessing the power of AI to enhance our capabilities in risk management and fraud detection, says a leading expert in the field.
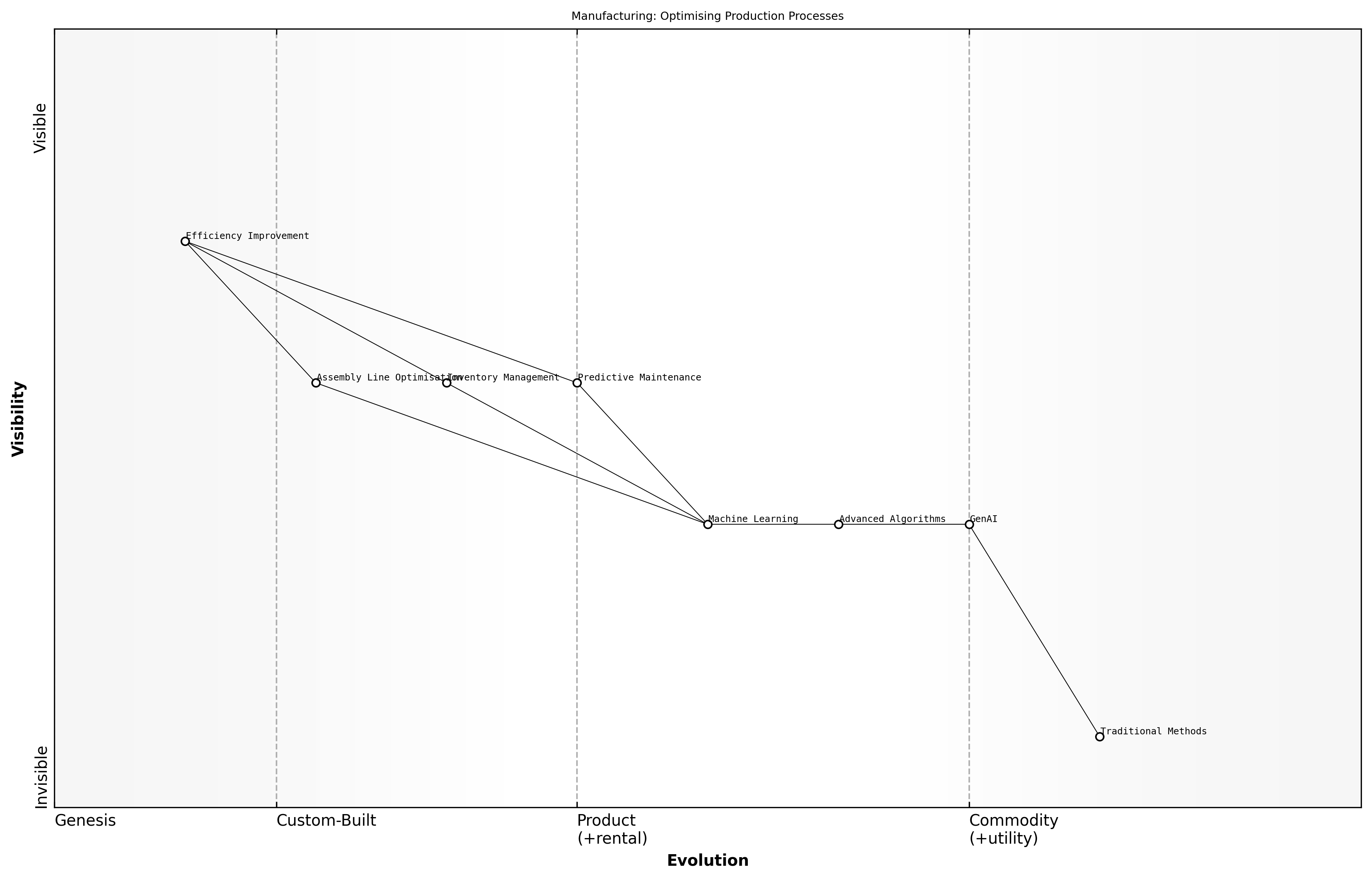
Manufacturing: Optimising Production Processes
The integration of GenAI in manufacturing processes has revolutionised the way production is optimised. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality. This subsection explores several case studies that illustrate the successful application of GenAI in various manufacturing settings.
- Case Study 1: A leading automotive manufacturer implemented GenAI to streamline its assembly line, resulting in a 20% reduction in production time and a significant decrease in defects.
- Case Study 2: A global electronics firm utilised predictive maintenance powered by GenAI, which decreased machine downtime by 30% and extended equipment lifespan.
- Case Study 3: A textile manufacturer adopted GenAI for inventory management, optimising stock levels and reducing excess inventory by 25%.
These case studies highlight the transformative potential of GenAI in manufacturing. By automating routine tasks and providing data-driven insights, organisations can focus on strategic decision-making and innovation.
The future of manufacturing lies in the seamless collaboration between humans and AI, enabling unprecedented levels of efficiency and creativity, says a leading expert in the field.
Lessons Learned from Successful Partnerships
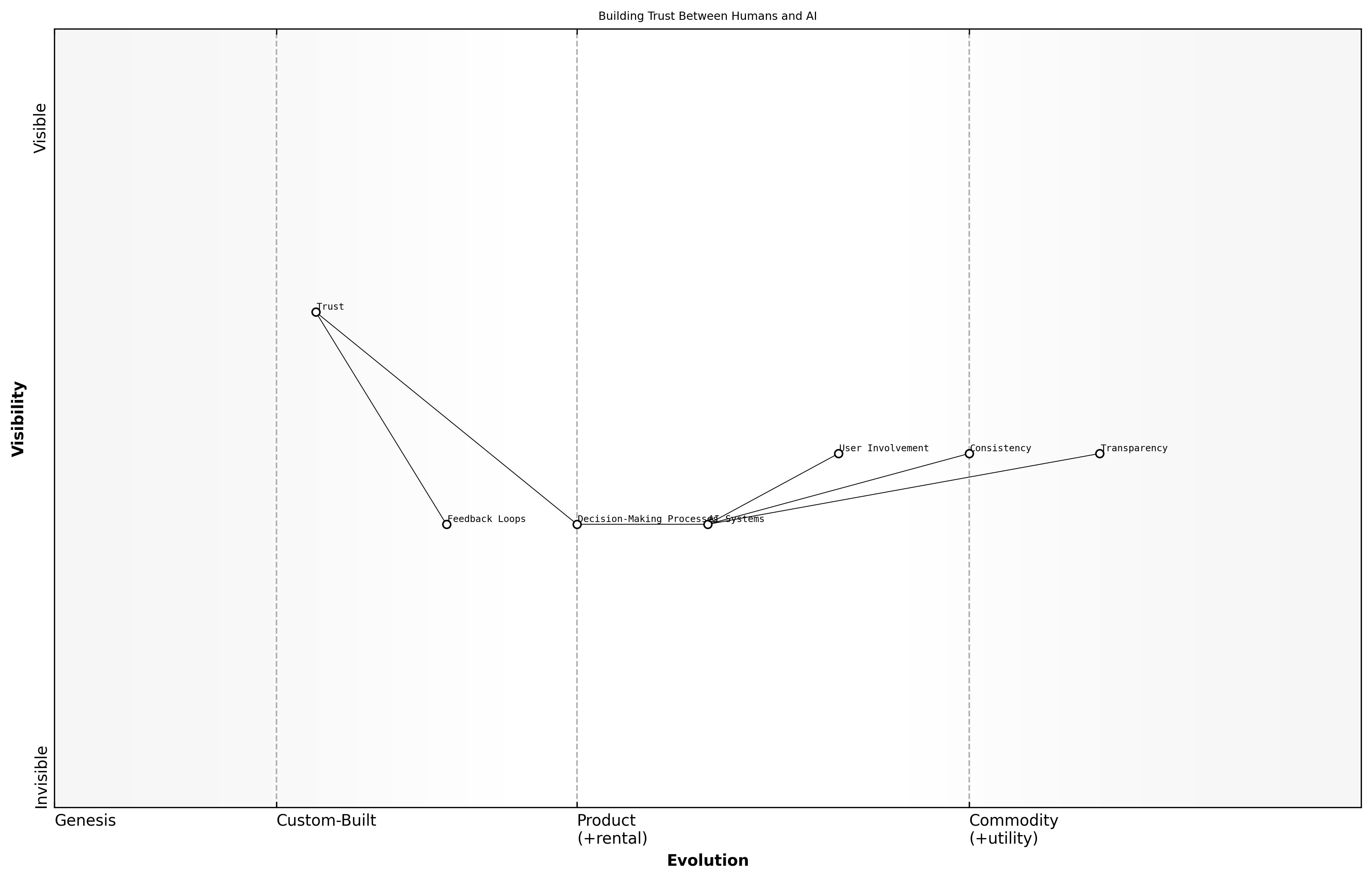
Building Trust Between Humans and AI
Building trust between humans and AI is paramount for successful collaboration. As AI systems become more integrated into decision-making processes, understanding how to foster this trust is essential for both individuals and organisations. Trust not only enhances user acceptance but also improves the overall effectiveness of AI applications.
- Transparency: Providing clear insights into how AI systems operate and make decisions fosters trust. Users are more likely to engage with AI when they understand its processes.
- Consistency: AI systems should demonstrate reliability in their outputs. Consistent performance builds confidence among users, making them more willing to rely on AI recommendations.
- User Involvement: Engaging users in the development and refinement of AI systems ensures that their needs and concerns are addressed, leading to a stronger sense of ownership and trust.
Practical applications of these principles can be seen in various sectors. For instance, in healthcare, AI-driven diagnostic tools that explain their reasoning to clinicians have shown higher acceptance rates. In finance, algorithms that provide insights into their decision-making processes help build trust with clients.
Trust is built through consistent interactions and the ability to explain decisions, says a leading expert in the field.
- Case Study: A government agency implemented an AI system for public service delivery, ensuring transparency in its operations. This led to increased public trust and engagement.
- Example: In a manufacturing setting, AI systems that provide real-time feedback to workers have improved collaboration and trust, resulting in enhanced productivity.
- Insight: Continuous feedback loops between users and AI systems can significantly enhance trust, as users feel their input is valued and acted upon.
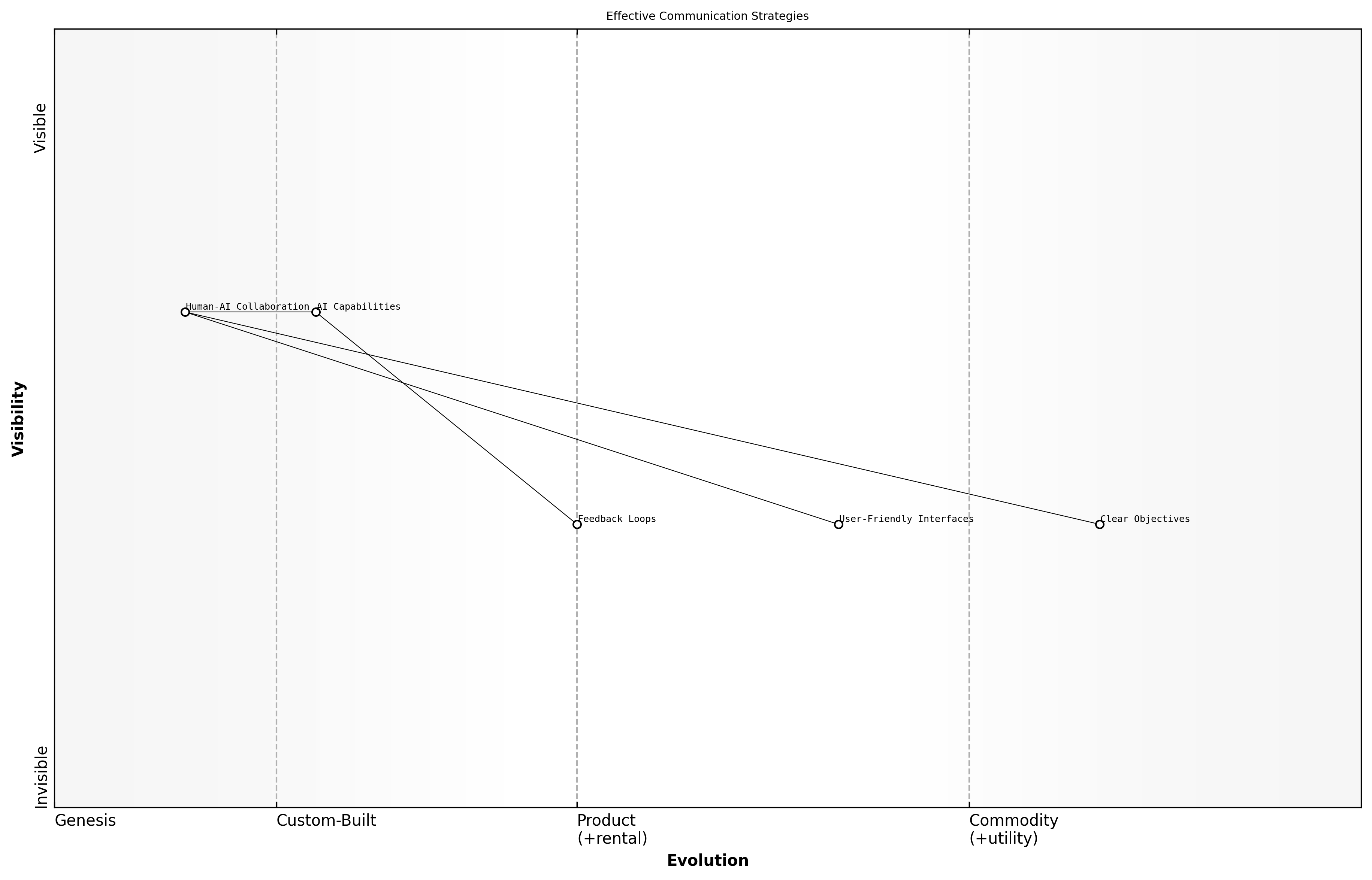
Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication strategies are essential for fostering successful partnerships between humans and AI systems. As AI technologies become increasingly integrated into various sectors, understanding how to communicate effectively with these systems can enhance collaboration, improve outcomes, and build trust among stakeholders.
- Establish clear objectives and expectations for AI interactions
- Utilise user-friendly interfaces that facilitate easy communication
- Encourage feedback loops to continuously improve AI performance
One of the key lessons learned from successful partnerships is the importance of establishing clear objectives and expectations. When both human users and AI systems understand their roles and the desired outcomes, the collaboration is more likely to yield positive results.
User-friendly interfaces play a critical role in effective communication. By designing systems that are intuitive and accessible, organisations can reduce the learning curve for users and encourage more meaningful interactions with AI.
Encouraging feedback loops is vital for continuous improvement, says a leading expert in the field.
Feedback loops allow users to provide input on AI performance, which can be used to refine algorithms and enhance the overall effectiveness of the system. This iterative process not only improves AI capabilities but also fosters a sense of ownership and collaboration among users.
The Importance of Continuous Learning
The integration of GenAI into various sectors has highlighted the critical role of continuous learning in fostering successful human-AI partnerships. As technology evolves, so too must the skills and knowledge of the workforce. Continuous learning not only enhances individual capabilities but also strengthens the overall effectiveness of AI systems.
- Emphasising adaptability: Professionals must be prepared to adjust their skills and approaches as GenAI technologies develop.
- Encouraging a growth mindset: Cultivating an environment where learning is valued promotes innovation and resilience.
- Leveraging diverse learning resources: Access to various training platforms and materials can enhance understanding and application of GenAI.
In successful partnerships, organisations have recognised that continuous learning is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. This perspective allows teams to stay ahead of technological advancements and maintain a competitive edge.
The most effective collaborations between humans and AI emerge when both parties are committed to learning and evolving together, says a leading expert in the field.
Case studies across various industries illustrate how continuous learning has been pivotal in maximising the benefits of GenAI. For instance, in healthcare, professionals who engage in regular training on AI tools have demonstrated improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies.
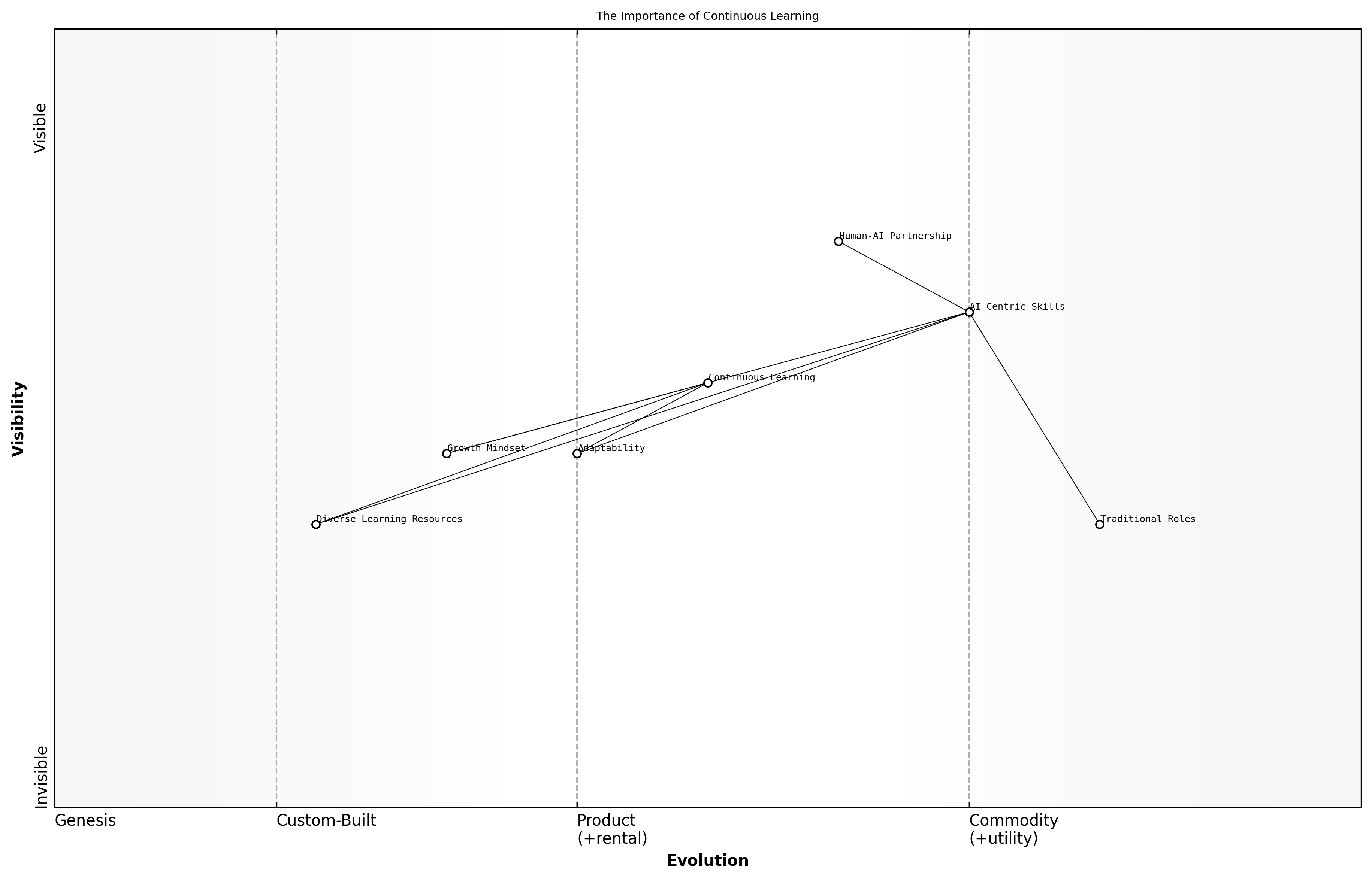
Ultimately, the lessons learned from successful partnerships underscore that continuous learning is not merely an organisational strategy but a fundamental principle that underpins the effective integration of GenAI into the workforce.
Chapter 3: Ethical Considerations
Moral Implications of AI Integration
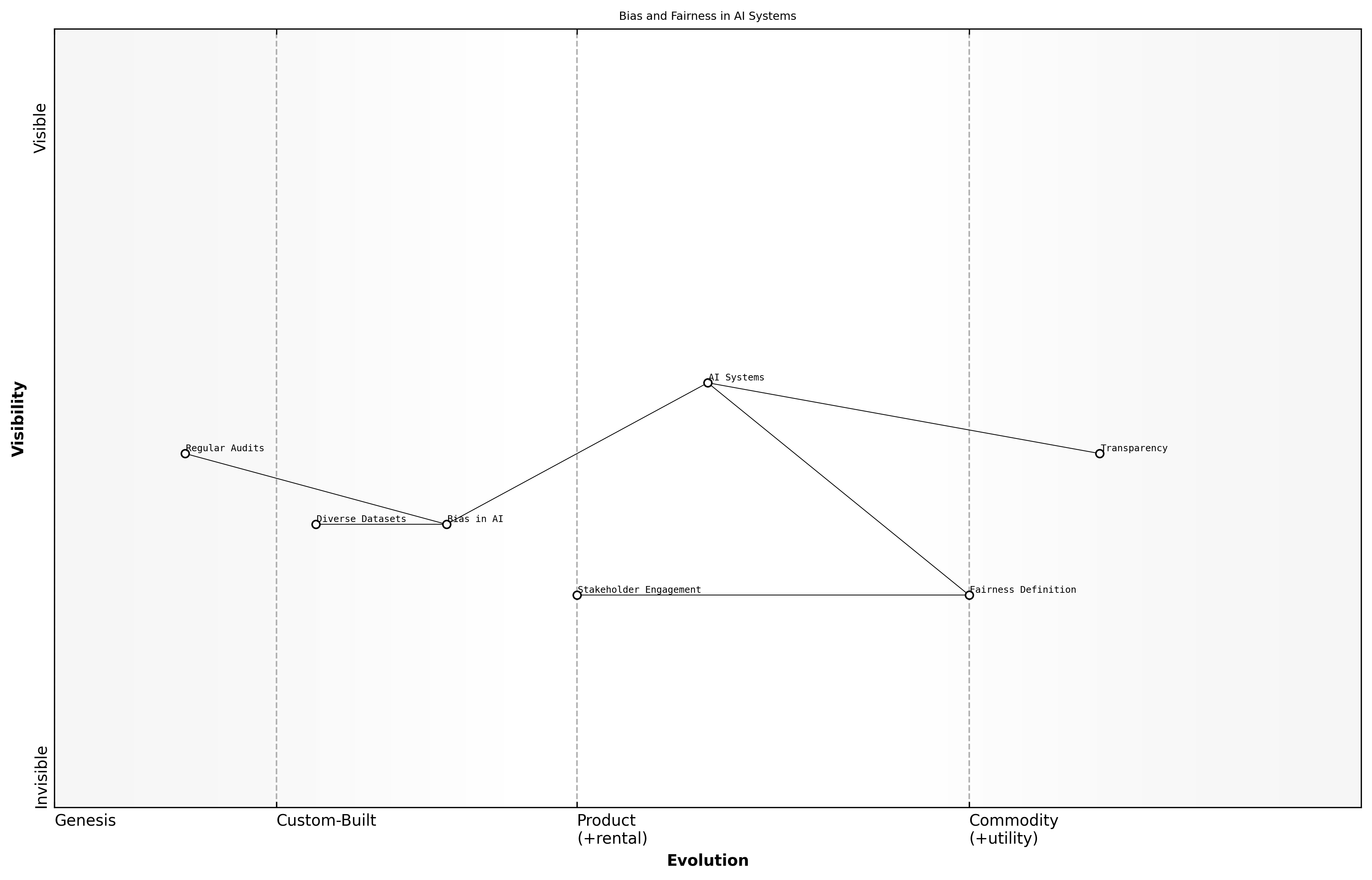
Bias and Fairness in AI Systems
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into various sectors has raised significant moral implications, particularly concerning bias and fairness. As AI systems increasingly influence decision-making processes in critical areas such as hiring, law enforcement, and healthcare, the potential for biased outcomes becomes a pressing ethical concern. Understanding these implications is essential for ensuring that AI technologies serve all segments of society equitably.
- The risk of perpetuating existing societal biases through AI algorithms
- The challenge of defining fairness in diverse contexts
- The importance of transparency in AI decision-making processes
A leading expert in the field notes that bias in AI can often stem from the data used to train these systems. If the training data reflects historical inequalities or prejudices, the AI is likely to replicate these biases in its outputs. This raises questions about accountability and the ethical responsibility of developers and organizations deploying AI technologies.
- Implementing diverse datasets to mitigate bias
- Conducting regular audits of AI systems for fairness
- Engaging stakeholders from various backgrounds in the AI development process
Fairness in AI is not just a technical challenge but a moral imperative that requires ongoing dialogue and commitment from all stakeholders involved.
Privacy Concerns and Data Security
The integration of AI technologies into various sectors raises significant privacy concerns and data security issues. As GenAI agents become more prevalent, they often require access to vast amounts of personal data to function effectively. This reliance on data can lead to ethical dilemmas surrounding consent, data ownership, and the potential for misuse of sensitive information.
- Informed consent: Ensuring that individuals are fully aware of how their data will be used and have the ability to opt-out.
- Data minimisation: Collecting only the data that is necessary for the intended purpose to reduce exposure to potential breaches.
- Robust security measures: Implementing strong encryption and access controls to protect data from unauthorized access.
The moral implications of AI integration extend beyond mere compliance with regulations. They encompass the responsibility of organisations to uphold ethical standards in their data handling practices. A leading expert in the field notes that the failure to address privacy concerns can erode public trust in AI technologies and hinder their adoption.
Organisations must prioritise transparency and accountability in their AI systems to foster trust among users, says a senior government official.
Moreover, the potential for bias in AI algorithms can exacerbate privacy issues. If data used to train AI systems is not representative, it can lead to discriminatory outcomes that affect marginalized groups disproportionately. This highlights the need for ethical oversight and continuous monitoring of AI systems to ensure fairness and equity.
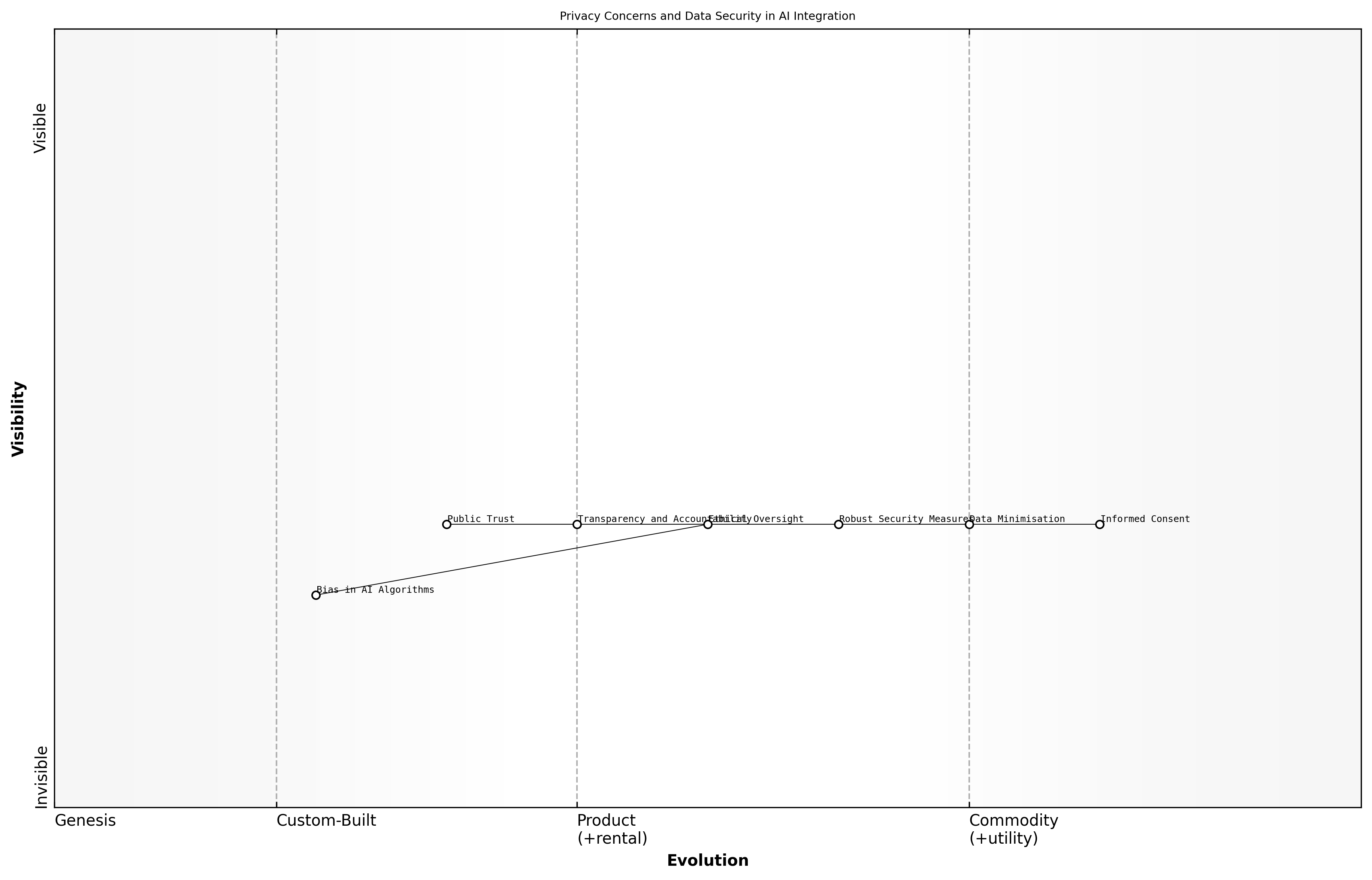
In conclusion, addressing privacy concerns and data security is not just a regulatory requirement but a moral imperative for organisations deploying AI technologies. By adopting best practices and fostering a culture of ethical responsibility, organisations can navigate the complexities of AI integration while safeguarding individual rights.
Accountability and Transparency in AI Decisions
The integration of AI into decision-making processes raises significant moral implications, particularly concerning accountability and transparency. As AI systems increasingly influence critical areas such as healthcare, law enforcement, and public policy, the ethical responsibility for their decisions becomes a pressing concern. Stakeholders must grapple with questions of who is accountable when AI systems make errors or produce biased outcomes.
- The need for clear accountability frameworks that delineate responsibility between AI developers, users, and affected individuals.
- The importance of transparency in AI algorithms to ensure that decision-making processes can be understood and scrutinised by stakeholders.
- The ethical obligation to mitigate biases in AI systems to prevent discrimination and ensure fairness in outcomes.
A leading expert in the field emphasises that accountability in AI is not merely a technical issue but a moral imperative that requires a multi-faceted approach involving policymakers, technologists, and ethicists.
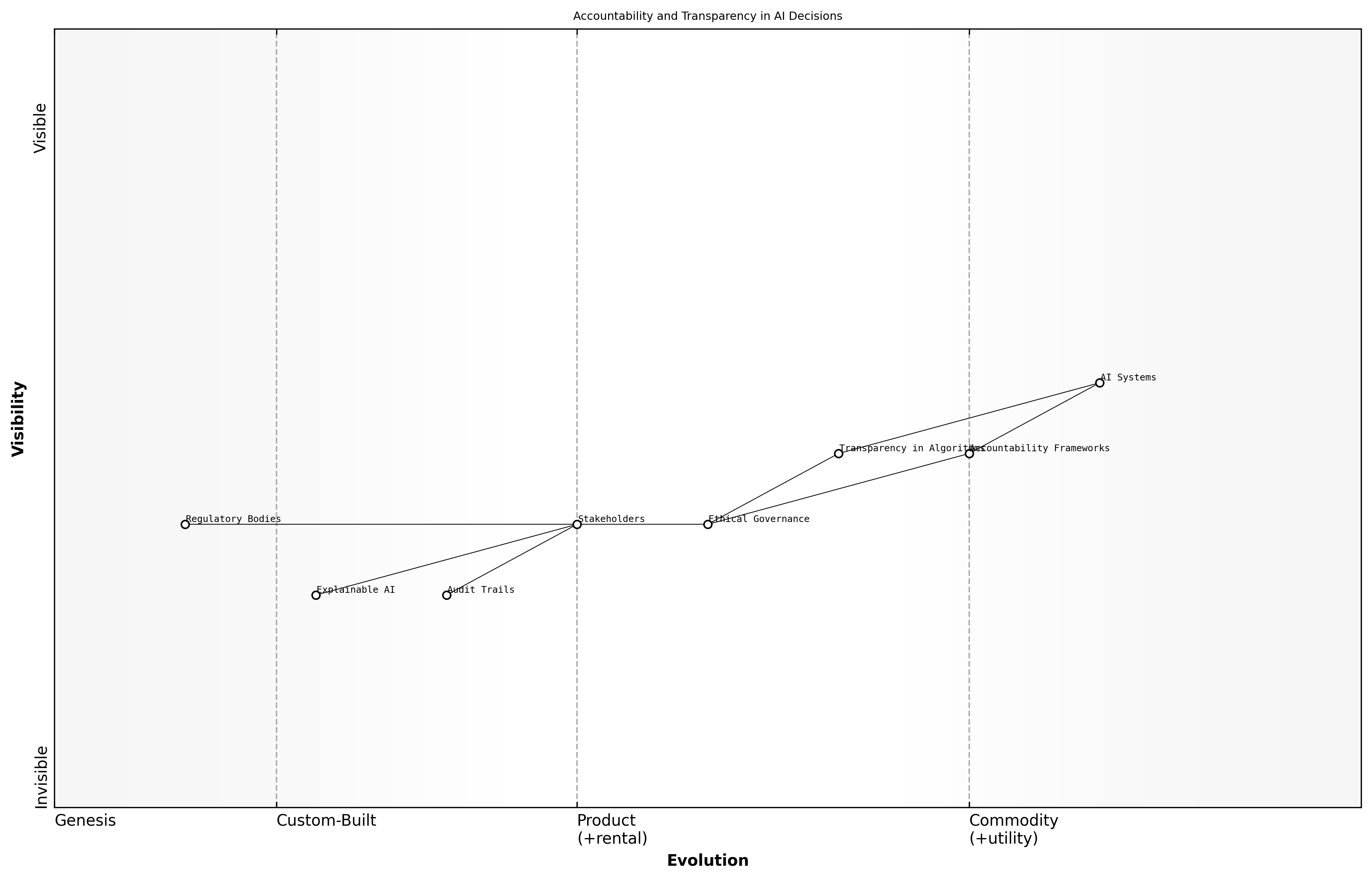
Practical applications of accountability and transparency in AI include the establishment of audit trails for AI decisions, the implementation of explainable AI techniques, and the creation of regulatory bodies tasked with overseeing AI deployment in sensitive areas.
Transparency in AI systems is crucial for fostering public trust and ensuring that AI technologies serve the common good, says a senior government official.
Case studies from the public sector illustrate the importance of these moral implications. For instance, in the deployment of AI in predictive policing, the lack of transparency in algorithms has led to public outcry and demands for accountability, highlighting the need for ethical governance in AI applications.
Regulatory and Policy Frameworks
Current Regulations Governing AI
As the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into various sectors accelerates, the need for robust regulatory and policy frameworks has become increasingly critical. These regulations aim to ensure that AI technologies are developed and deployed in a manner that is ethical, transparent, and accountable, particularly within the public sector where the implications of AI can significantly affect citizens' lives.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, which sets strict guidelines on data privacy and protection, impacting AI systems that process personal data.
- The Algorithmic Accountability Act in the United States, which mandates companies to assess the impact of their automated decision-making systems.
- The proposed AI Act by the European Commission, which categorizes AI applications based on risk levels and establishes compliance requirements for high-risk AI systems.
These regulations reflect a growing recognition of the ethical challenges posed by AI, such as bias, discrimination, and privacy violations. By establishing clear guidelines, governments can foster public trust in AI technologies while promoting innovation.
Regulatory frameworks must evolve alongside technological advancements to address the unique challenges posed by AI, says a leading expert in the field.
In addition to existing regulations, there is an increasing call for the establishment of ethics committees and advisory boards to oversee AI implementations in government. These bodies can provide guidance on ethical considerations and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Establishing clear accountability mechanisms for AI decision-making processes.
- Promoting transparency in AI algorithms to allow for public scrutiny.
- Encouraging collaboration between government, industry, and academia to develop best practices for AI governance.
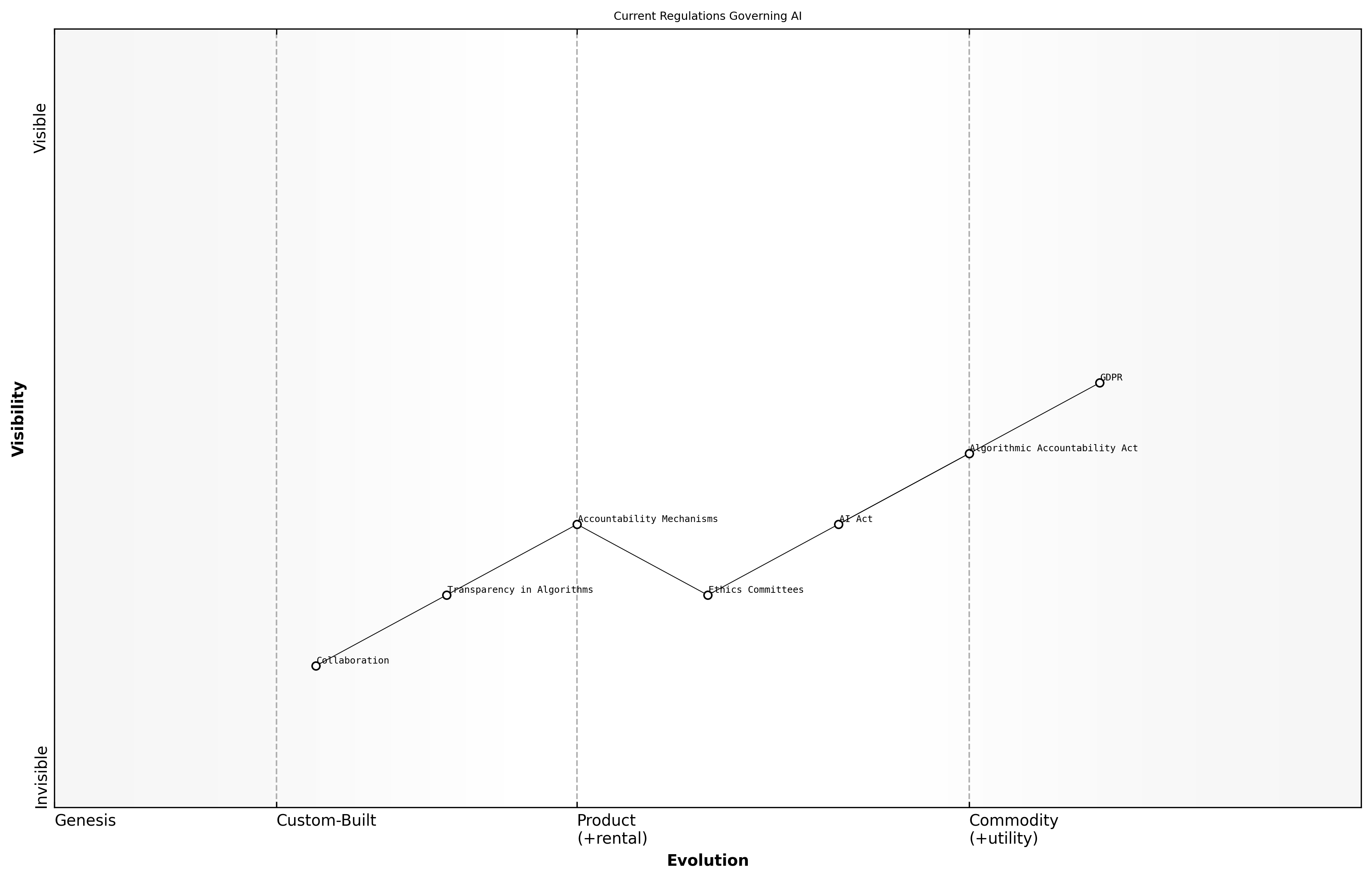
As we navigate the complexities of AI regulation, it is essential for policymakers to engage with stakeholders across various sectors. This collaborative approach will help to create a regulatory landscape that is not only effective but also adaptable to the rapid changes inherent in AI technology.
The Role of Ethics Committees
Ethics committees play a crucial role in the governance of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, particularly in the context of GenAI. As AI technologies become increasingly integrated into public sector operations, the need for ethical oversight has never been more pressing. These committees are tasked with ensuring that AI implementations adhere to ethical standards, protect individual rights, and promote fairness and transparency.
- Reviewing AI projects for ethical compliance before implementation
- Providing guidance on ethical dilemmas encountered during AI development
- Monitoring ongoing AI systems to ensure they operate within ethical guidelines
The establishment of ethics committees is aligned with the growing recognition of the moral implications of AI integration. These committees often consist of diverse stakeholders, including ethicists, technologists, legal experts, and representatives from affected communities. This diversity ensures that multiple perspectives are considered in decision-making processes.
Ethics committees serve as a vital checkpoint in the deployment of AI technologies, ensuring that ethical considerations are not an afterthought but a fundamental part of the design and implementation process, says a leading expert in the field.
In practice, ethics committees can help mitigate risks associated with AI, such as bias, discrimination, and privacy violations. By establishing clear ethical guidelines and frameworks, these committees can foster trust among the public and stakeholders, ultimately leading to more successful AI initiatives.
- Regular training on emerging ethical issues in AI
- Engagement with the community to understand public concerns
- Transparency in decision-making processes and outcomes
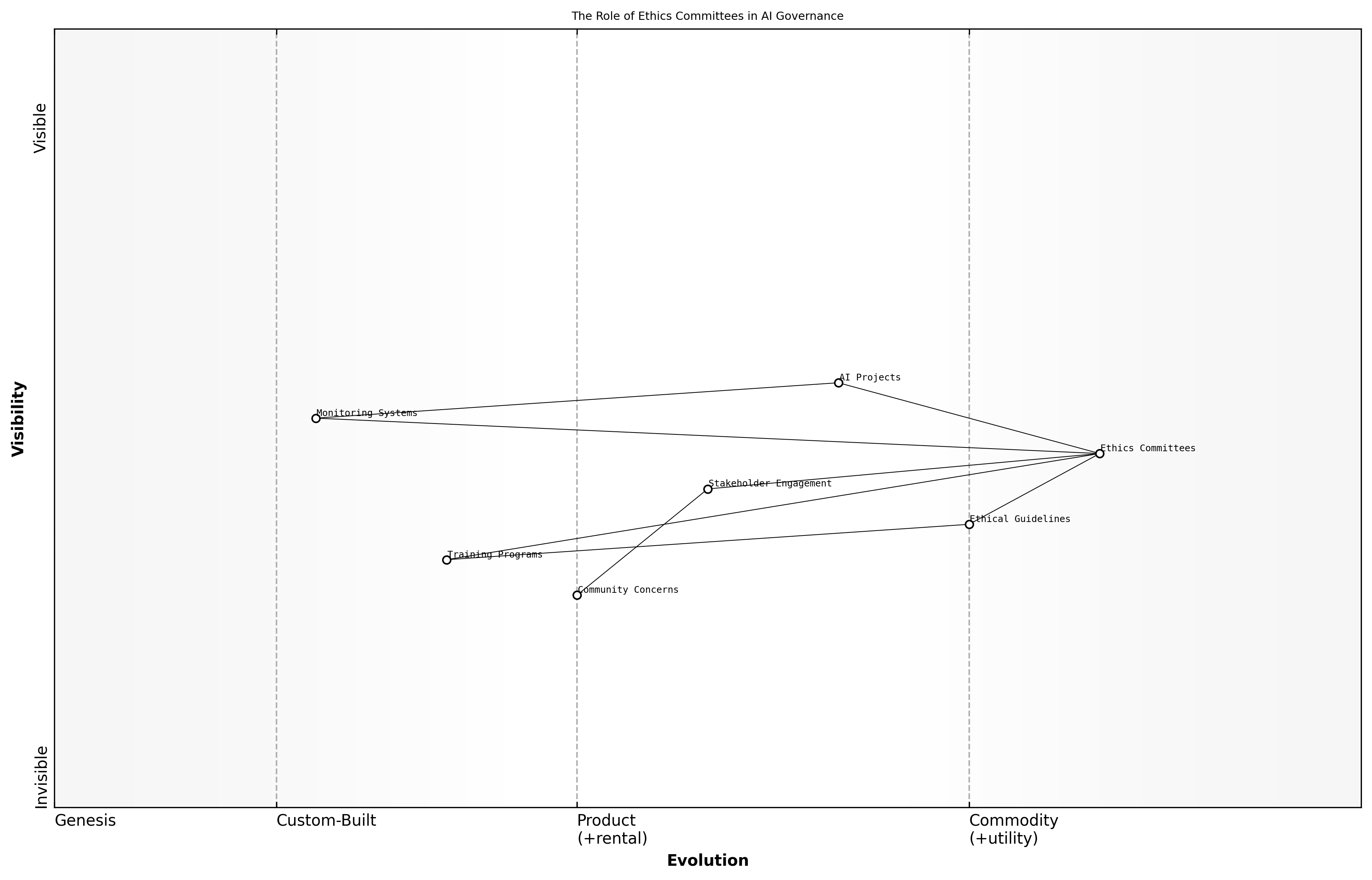
Case studies from various government sectors illustrate the effectiveness of ethics committees. For instance, a senior government official noted that the establishment of an ethics committee in their department led to more robust discussions around AI deployment, ultimately resulting in policies that better protected citizen rights.
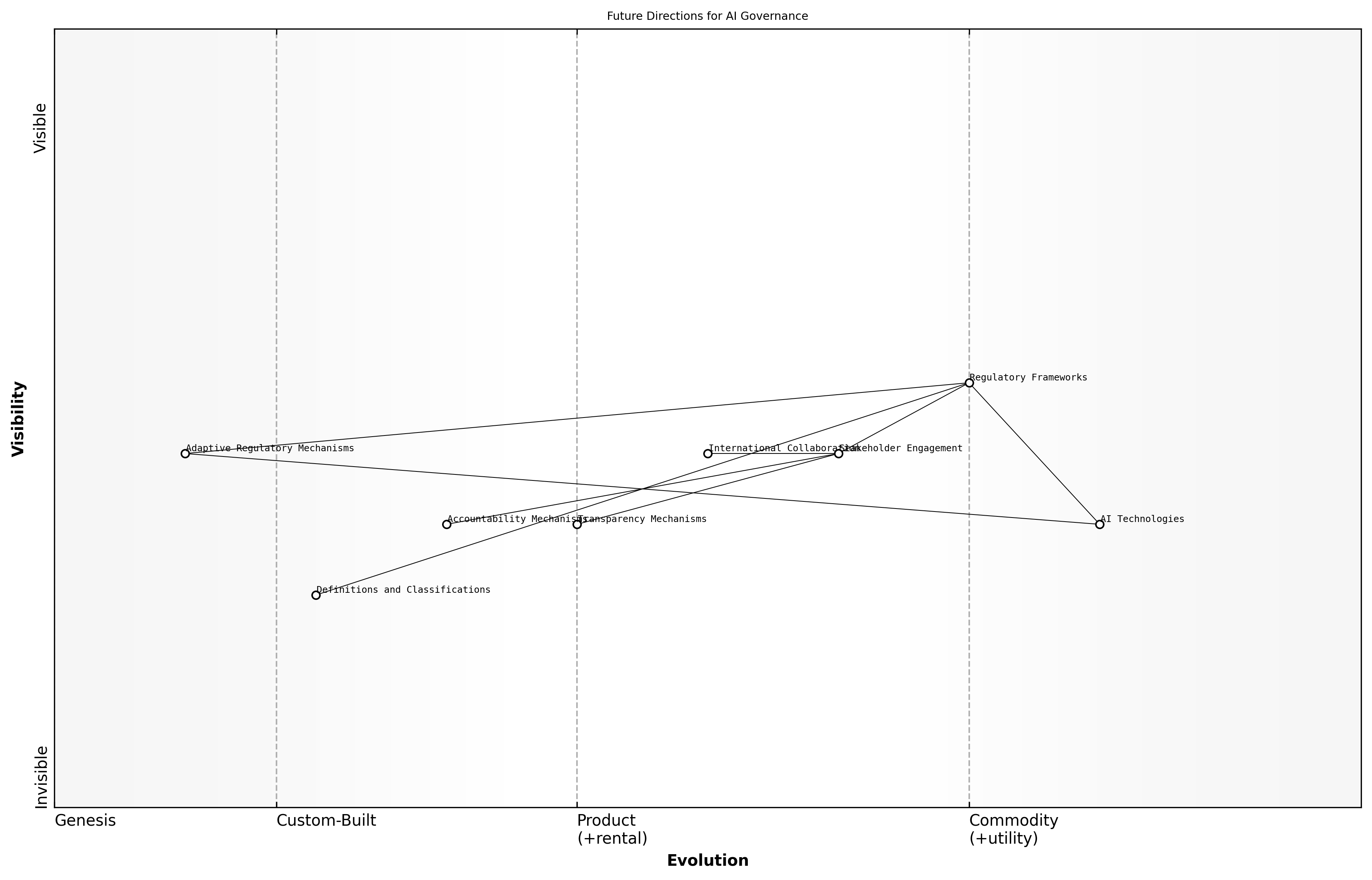
Future Directions for AI Governance
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve and integrate into various sectors, the need for robust regulatory and policy frameworks becomes increasingly critical. Effective governance of AI technologies is essential not only to ensure compliance with existing laws but also to address the unique challenges posed by AI systems. This section explores the current landscape of AI governance and outlines future directions for developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks that can adapt to the rapid pace of technological advancement.
- Establishing clear definitions and classifications of AI technologies to facilitate regulation
- Creating adaptive regulatory mechanisms that can evolve with technological advancements
- Ensuring stakeholder engagement in the development of policies to reflect diverse perspectives
A leading expert in the field notes that the complexity of AI systems necessitates a multi-faceted approach to governance, incorporating insights from technology, ethics, and law. This holistic perspective is crucial for developing frameworks that not only mitigate risks but also promote innovation.
- Enhancing international collaboration to create unified standards and regulations
- Promoting transparency in AI decision-making processes to build public trust
- Implementing mechanisms for accountability that hold developers and users responsible for AI outcomes
The future of AI governance will require a balance between regulation and innovation, ensuring that we do not stifle technological progress while safeguarding public interest, says a senior government official.
Chapter 4: The Future Job Landscape
Predictions for Job Roles
Emerging Job Categories in the Age of GenAI
The advent of Generative AI (GenAI) technologies is reshaping the job landscape, creating new roles that were previously unimaginable. As organisations increasingly integrate AI into their operations, the demand for professionals who can effectively collaborate with these systems is growing. This section explores predictions for job roles that are likely to emerge in the age of GenAI, focusing on the skills and competencies required to thrive in this evolving environment.
- AI Ethics Consultant: Professionals who ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed ethically, addressing concerns such as bias, fairness, and accountability.
- AI Trainers and Educators: Individuals responsible for training AI systems, including curating data sets and refining algorithms to enhance performance.
- Human-AI Interaction Specialists: Experts who design and optimise the interfaces between humans and AI systems, ensuring seamless collaboration and user experience.
- Data Curators: Professionals tasked with managing and maintaining high-quality data sets that AI systems rely on for learning and decision-making.
- AI Policy Advisors: Specialists who provide guidance on the regulatory and policy frameworks governing the use of AI in various sectors.
These emerging roles highlight the necessity for a workforce that is not only technically proficient but also adept in ethical considerations and human-centric design. As organisations adapt to the capabilities of GenAI, the emphasis will shift towards interdisciplinary skills that combine technical knowledge with an understanding of societal impacts.
The future of work will demand a new breed of professionals who can navigate the complexities of AI technologies while ensuring that human values remain at the forefront, says a leading expert in workforce development.
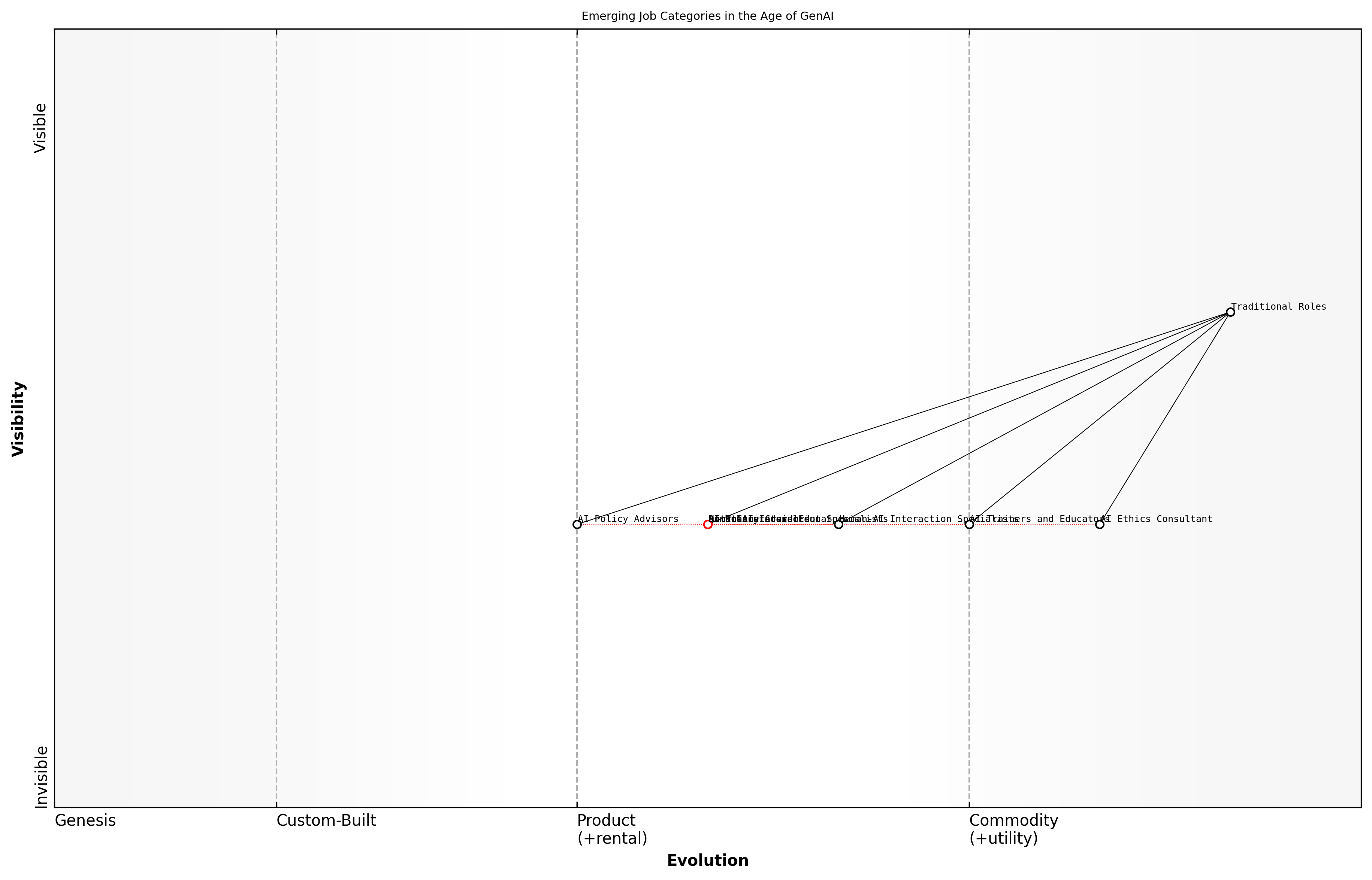
In conclusion, as GenAI continues to evolve, the job market will reflect this transformation. Professionals must be prepared to embrace lifelong learning and adapt to new roles that prioritise collaboration with AI technologies, ensuring that they remain relevant and valuable in an increasingly automated world.
The Decline of Traditional Roles
As we navigate the evolving landscape of work influenced by Generative AI (GenAI), it is crucial to understand the implications for traditional job roles. The integration of GenAI technologies is expected to reshape the workforce significantly, leading to the decline of certain roles while simultaneously creating new opportunities. This transformation is not merely a trend but a fundamental shift in how work is conceptualised and executed, particularly within the public sector.
- Routine and Repetitive Tasks: Roles that primarily involve routine tasks are at high risk of automation. Positions in data entry, basic customer service, and assembly line work are likely to see significant declines as GenAI systems take over these functions.
- Middle Management: The rise of AI-driven analytics and decision-making tools may reduce the need for traditional middle management roles. AI can provide insights and recommendations that allow organisations to streamline operations without the need for extensive managerial oversight.
- Creative Roles: While some may argue that creativity is inherently human, GenAI is increasingly capable of generating content, designs, and even strategic ideas. This could lead to a redefinition of creative roles, where human input is focused on higher-level conceptualisation rather than execution.
The decline of traditional roles necessitates a proactive approach to workforce development. As certain jobs become obsolete, it is essential for individuals and organisations to adapt by reskilling and upskilling their workforce. This shift will not only mitigate the impact of job loss but also prepare employees for emerging roles that leverage GenAI technologies.
The future of work will require a workforce that is agile and adaptable, capable of embracing new technologies and methodologies, says a leading expert in workforce development.
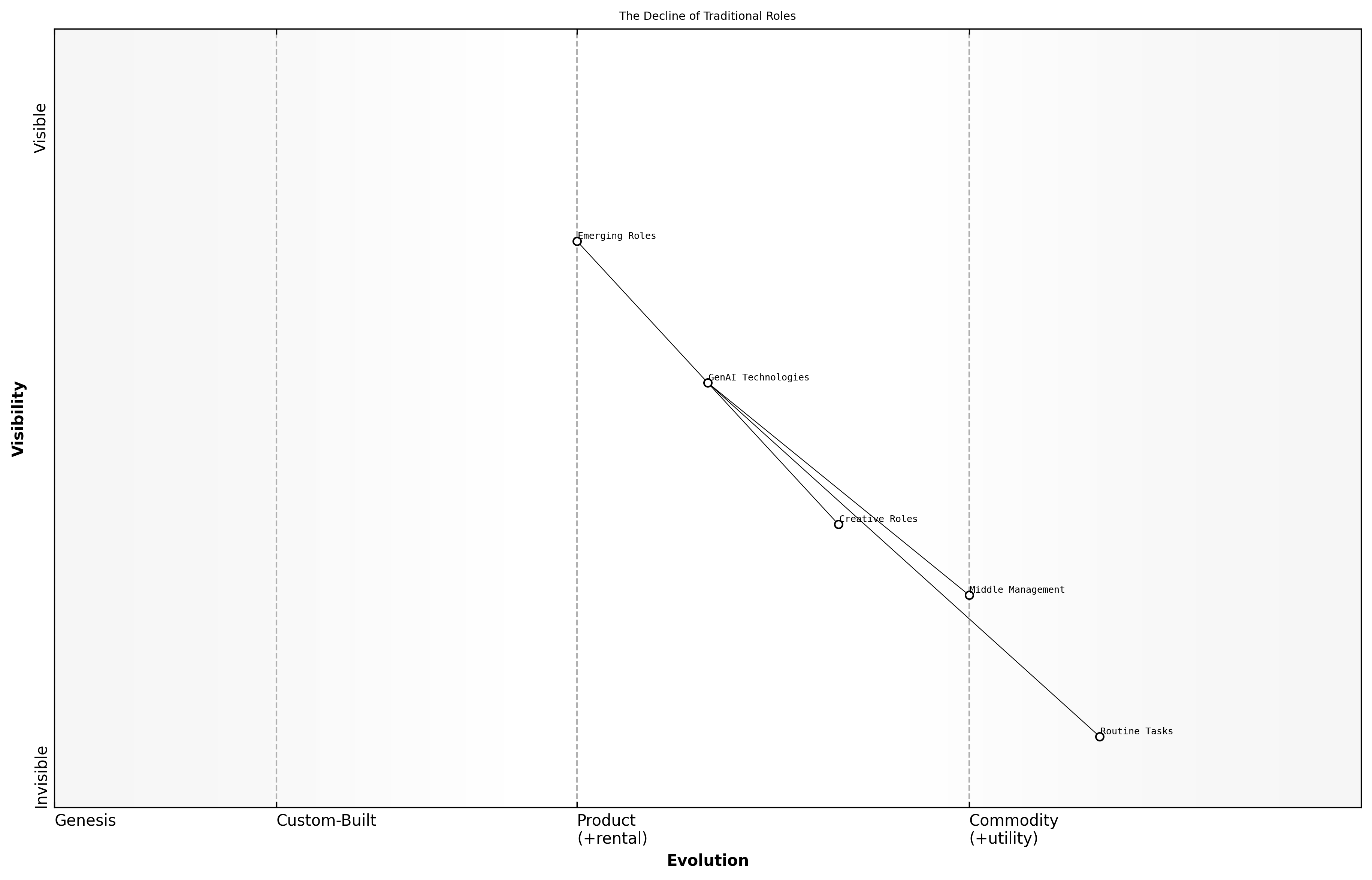
Skills That Will Be in Demand
As we navigate the evolving landscape shaped by GenAI, it is crucial to understand the types of job roles that will emerge and those that will become obsolete. The integration of GenAI into various sectors is not merely a trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how work is conducted, necessitating a reevaluation of skills and roles within the workforce.
- Data Analysts: With the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making, roles focused on data analysis and interpretation will see significant growth.
- AI Ethics Specialists: As ethical considerations around AI become paramount, professionals dedicated to ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI systems will be in high demand.
- Human-AI Interaction Designers: The need for specialists who can design effective interfaces and interactions between humans and AI systems will rise as organisations seek to enhance user experience.
Furthermore, traditional roles in sectors like manufacturing and administration may decline as automation and AI take over repetitive tasks. However, this shift will also create opportunities for roles that require complex problem-solving, creativity, and emotional intelligence—skills that are inherently human.
The future job landscape will not only require technical skills but also a blend of soft skills that enable individuals to work effectively alongside AI technologies, says a leading expert in workforce development.
Insights into Skill Requirements
Technical Skills vs. Soft Skills
In the evolving landscape shaped by GenAI, the distinction between technical skills and soft skills has become increasingly significant. While technical skills such as programming, data analysis, and machine learning are essential for operating and developing AI systems, soft skills like communication, empathy, and adaptability are equally crucial for fostering collaboration between humans and AI agents.
- Technical skills enable individuals to understand and manipulate GenAI technologies effectively.
- Soft skills facilitate teamwork and enhance the ability to navigate complex interpersonal dynamics in AI-driven environments.
- A balanced skill set is necessary for professionals to thrive in a future where GenAI plays a central role.
As organisations increasingly rely on GenAI, they must recognise the importance of both skill types. Technical skills can often be acquired through formal education and training, whereas soft skills require ongoing personal development and experiential learning.
The future workforce will need to blend technical expertise with strong interpersonal skills to effectively collaborate with AI systems and each other, says a leading expert in workforce development.
To prepare for this new reality, individuals should focus on developing a comprehensive skill set that includes both technical and soft skills. This dual approach not only enhances employability but also ensures that professionals can adapt to the rapid changes brought about by GenAI.
The Importance of Lifelong Learning
In the rapidly evolving landscape shaped by GenAI, the importance of lifelong learning cannot be overstated. As industries adapt to new technologies and methodologies, the skills required for success are constantly changing. Professionals must embrace a mindset of continuous education to remain relevant and competitive in their fields.
- Adaptability: The ability to adjust to new tools and processes is crucial as GenAI technologies evolve.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in data analysis, programming, and AI-related technologies will be increasingly in demand.
- Soft Skills: Communication, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence are essential for effective collaboration with AI systems and human teams.
The integration of GenAI into various sectors necessitates a shift in how we perceive skill acquisition. Traditional education models may not suffice, and professionals must seek out alternative learning pathways, such as online courses, workshops, and peer-to-peer learning opportunities.
The future of work will require individuals to be proactive in their learning journeys, constantly seeking new knowledge and skills to thrive in an AI-enhanced environment, says a leading expert in workforce development.
Organisations also play a critical role in fostering a culture of lifelong learning. By investing in employee development and creating an environment that encourages curiosity and innovation, they can ensure that their workforce remains equipped to navigate the challenges posed by GenAI.
Reskilling and Upskilling Strategies
As we navigate the evolving landscape shaped by GenAI, understanding the skill requirements for the future workforce becomes paramount. The integration of GenAI technologies into various sectors necessitates a shift in the skills that employees must possess to remain relevant and effective. This section explores the critical skills needed in an AI-driven world, focusing on both technical and soft skills.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in data analysis, programming languages, and familiarity with AI tools and platforms.
- Soft Skills: Enhanced communication, adaptability, and problem-solving abilities to work effectively alongside AI systems.
- Interdisciplinary Knowledge: Understanding how AI intersects with various fields, such as ethics, law, and social sciences.
The demand for technical skills is evident, as organisations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making. Employees must be adept at using AI tools to analyse large datasets and derive actionable insights. Furthermore, as AI systems become more prevalent, the ability to communicate effectively with both human and AI counterparts is crucial.
The future workforce will need to blend technical prowess with soft skills, creating a synergy that enhances productivity and innovation, says a leading expert in workforce development.
Moreover, the importance of lifelong learning cannot be overstated. Professionals must embrace continuous education and training to keep pace with technological advancements. This commitment to learning will not only enhance individual career prospects but also contribute to organisational resilience in the face of rapid change.
- Online Learning Platforms: Utilising resources like MOOCs and webinars to gain new skills.
- Mentorship Programs: Engaging with experienced professionals to gain insights and guidance.
- Cross-Training Opportunities: Encouraging employees to learn different roles within the organisation to foster versatility.
In conclusion, the future job landscape will be characterised by a dynamic interplay of skills. By focusing on both technical and soft skills, and fostering a culture of continuous learning, organisations can prepare their workforce for the challenges and opportunities presented by GenAI.
Chapter 5: Strategies for Adaptation
Frameworks for Individuals
Personal Development Plans
Personal Development Plans (PDPs) are essential tools for individuals seeking to navigate the evolving landscape shaped by GenAI. These plans provide a structured approach to identifying personal goals, assessing current skills, and outlining actionable steps for improvement. In the context of GenAI, where the demand for new skills is rapidly changing, having a PDP can empower individuals to take charge of their career trajectories and adapt to emerging opportunities.
- Identify personal strengths and weaknesses in relation to GenAI technologies.
- Set clear, measurable goals that align with future job market demands.
- Create a timeline for achieving these goals, incorporating milestones for tracking progress.
A well-structured PDP should include a variety of elements that cater to both technical and soft skills. As the landscape of work continues to shift, individuals must be proactive in their learning and development efforts. This includes not only acquiring new technical skills related to GenAI but also enhancing interpersonal skills that facilitate collaboration with AI systems.
- Technical skills: Data analysis, machine learning, programming languages.
- Soft skills: Communication, problem-solving, adaptability.
A personal development plan is not just a document; it is a living guide that evolves as you grow and as the industry changes, says a leading expert in career development.
Incorporating feedback mechanisms is crucial for the effectiveness of a PDP. Regularly reviewing and updating the plan based on new insights, experiences, and changes in the job market will ensure that individuals remain relevant and competitive. This iterative process aligns with the principles of lifelong learning, which are vital in an era dominated by rapid technological advancements.
Ultimately, a Personal Development Plan serves as a roadmap for individuals to navigate their careers in the age of GenAI. By taking a proactive approach to their development, individuals can not only enhance their employability but also contribute meaningfully to their organisations and society as a whole.
Networking and Community Building
Networking and community building are essential components for individuals navigating the evolving landscape shaped by GenAI. As the workforce adapts to new technologies, establishing connections and fostering relationships can provide invaluable support and resources. This section explores frameworks that individuals can utilise to enhance their networking efforts and build robust communities.
- Identify your goals: Understand what you want to achieve through networking, whether it's finding a mentor, exploring job opportunities, or sharing knowledge.
- Leverage online platforms: Utilise social media and professional networking sites to connect with like-minded individuals and industry leaders.
- Engage in local events: Attend workshops, seminars, and meetups to meet people face-to-face and build lasting relationships.
Building a strong network requires a proactive approach. Individuals should not only focus on expanding their connections but also on nurturing existing relationships. This can involve regular communication, offering assistance, and sharing relevant resources.
In an interconnected world, the strength of your network can significantly influence your career trajectory, says a leading expert in professional development.
- Participate in online forums and discussion groups related to your field to share insights and learn from others.
- Collaborate on projects with peers to enhance your skills and expand your visibility within your community.
- Seek feedback and advice from your network to improve your professional development and adapt to changes in your industry.
Ultimately, effective networking and community building are about creating a supportive ecosystem that fosters growth and innovation. By leveraging these frameworks, individuals can position themselves to thrive in the age of GenAI.
Leveraging Online Learning Platforms
In the rapidly evolving landscape of GenAI, online learning platforms have emerged as vital tools for individuals seeking to adapt and thrive in their careers. These platforms provide accessible, flexible, and diverse learning opportunities that cater to a wide range of skill levels and professional needs. As the demand for new skills continues to grow, leveraging these resources becomes essential for personal and professional development.
- Wide variety of courses covering technical and soft skills
- Flexibility to learn at one's own pace and schedule
- Access to expert instructors and industry leaders
To effectively utilise online learning platforms, individuals should consider several frameworks that can guide their learning journey. These frameworks not only help in identifying relevant courses but also in setting achievable learning goals.
- Identify personal learning objectives based on career aspirations
- Select courses that align with these objectives and current job market trends
- Establish a consistent learning schedule to maintain momentum
Moreover, engaging with online learning communities can enhance the learning experience. These communities provide networking opportunities, peer support, and collaborative learning environments that can significantly enrich the educational process.
- Participate in discussion forums to share insights and experiences
- Collaborate on projects or study groups to deepen understanding
- Seek feedback and mentorship from peers and instructors
Online learning platforms empower individuals to take charge of their education and adapt to the changing job landscape, says a leading expert in workforce development.
In conclusion, leveraging online learning platforms is not merely about acquiring new knowledge; it is about fostering a mindset of continuous learning and adaptability. By embracing these resources, individuals can position themselves for success in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Methodologies for Organizations
Creating a Culture of Innovation
Creating a culture of innovation within organizations is essential for adapting to the rapidly changing landscape influenced by GenAI. This culture encourages creativity, experimentation, and a willingness to embrace change, which are vital for leveraging the capabilities of GenAI effectively.
Methodologies for fostering such a culture can vary, but they generally focus on empowering employees, promoting collaboration, and integrating innovative practices into everyday operations. This section will explore several effective methodologies that organizations can adopt to cultivate an innovative environment.
- Design Thinking: A human-centred approach that encourages teams to empathise with users, define problems, ideate solutions, prototype, and test.
- Agile Methodology: A framework that promotes iterative development, allowing teams to respond quickly to changes and continuously improve products and processes.
- Lean Startup: A methodology that emphasises rapid prototyping and validated learning to develop products that meet customer needs effectively.
Implementing these methodologies requires a commitment from leadership to create an environment where failure is seen as a learning opportunity rather than a setback. This shift in mindset is crucial for encouraging innovation.
Innovation is not just about having great ideas; it's about creating an environment where those ideas can thrive, says a leading expert in organisational development.
In addition to these methodologies, organizations should consider establishing cross-functional teams that bring together diverse perspectives and expertise. This diversity can lead to more creative solutions and a greater willingness to challenge the status quo.
- Encourage open communication: Create channels for employees to share ideas and feedback without fear of criticism.
- Provide resources and support: Allocate time and funding for innovation initiatives and training.
- Recognise and reward innovation: Implement recognition programmes that celebrate innovative contributions and successes.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can create a sustainable culture of innovation that not only enhances their adaptability to GenAI but also positions them as leaders in their respective fields.
Integrating GenAI into Business Processes
Integrating GenAI into business processes is not merely about adopting new technologies; it is a transformative journey that requires a strategic approach. This integration can enhance efficiency, drive innovation, and improve decision-making across various sectors, particularly within government and public organisations. Understanding the methodologies for successful integration is crucial for leaders aiming to leverage GenAI effectively.
- Assessing Current Processes: Evaluate existing workflows to identify areas where GenAI can add value.
- Defining Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals for what the integration aims to achieve, such as cost reduction or improved service delivery.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders from the outset to ensure buy-in and gather diverse perspectives on the integration process.
- Pilot Testing: Implement pilot projects to test GenAI applications in controlled environments before full-scale deployment.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly assess the performance of GenAI systems and make necessary adjustments to optimise outcomes.
A leading expert in the field emphasises that successful integration hinges on a culture of collaboration between human employees and GenAI systems. This collaboration can lead to enhanced creativity and problem-solving capabilities, ultimately benefiting the organisation.
- Training and Development: Provide training for employees to understand and effectively use GenAI tools.
- Change Management: Implement change management strategies to facilitate a smooth transition and address resistance.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for ongoing feedback from users to refine GenAI applications continuously.
Organisations that embrace GenAI as a partner rather than a replacement for human intelligence will find themselves at the forefront of innovation and efficiency, says a senior government official.
Measuring Success and Impact
In the rapidly evolving landscape shaped by GenAI, organizations must adopt robust methodologies to measure success and impact effectively. This involves not only evaluating the performance of AI systems but also understanding their broader implications on organizational culture, employee engagement, and service delivery.
- Define clear objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with strategic goals.
- Utilize a balanced scorecard approach to assess both quantitative and qualitative outcomes.
- Implement regular feedback loops to gather insights from stakeholders, including employees and service users.
A leading expert in the field emphasises that organizations should not solely focus on financial metrics but also consider the social and ethical dimensions of AI deployment. This holistic view ensures that the integration of GenAI contributes positively to the community and enhances public trust.
- Conduct impact assessments to evaluate the effects of GenAI on service delivery and stakeholder satisfaction.
- Leverage data analytics to track performance trends and identify areas for improvement.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation to respond to the dynamic nature of AI technologies.
Measuring success in the age of GenAI requires a paradigm shift in how we evaluate performance, focusing on long-term impact rather than short-term gains, says a senior government official.
Case studies from various government sectors illustrate the effectiveness of these methodologies. For instance, a public health agency implemented a balanced scorecard to measure the impact of AI-driven patient management systems, resulting in improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with GenAI
Reflecting on the Journey
Key Takeaways from Each Chapter
As we conclude this exploration of GenAI and its implications for the future of work and society, it is essential to reflect on the key takeaways from each chapter. These insights not only encapsulate the evolution of GenAI but also highlight the critical role of human collaboration, ethical considerations, and the transformative impact on job landscapes.
- The evolution of GenAI has been marked by significant technological advancements, particularly in natural language processing and machine learning.
- Human-AI collaboration is not just beneficial; it is essential for enhancing productivity and innovation across various sectors.
- Ethical considerations, including bias, privacy, and accountability, must be at the forefront of AI integration to ensure fair and responsible use.
- The job landscape is undergoing a transformation, with emerging roles requiring a blend of technical and soft skills, underscoring the importance of lifelong learning.
- Adaptation strategies for individuals and organizations are crucial for navigating the changes brought about by GenAI, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
The journey through the chapters reveals that embracing GenAI is not merely about technology; it is about reimagining our roles and responsibilities in an increasingly automated world, says a leading expert in the field.
The Role of Humans in an AI-Driven World
As we conclude our exploration of the role of humans in an AI-driven world, it is essential to reflect on the journey we have undertaken. The integration of GenAI into various sectors has not only transformed workflows but has also redefined the relationship between humans and technology. This evolution prompts us to consider the implications for our future, particularly in terms of collaboration, ethical considerations, and the necessity for continuous adaptation.
- The importance of human oversight in AI decision-making processes
- The need for ethical frameworks to guide AI development
- The role of education and training in preparing the workforce for AI integration
The journey has highlighted that while GenAI agents can enhance efficiency and productivity, the human element remains irreplaceable. A leading expert in the field notes that the synergy between human creativity and AI capabilities can lead to unprecedented innovations.
The future will not be about humans versus machines, but rather humans working alongside machines, says a senior government official.
In reflecting on this journey, it is clear that embracing GenAI requires a mindset shift. We must move from viewing AI as a replacement for human roles to recognising it as a tool that can augment our capabilities. This perspective will be crucial as we navigate the complexities of an AI-driven future.
Final Thoughts on Coexistence with GenAI
As we conclude our exploration of the coexistence with GenAI, it is essential to reflect on the multifaceted journey we have undertaken. The integration of Generative AI into various sectors has not only transformed workflows but has also reshaped our understanding of collaboration between humans and machines. This journey has been marked by significant advancements, challenges, and the continuous evolution of our societal frameworks.
- Recognition of the transformative potential of GenAI in enhancing productivity and innovation.
- Acknowledgment of the ethical implications and the need for responsible AI governance.
- Understanding the importance of human skills in complementing AI capabilities.
The path forward requires a balanced approach, where we embrace the capabilities of GenAI while remaining vigilant about the ethical and societal implications. The journey has taught us that coexistence is not merely about integration but about fostering a partnership that enhances human potential.
The future will be defined by those who can navigate the complexities of human-AI collaboration, says a leading expert in the field.
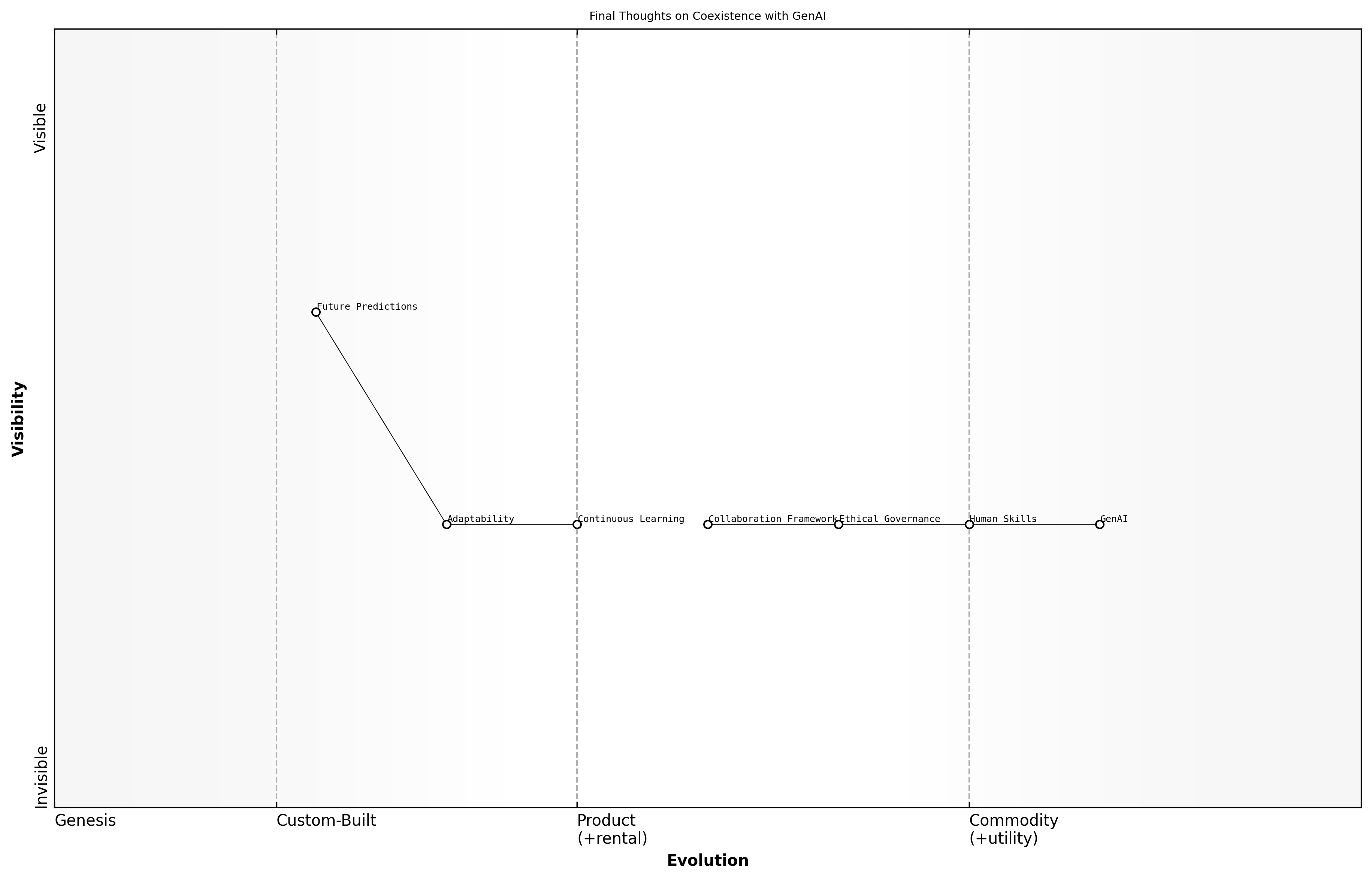
In reflecting on our journey, we must also consider the lessons learned. The importance of adaptability, continuous learning, and ethical considerations cannot be overstated. As we move forward, it is imperative that we cultivate a culture that embraces change and prioritises the well-being of all stakeholders in this new landscape.
Appendix: Further Reading on Wardley Mapping
The following books, primarily authored by Mark Craddock, offer comprehensive insights into various aspects of Wardley Mapping:
Core Wardley Mapping Series
-
Wardley Mapping, The Knowledge: Part One, Topographical Intelligence in Business
- Author: Simon Wardley
- Editor: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This foundational text introduces readers to the Wardley Mapping approach:
- Covers key principles, core concepts, and techniques for creating situational maps
- Teaches how to anchor mapping in user needs and trace value chains
- Explores anticipating disruptions and determining strategic gameplay
- Introduces the foundational doctrine of strategic thinking
- Provides a framework for assessing strategic plays
- Includes concrete examples and scenarios for practical application
The book aims to equip readers with:
- A strategic compass for navigating rapidly shifting competitive landscapes
- Tools for systematic situational awareness
- Confidence in creating strategic plays and products
- An entrepreneurial mindset for continual learning and improvement
-
Wardley Mapping Doctrine: Universal Principles and Best Practices that Guide Strategic Decision-Making
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This book explores how doctrine supports organizational learning and adaptation:
- Standardisation: Enhances efficiency through consistent application of best practices
- Shared Understanding: Fosters better communication and alignment within teams
- Guidance for Decision-Making: Offers clear guidelines for navigating complexity
- Adaptability: Encourages continuous evaluation and refinement of practices
Key features:
- In-depth analysis of doctrine's role in strategic thinking
- Case studies demonstrating successful application of doctrine
- Practical frameworks for implementing doctrine in various organizational contexts
- Exploration of the balance between stability and flexibility in strategic planning
Ideal for:
- Business leaders and executives
- Strategic planners and consultants
- Organizational development professionals
- Anyone interested in enhancing their strategic decision-making capabilities
-
Wardley Mapping Gameplays: Transforming Insights into Strategic Actions
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This book delves into gameplays, a crucial component of Wardley Mapping:
- Gameplays are context-specific patterns of strategic action derived from Wardley Maps
- Types of gameplays include:
- User Perception plays (e.g., education, bundling)
- Accelerator plays (e.g., open approaches, exploiting network effects)
- De-accelerator plays (e.g., creating constraints, exploiting IPR)
- Market plays (e.g., differentiation, pricing policy)
- Defensive plays (e.g., raising barriers to entry, managing inertia)
- Attacking plays (e.g., directed investment, undermining barriers to entry)
- Ecosystem plays (e.g., alliances, sensing engines)
Gameplays enhance strategic decision-making by:
- Providing contextual actions tailored to specific situations
- Enabling anticipation of competitors' moves
- Inspiring innovative approaches to challenges and opportunities
- Assisting in risk management
- Optimizing resource allocation based on strategic positioning
The book includes:
- Detailed explanations of each gameplay type
- Real-world examples of successful gameplay implementation
- Frameworks for selecting and combining gameplays
- Strategies for adapting gameplays to different industries and contexts
-
Navigating Inertia: Understanding Resistance to Change in Organisations
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This comprehensive guide explores organizational inertia and strategies to overcome it:
Key Features:
- In-depth exploration of inertia in organizational contexts
- Historical perspective on inertia's role in business evolution
- Practical strategies for overcoming resistance to change
- Integration of Wardley Mapping as a diagnostic tool
The book is structured into six parts:
- Understanding Inertia: Foundational concepts and historical context
- Causes and Effects of Inertia: Internal and external factors contributing to inertia
- Diagnosing Inertia: Tools and techniques, including Wardley Mapping
- Strategies to Overcome Inertia: Interventions for cultural, behavioral, structural, and process improvements
- Case Studies and Practical Applications: Real-world examples and implementation frameworks
- The Future of Inertia Management: Emerging trends and building adaptive capabilities
This book is invaluable for:
- Organizational leaders and managers
- Change management professionals
- Business strategists and consultants
- Researchers in organizational behavior and management
-
Wardley Mapping Climate: Decoding Business Evolution
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This comprehensive guide explores climatic patterns in business landscapes:
Key Features:
- In-depth exploration of 31 climatic patterns across six domains: Components, Financial, Speed, Inertia, Competitors, and Prediction
- Real-world examples from industry leaders and disruptions
- Practical exercises and worksheets for applying concepts
- Strategies for navigating uncertainty and driving innovation
- Comprehensive glossary and additional resources
The book enables readers to:
- Anticipate market changes with greater accuracy
- Develop more resilient and adaptive strategies
- Identify emerging opportunities before competitors
- Navigate complexities of evolving business ecosystems
It covers topics from basic Wardley Mapping to advanced concepts like the Red Queen Effect and Jevon's Paradox, offering a complete toolkit for strategic foresight.
Perfect for:
- Business strategists and consultants
- C-suite executives and business leaders
- Entrepreneurs and startup founders
- Product managers and innovation teams
- Anyone interested in cutting-edge strategic thinking
Practical Resources
-
Wardley Mapping Cheat Sheets & Notebook
- Author: Mark Craddock
- 100 pages of Wardley Mapping design templates and cheat sheets
- Available in paperback format
- Amazon Link
This practical resource includes:
- Ready-to-use Wardley Mapping templates
- Quick reference guides for key Wardley Mapping concepts
- Space for notes and brainstorming
- Visual aids for understanding mapping principles
Ideal for:
- Practitioners looking to quickly apply Wardley Mapping techniques
- Workshop facilitators and educators
- Anyone wanting to practice and refine their mapping skills
Specialized Applications
-
UN Global Platform Handbook on Information Technology Strategy: Wardley Mapping The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Explores the use of Wardley Mapping in the context of sustainable development
- Available for free with Kindle Unlimited or for purchase
- Amazon Link
This specialized guide:
- Applies Wardley Mapping to the UN's Sustainable Development Goals
- Provides strategies for technology-driven sustainable development
- Offers case studies of successful SDG implementations
- Includes practical frameworks for policy makers and development professionals
-
AIconomics: The Business Value of Artificial Intelligence
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Applies Wardley Mapping concepts to the field of artificial intelligence in business
- Amazon Link
This book explores:
- The impact of AI on business landscapes
- Strategies for integrating AI into business models
- Wardley Mapping techniques for AI implementation
- Future trends in AI and their potential business implications
Suitable for:
- Business leaders considering AI adoption
- AI strategists and consultants
- Technology managers and CIOs
- Researchers in AI and business strategy
These resources offer a range of perspectives and applications of Wardley Mapping, from foundational principles to specific use cases. Readers are encouraged to explore these works to enhance their understanding and application of Wardley Mapping techniques.
Note: Amazon links are subject to change. If a link doesn't work, try searching for the book title on Amazon directly.