AI Supremacy: The Battle Between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google
Artificial IntelligenceAI Supremacy: The Battle Between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google
Table of Contents
- AI Supremacy: The Battle Between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google
Introduction to AI Supremacy
The Rise of AI
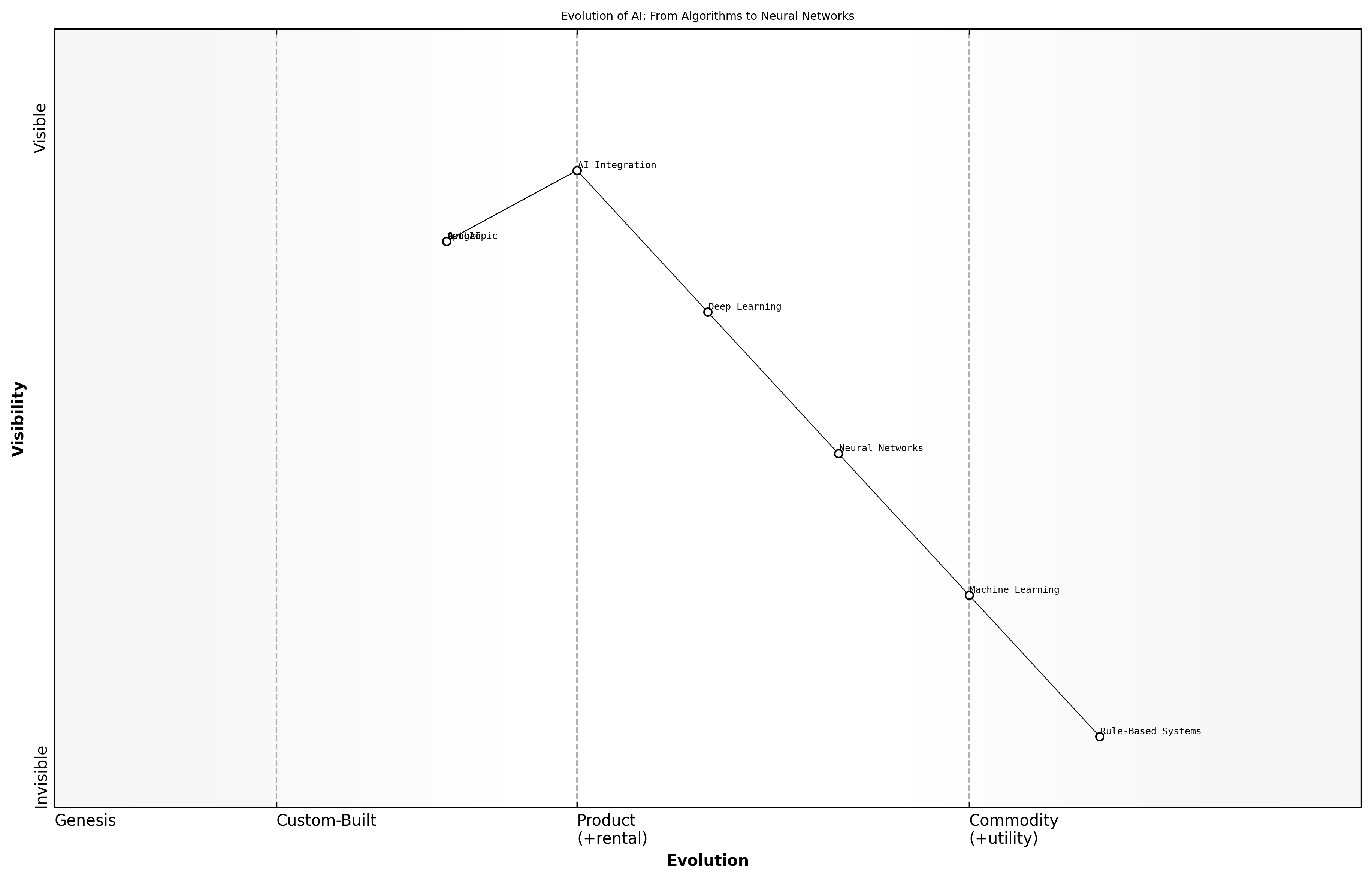
The Evolution of AI: From Algorithms to Neural Networks
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) marks a significant milestone in the evolution of technology, fundamentally altering how we interact with machines and process information. This transformation has been driven by advancements in algorithms, computational power, and the availability of vast amounts of data. As we delve into the evolution of AI, it is essential to understand the trajectory that has led us from simple algorithms to sophisticated neural networks, which now underpin many of the most powerful AI systems.
- The early days of AI focused on rule-based systems and symbolic reasoning.
- The introduction of machine learning algorithms allowed systems to learn from data rather than relying solely on pre-defined rules.
- The advent of neural networks, particularly deep learning, revolutionised the field by enabling models to learn complex patterns and representations.
The shift from traditional algorithms to neural networks has not only enhanced the capabilities of AI but has also led to its integration into various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. This evolution underscores the importance of understanding the foundational technologies that drive AI supremacy among key players like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google.
The evolution of AI from simple algorithms to complex neural networks has opened up new possibilities for innovation and efficiency, says a leading expert in the field.
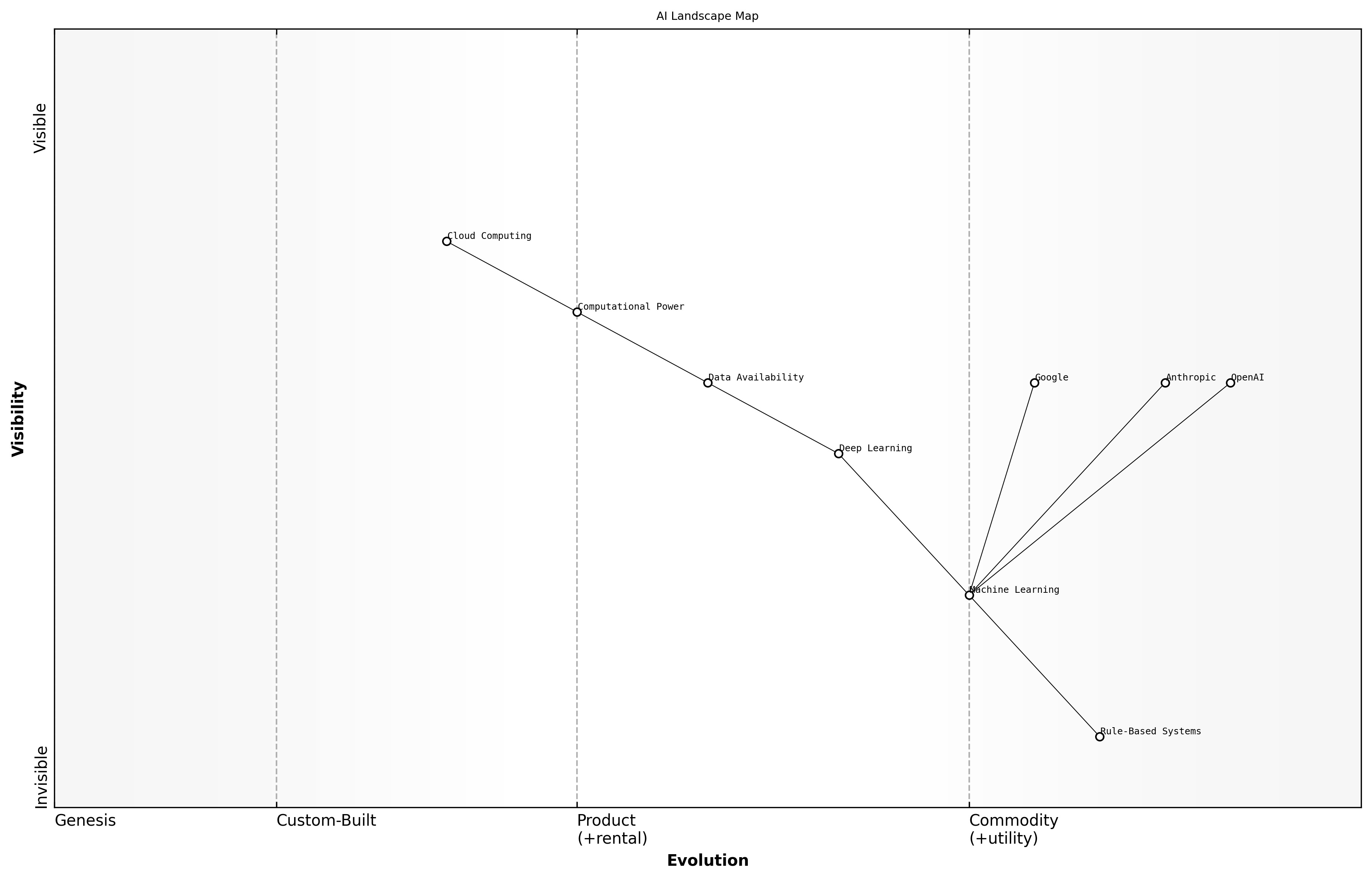
Key Players in the AI Landscape
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) marks a transformative era in technology, influencing various sectors from healthcare to finance. This evolution is not merely a technological advancement; it represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with machines and leverage data for decision-making. Understanding the trajectory of AI is crucial for comprehending the competitive dynamics between key players such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google.
- The transition from rule-based systems to machine learning and deep learning techniques.
- The increasing availability of vast datasets and computational power.
- The emergence of cloud computing, enabling scalable AI solutions.
The initial phase of AI development was characterised by rule-based systems, which relied on predefined logic to perform tasks. However, the limitations of these systems became apparent, leading to the adoption of machine learning algorithms that could learn from data. This shift was further accelerated by the advent of deep learning, which utilises neural networks to process complex data patterns.
The growth of AI is driven by the convergence of advanced algorithms, increased data availability, and powerful computing resources, says a leading expert in the field.
As AI technologies matured, the competitive landscape began to take shape. Companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google emerged as frontrunners, each bringing unique strengths and innovations to the table. Their approaches to AI development not only reflect their corporate philosophies but also influence the broader societal implications of AI deployment.
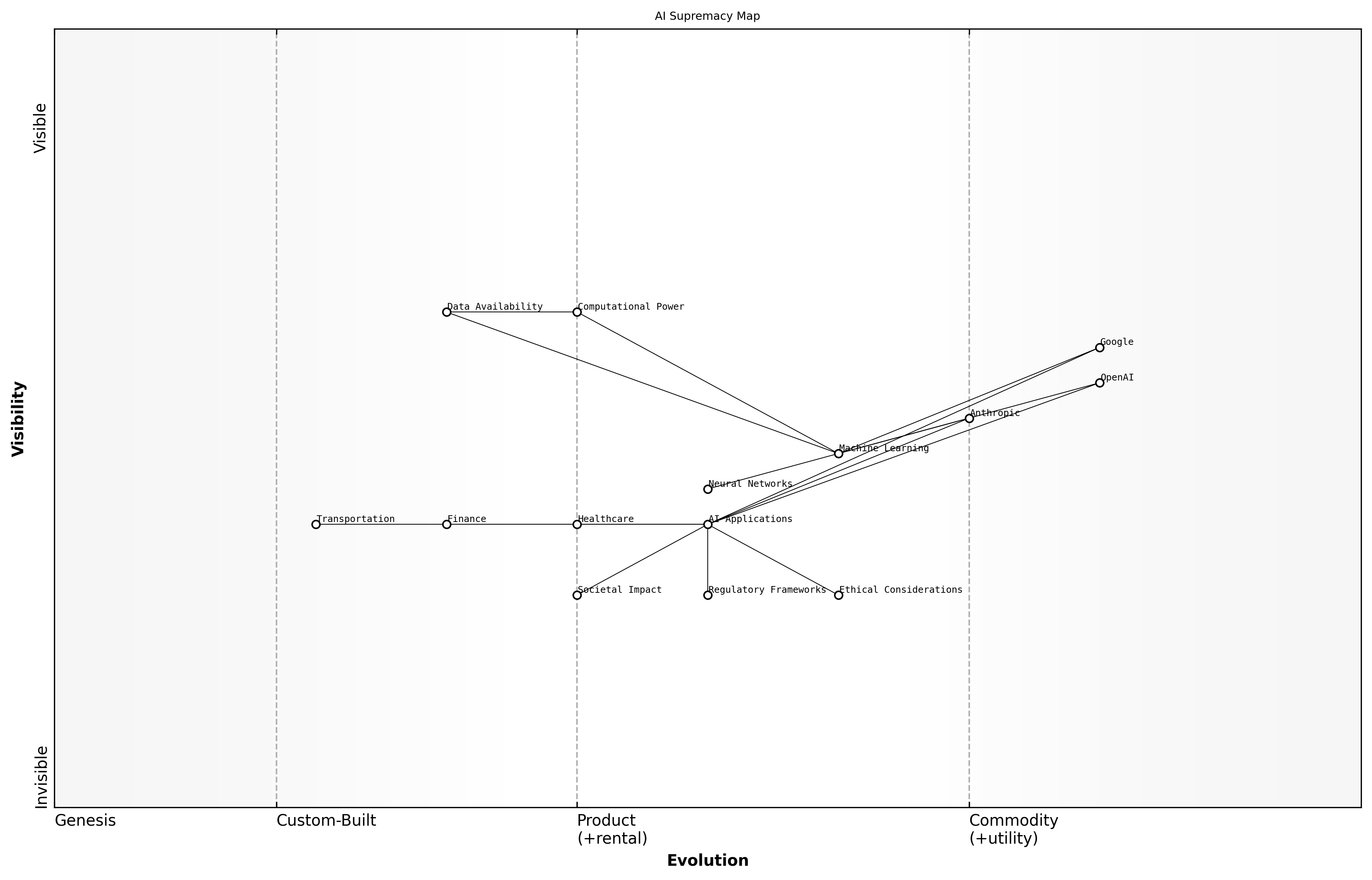
Defining AI Supremacy
The concept of AI supremacy has emerged as a critical focal point in the ongoing competition among leading technology firms, particularly OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. As these entities strive to establish themselves as the foremost authorities in artificial intelligence, understanding the dynamics of this supremacy is essential for stakeholders in both the public and private sectors. The rise of AI has not only transformed industries but has also reshaped societal norms and expectations regarding technology's role in everyday life.
- The rapid advancement of machine learning and neural networks has propelled AI into the mainstream.
- Key players are investing heavily in research and development to secure a competitive edge.
- The implications of AI supremacy extend beyond technology, influencing economic, ethical, and regulatory landscapes.
AI supremacy is not merely about technological advancement; it encompasses ethical considerations, regulatory frameworks, and the societal impact of AI innovations, notes a leading expert in the field.
The rise of AI can be traced back to significant breakthroughs in computational power and data availability, which have enabled the development of sophisticated algorithms capable of learning and adapting. This evolution has led to the proliferation of AI applications across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and transportation, each vying for the benefits that AI can provide. As these technologies continue to evolve, the competition for supremacy intensifies, with each player seeking to define the future of AI.
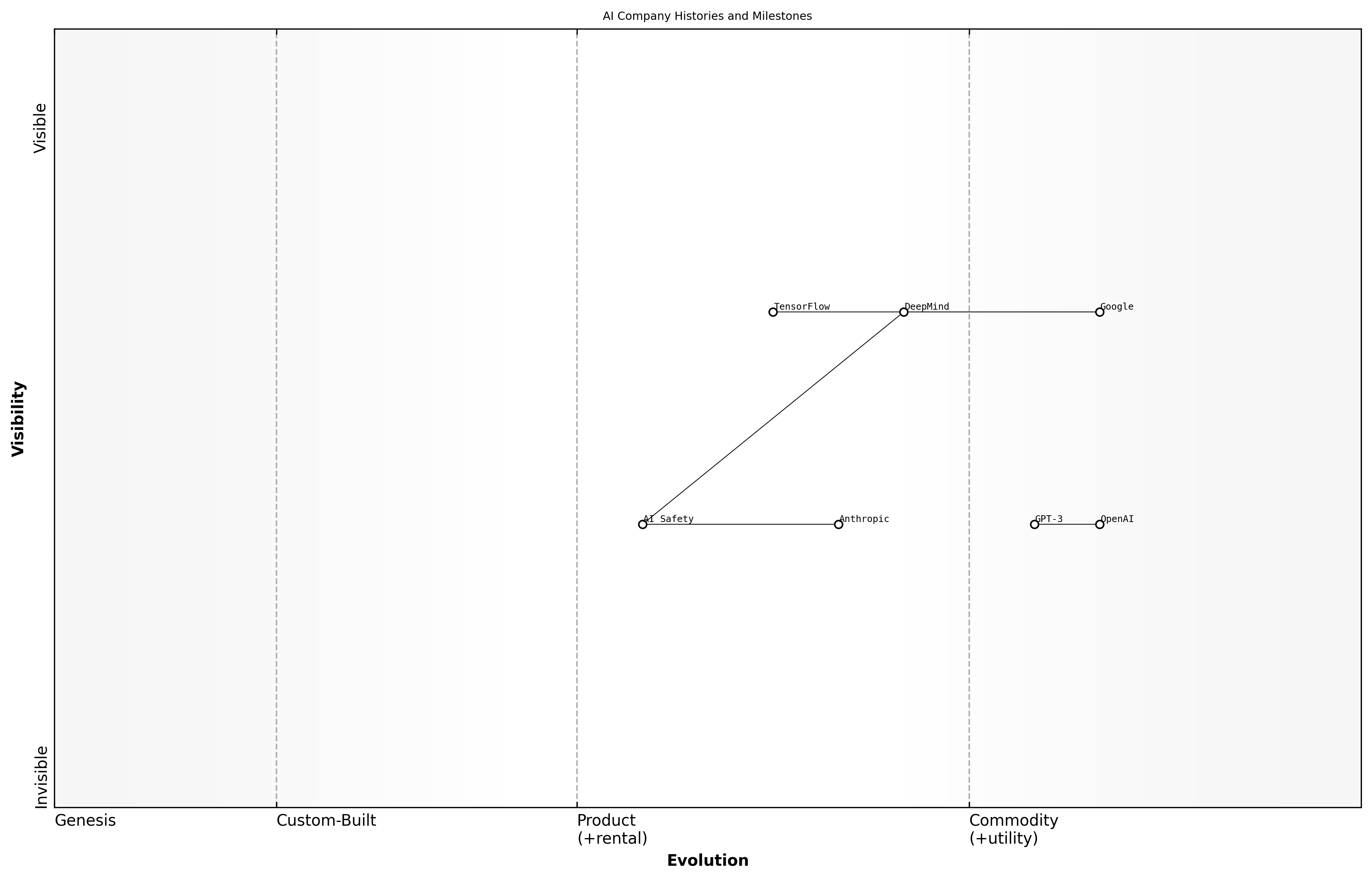
Overview of OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google
Company Histories and Milestones
The evolution of artificial intelligence has been significantly shaped by the contributions of three major players: OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. Each of these organisations has carved out a unique niche within the AI landscape, driven by distinct philosophies, technological innovations, and strategic goals. Understanding their histories and milestones is crucial for grasping the competitive dynamics that define the current AI supremacy landscape.
- OpenAI founded in December 2015 with a mission to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all of humanity.
- Anthropic established in 2020 by former OpenAI employees, focusing on AI safety and alignment.
- Google's AI efforts began in earnest with the acquisition of DeepMind in 2014, leading to significant advancements in machine learning and neural networks.
OpenAI has made headlines with its groundbreaking models, such as GPT-3, which revolutionised natural language processing. Anthropic, on the other hand, has prioritised ethical considerations in AI development, advocating for safer AI systems. Google, with its extensive resources and research capabilities, has maintained a dominant position in AI through innovations like TensorFlow and advancements in search algorithms.
The future of AI will be defined by those who prioritise safety and ethical considerations, says a leading expert in the field.
The interplay between these companies not only highlights their individual achievements but also underscores the broader implications for the AI industry as a whole. As they continue to innovate and compete, the outcomes of their strategies will shape the future landscape of AI technology and its applications across various sectors.
Core Technologies and Innovations
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google stand out as key players, each leveraging unique core technologies and innovations to establish their positions within the competitive arena. Understanding these technologies is crucial for grasping how each organisation aims to achieve AI supremacy.
- OpenAI's focus on transformer models and reinforcement learning
- Anthropic's emphasis on safety and interpretability in AI systems
- Google's advancements in neural architecture and large-scale data processing
OpenAI has pioneered the use of transformer models, particularly with its GPT series, which has revolutionised natural language processing. These models are designed to understand and generate human-like text, enabling a wide range of applications from chatbots to content creation. The reinforcement learning aspect further enhances the adaptability of these models in real-world scenarios.
Anthropic, on the other hand, is distinguished by its commitment to creating AI systems that are not only powerful but also safe and interpretable. By prioritising ethical considerations and human alignment, Anthropic aims to mitigate risks associated with AI deployment, a critical factor as AI systems become more integrated into society.
Google's technological dominance is underpinned by its extensive research in neural networks and machine learning algorithms. The company's ability to process vast amounts of data through its advanced infrastructure allows it to develop AI solutions that are both scalable and efficient, further solidifying its competitive edge.
The race for AI supremacy is not just about technology; it's about how these technologies are applied responsibly and ethically, says a leading expert in the field.
Business Models and Market Strategies
Understanding the business models and market strategies of OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google is crucial for grasping their competitive positions in the AI landscape. Each of these organisations has adopted distinct approaches that reflect their core values, technological capabilities, and target markets.
- OpenAI's subscription-based model for access to its API and premium services, focusing on broad accessibility and innovation.
- Anthropic's emphasis on ethical AI development, which informs its business strategy and partnerships, aiming to build trust and long-term relationships.
- Google's integration of AI across its vast ecosystem of products and services, leveraging its existing infrastructure to enhance user experience and drive revenue.
These differing strategies not only highlight the unique identities of each company but also illustrate the broader trends in the AI industry, where ethical considerations, accessibility, and technological integration play pivotal roles.
The future of AI will be shaped by those who can balance innovation with responsibility, says a leading expert in the field.
Competitive Analysis
Strengths and Weaknesses
OpenAI's Unique Offerings
OpenAI has established itself as a pioneering force in the AI landscape, particularly through its unique offerings that distinguish it from competitors like Anthropic and Google. Understanding these strengths and weaknesses is essential for grasping OpenAI's position in the ongoing battle for AI supremacy.
- Cutting-edge language models such as GPT-3 and GPT-4 that excel in natural language understanding and generation.
- A strong commitment to ethical AI development, focusing on safety and alignment with human values.
- Robust community engagement and open-source initiatives that foster collaboration and innovation.
However, OpenAI also faces notable weaknesses that could impact its competitive edge. These include challenges related to scalability, public perception issues, and the potential for bias in AI outputs.
- Scalability challenges in deploying AI solutions across diverse sectors and applications.
- Public perception issues stemming from past controversies and misunderstandings about AI capabilities.
- Concerns regarding bias and fairness in AI systems, which can undermine trust and effectiveness.
OpenAI's unique offerings position it as a leader in the AI field, yet it must navigate the complexities of public trust and ethical considerations, says a leading expert in AI development.
Anthropic's Ethical Focus
Anthropic's commitment to ethical AI development is a defining strength that sets it apart from competitors like OpenAI and Google. This focus on ethics not only influences the company's internal culture but also shapes its product offerings and market positioning. By prioritising safety and alignment in AI systems, Anthropic aims to build trust with users and stakeholders, which is increasingly crucial in a landscape fraught with concerns about bias, privacy, and accountability.
- Strength: Strong emphasis on AI alignment and safety, which appeals to ethically conscious consumers and organisations.
- Strength: Development of transparent AI systems that allow for better understanding and trust from users.
- Weakness: Potentially slower innovation pace due to rigorous ethical considerations and safety protocols.
- Weakness: Limited market presence compared to larger competitors, which may hinder scalability and resource acquisition.
The ethical focus of Anthropic is not merely a marketing strategy; it is embedded in the company's operational framework. This approach aligns with the growing demand for responsible AI practices in both public and private sectors. However, the challenge remains in balancing ethical considerations with the need for rapid technological advancement, a tension that could impact Anthropic's competitive edge.
Ethical AI is not just a buzzword; it is a necessity for sustainable growth in the technology sector, says a leading expert in AI ethics.
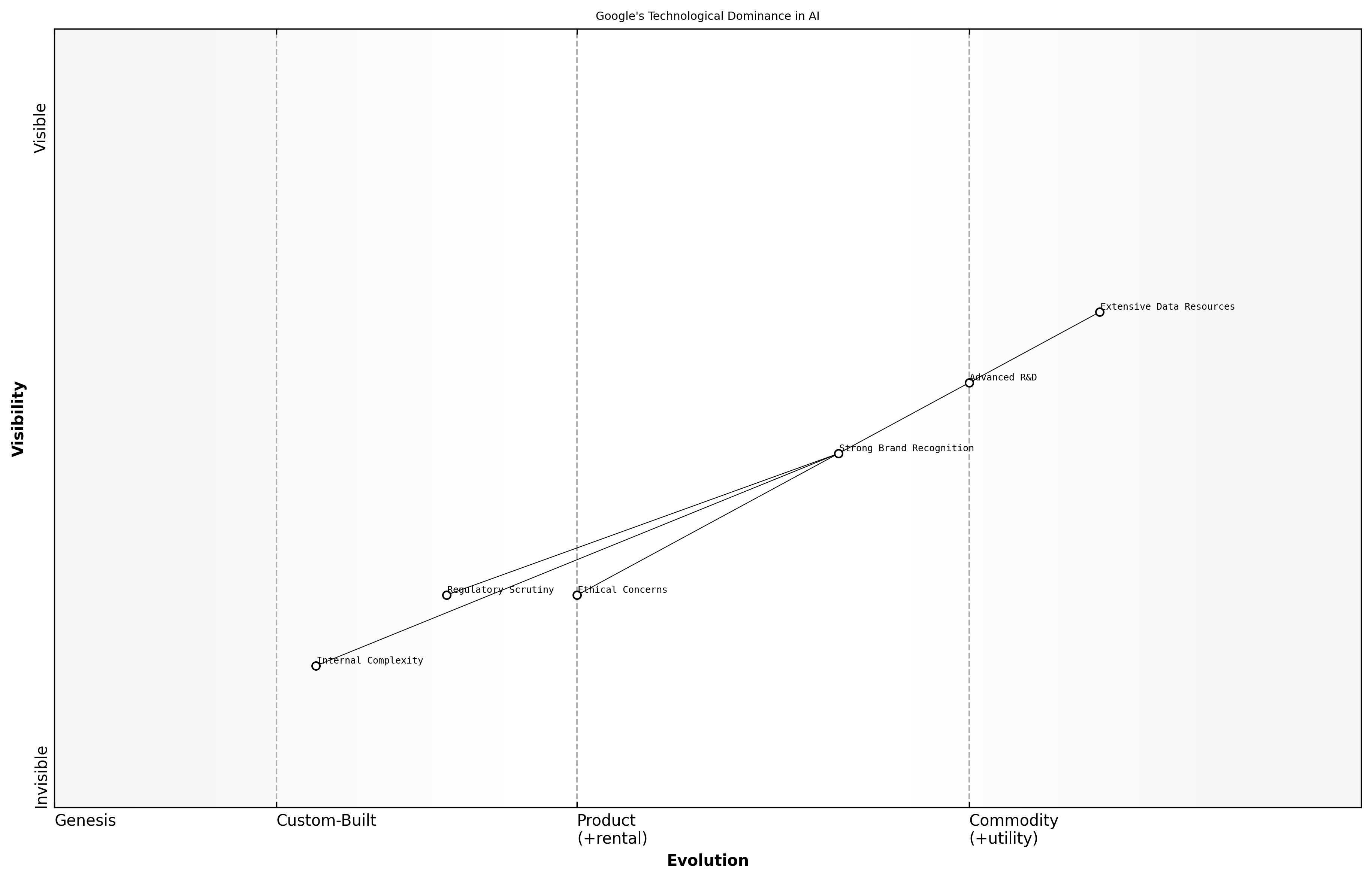
Google's Technological Dominance
Google's technological dominance in the AI landscape is underpinned by a multitude of strengths that position it as a formidable player against competitors like OpenAI and Anthropic. However, this dominance is not without its weaknesses, which can be critical in understanding the competitive dynamics at play.
- Extensive Data Resources: Google's vast trove of data from its various services provides a significant advantage in training AI models, enabling them to achieve higher accuracy and performance.
- Advanced Research and Development: Google has invested heavily in AI research, leading to groundbreaking innovations such as TensorFlow and the development of state-of-the-art models like BERT and LaMDA.
- Strong Brand Recognition: As a household name, Google benefits from a strong brand that instills trust and credibility in its AI offerings, attracting both consumers and enterprise clients.
Despite these strengths, Google faces several weaknesses that could hinder its ability to maintain its competitive edge. These include challenges related to ethical considerations, regulatory scrutiny, and internal complexities.
- Ethical Concerns: Google has faced criticism over its handling of AI ethics, particularly regarding bias in algorithms and the implications of its technologies on privacy.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As a major player in the tech industry, Google is subject to intense scrutiny from regulators worldwide, which can impact its operations and innovation pace.
- Internal Complexity: The size and scale of Google can lead to bureaucratic challenges that may slow down decision-making processes and hinder agility in responding to market changes.
Google's ability to leverage its extensive resources is impressive, but it must navigate the complexities of public perception and regulatory landscapes, says a leading expert in the field.
Market Positioning
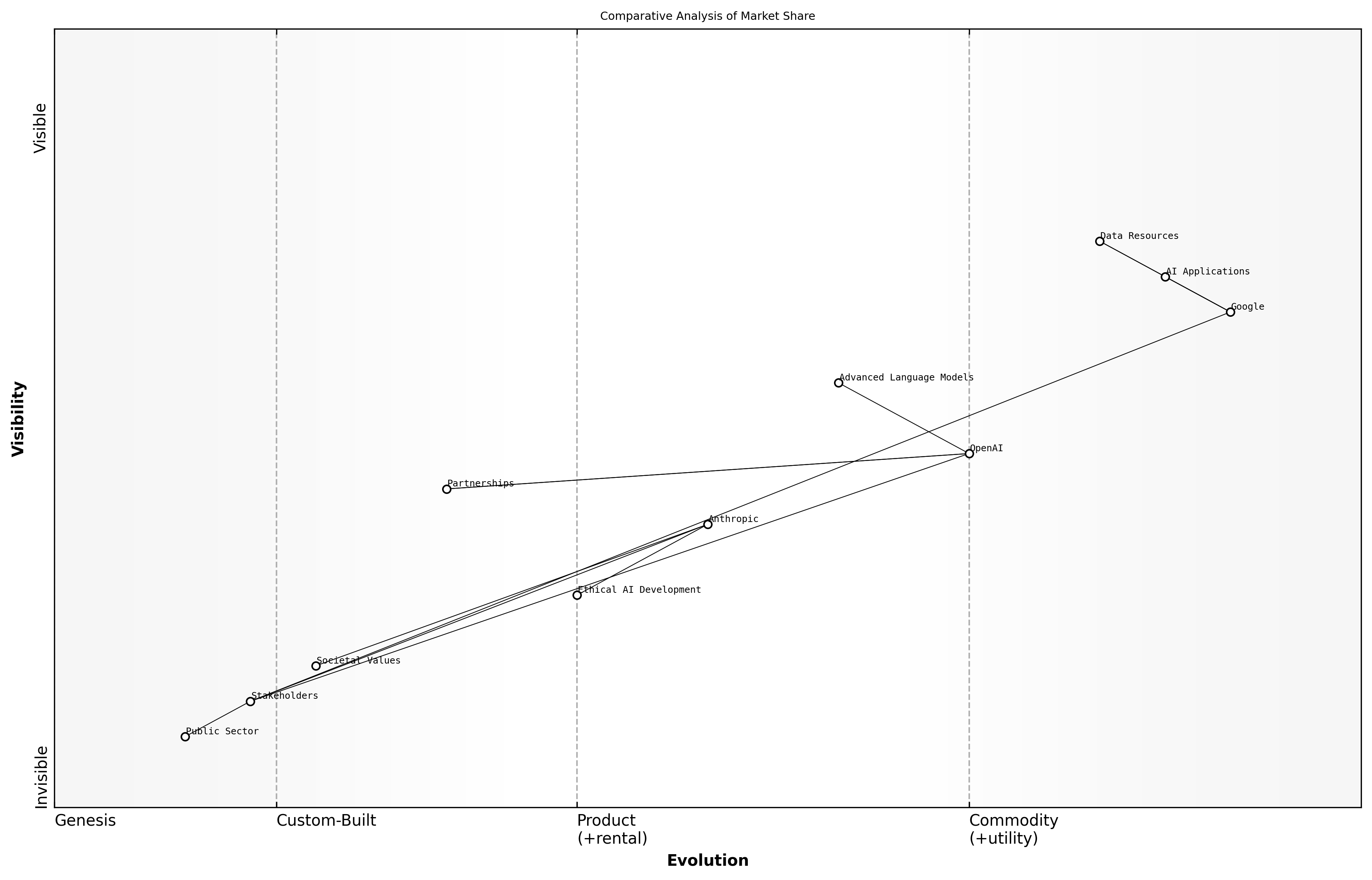
Comparative Analysis of Market Share
Market positioning is a critical aspect of understanding the competitive dynamics between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. Each of these companies has carved out distinct niches within the AI landscape, influencing their market share and competitive strategies. This section delves into how these organisations position themselves in relation to one another and the implications of these strategies for their market dominance.
- OpenAI focuses on developing advanced language models and fostering partnerships with various sectors, including education and healthcare.
- Anthropic emphasises ethical AI development, positioning itself as a leader in responsible AI practices, which appeals to socially conscious organisations.
- Google leverages its extensive data resources and technological infrastructure to dominate in AI applications across search, advertising, and cloud services.
Understanding these positioning strategies is essential for stakeholders in the public sector, as they inform decisions regarding partnerships, investments, and regulatory considerations. The competitive landscape is continually evolving, and organisations must adapt to these changes to maintain relevance and influence.
The positioning of AI companies is not just about technology; it's about aligning with societal values and market needs, says a leading expert in the field.
Strategic Partnerships and Alliances
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI, strategic partnerships and alliances have become crucial for companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google to enhance their market positioning. These collaborations not only enable access to complementary technologies and expertise but also facilitate the sharing of resources, data, and insights that can drive innovation and accelerate development.
- Enhanced technological capabilities through shared resources
- Access to new markets and customer bases
- Increased agility in responding to market changes
- Improved research and development outcomes
- Strengthened competitive positioning against rivals
For instance, OpenAI's collaboration with Microsoft has allowed it to leverage Azure's cloud infrastructure, significantly enhancing its computational power and scalability. This partnership illustrates how strategic alliances can provide a competitive edge in the AI sector.
Strategic partnerships are not just about sharing technology; they are about creating ecosystems that foster innovation and drive growth, says a leading expert in the field.
Moreover, the dynamics of these partnerships can shift based on market conditions, regulatory environments, and technological advancements. Companies must remain vigilant and adaptable to ensure that their alliances continue to serve their strategic objectives.
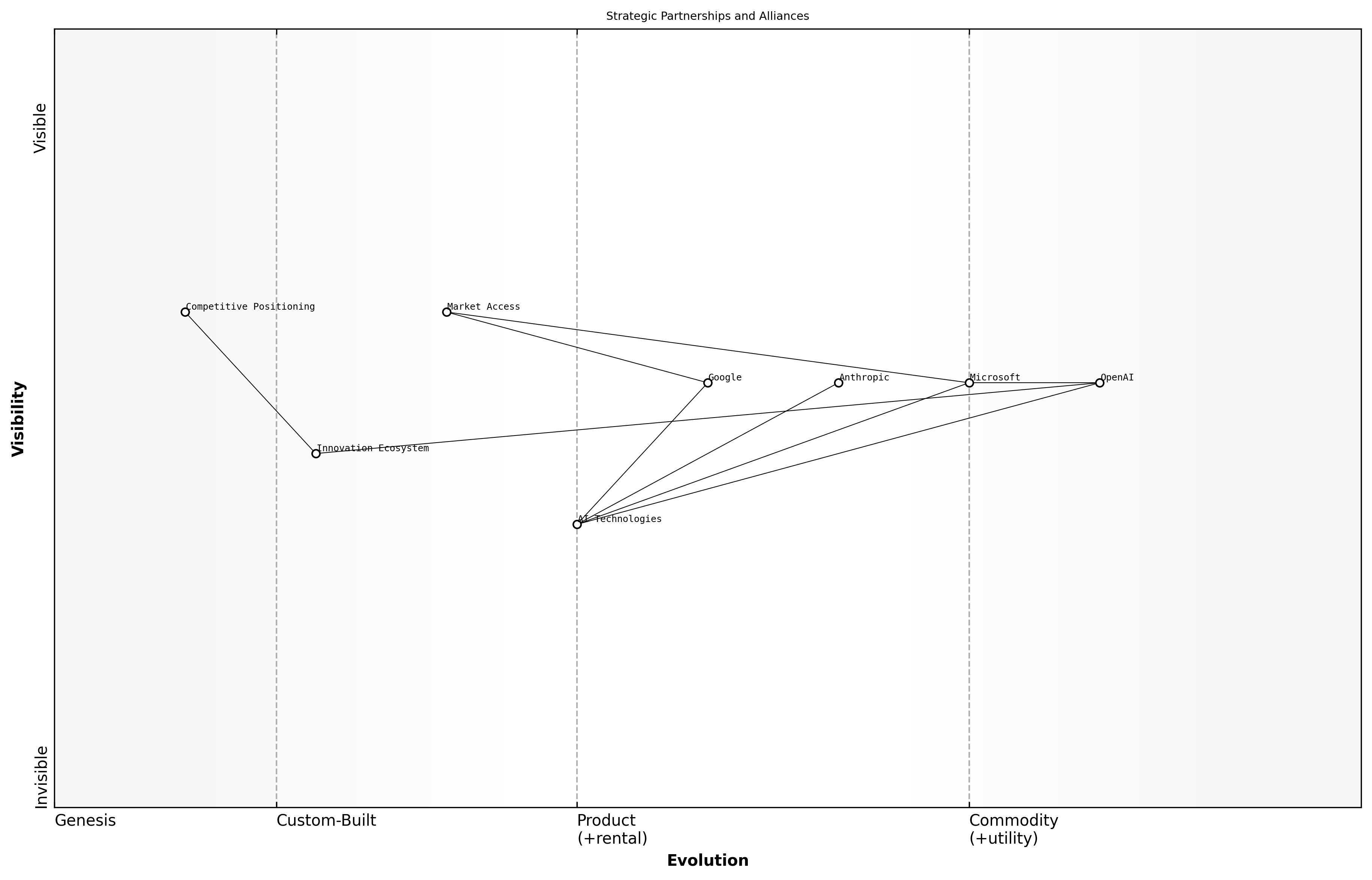
In conclusion, the ability to form and maintain effective strategic partnerships will be a defining factor in the competitive positioning of AI companies. As the landscape continues to evolve, those who can forge meaningful alliances will likely emerge as leaders in the race for AI supremacy.
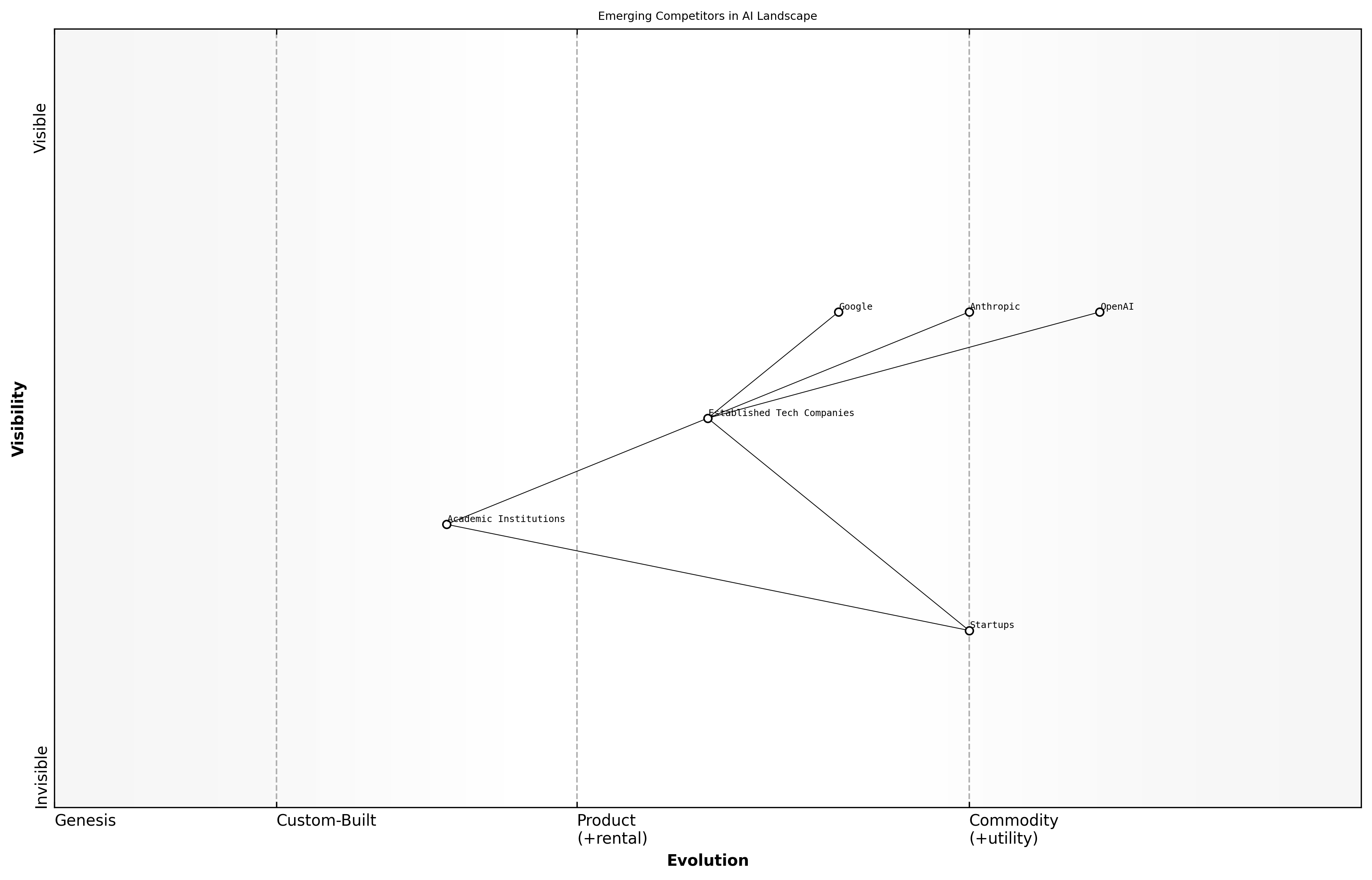
Emerging Competitors
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, emerging competitors are reshaping the competitive dynamics among established giants like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. These newcomers often bring innovative approaches and unique value propositions that challenge the status quo, making it essential to analyse their market positioning and potential impact on the AI supremacy battle.
- Startups leveraging niche technologies to solve specific problems
- Established tech companies diversifying into AI solutions
- Academic institutions and research labs developing cutting-edge AI applications
Emerging competitors can be categorised into three primary groups: startups, established tech companies, and academic institutions. Each group brings distinct advantages and challenges that influence their market positioning.
Startups often operate with agility and innovation, focusing on niche markets that larger companies may overlook. Their ability to pivot quickly allows them to adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements.
Established tech companies, on the other hand, leverage their existing infrastructure and customer base to integrate AI solutions into their offerings. This can lead to rapid scaling of AI technologies, but they may face challenges in fostering a culture of innovation.
Academic institutions and research labs contribute significantly to the AI landscape by pushing the boundaries of knowledge and technology. Their focus on fundamental research can lead to breakthroughs that fuel the development of new AI applications.
Emerging competitors are not just threats; they are catalysts for innovation that can drive the entire industry forward, says a leading expert in AI competition.
The interplay between these emerging competitors and established players will shape the future of AI. As these new entrants continue to innovate, they will force established companies to adapt their strategies, leading to a more dynamic and competitive environment.
Ethical Implications
Moral Dilemmas in AI
Bias and Fairness in AI Systems
Bias and fairness in AI systems represent some of the most pressing moral dilemmas in the field of artificial intelligence. As AI technologies become increasingly integrated into decision-making processes across various sectors, the potential for biased outcomes raises significant ethical concerns. This topic is crucial within the context of OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, as each organisation grapples with the implications of their AI systems on society.
- Understanding Bias: Bias in AI can arise from various sources, including biased training data, flawed algorithms, and human prejudices embedded in the design process.
- Consequences of Bias: The impact of biased AI systems can lead to unfair treatment of individuals, perpetuation of stereotypes, and erosion of trust in AI technologies.
- Strategies for Fairness: Implementing fairness-aware algorithms, conducting regular audits, and involving diverse stakeholders in the AI development process are essential steps to mitigate bias.
The ethical implications of bias in AI systems extend beyond technical considerations; they touch upon fundamental human rights and societal values. A leading expert in the field notes that addressing bias is not merely a technical challenge but a moral imperative that requires a commitment to fairness and justice in AI deployment.
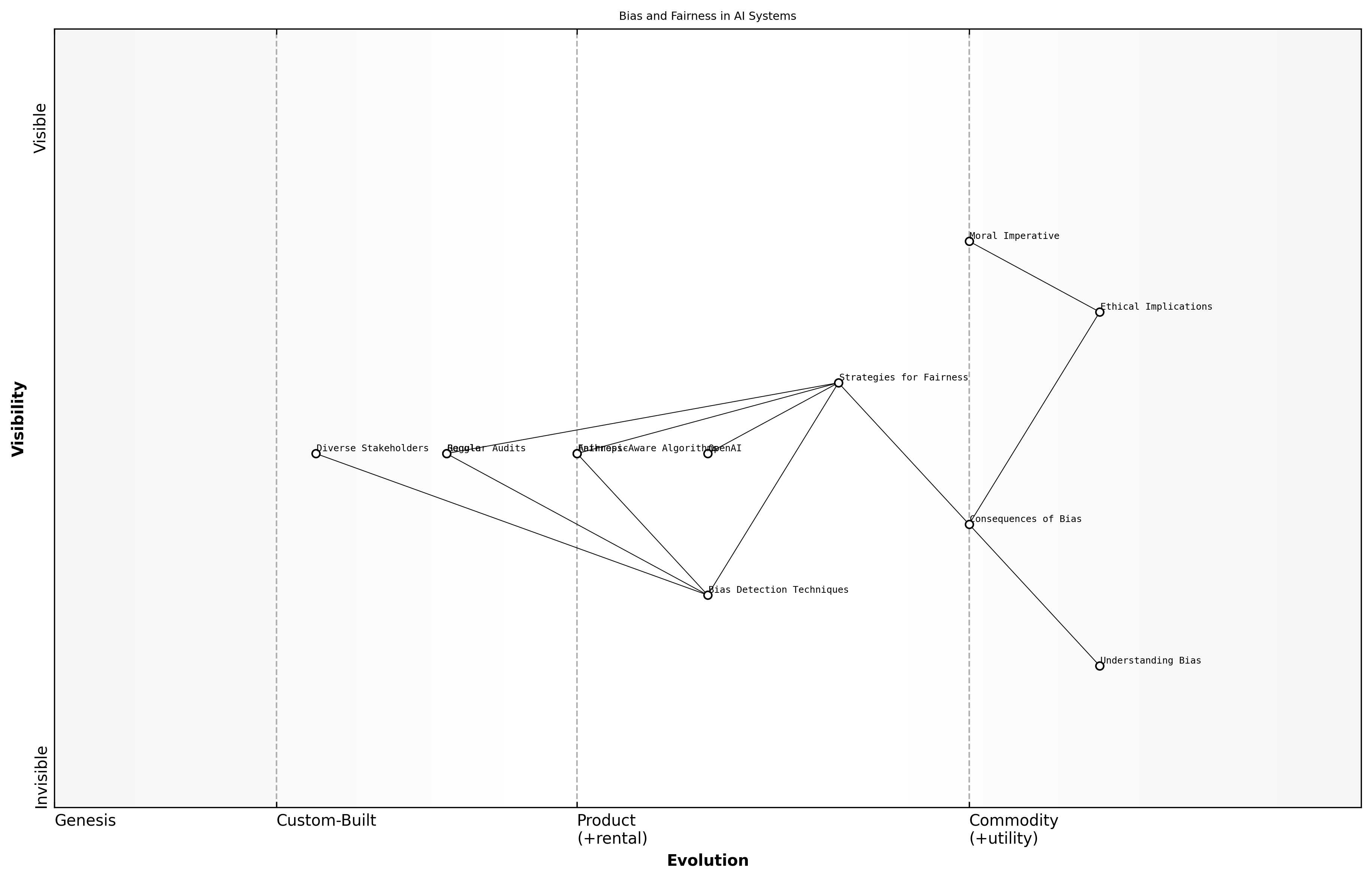
The challenge of bias in AI systems necessitates a multi-faceted approach that includes technical innovation, ethical reflection, and active engagement with affected communities, says a senior government official.
Privacy Concerns and Data Security
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, privacy concerns and data security have emerged as critical ethical dilemmas. As AI systems become increasingly integrated into government and public sector operations, the handling of sensitive data raises significant questions about user privacy, consent, and the potential for misuse of information. This section delves into the complexities surrounding these issues, highlighting the importance of establishing robust frameworks to safeguard personal data while leveraging AI technologies.
- The necessity of data minimisation: Collecting only the data that is essential for AI operations.
- Implementing strong encryption methods to protect sensitive information from breaches.
- Ensuring transparency in data usage policies to build public trust.
The ethical implications of data privacy in AI are profound. As a leading expert in the field notes, the balance between innovation and ethical responsibility is delicate, requiring ongoing dialogue among stakeholders to navigate the challenges effectively.
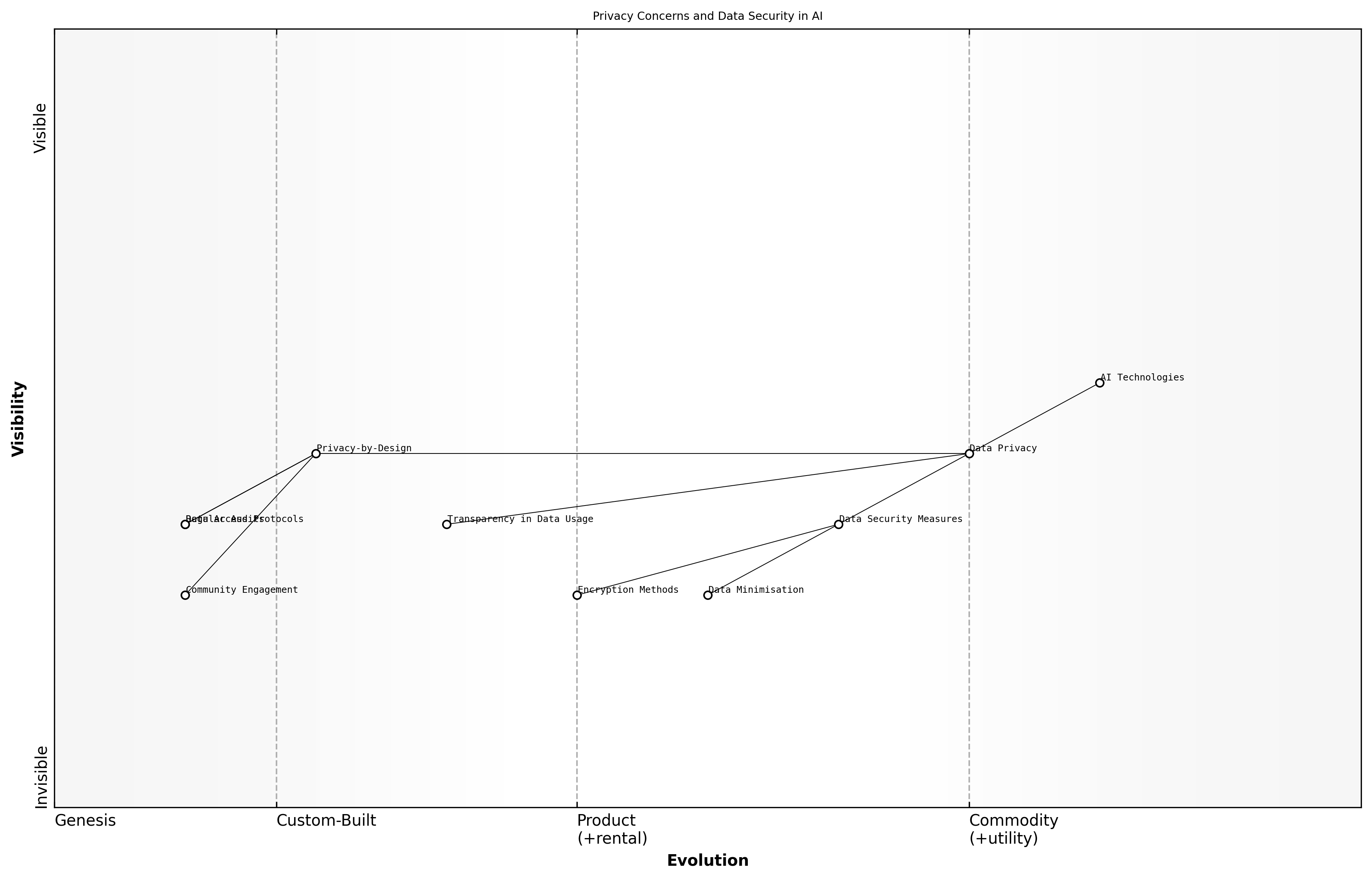
Practical applications of these principles are essential for professionals in the public sector. Implementing privacy-by-design approaches in AI development can help mitigate risks associated with data breaches and misuse. This involves integrating privacy considerations into the entire lifecycle of AI systems, from initial design to deployment and ongoing management.
- Conducting regular audits of AI systems to ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Engaging with communities to understand public concerns about data privacy.
- Developing clear protocols for data access and sharing among stakeholders.
Case studies from various government initiatives illustrate the importance of addressing privacy concerns. For instance, a senior government official highlighted how a public sector AI project successfully implemented stringent data security measures, resulting in enhanced public trust and increased adoption of AI technologies.
Impact on Workforce Dynamics and Economy
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into various sectors is reshaping workforce dynamics and the broader economy. As AI technologies become more prevalent, they bring forth significant moral dilemmas that must be addressed to ensure a balanced transition. Understanding these dilemmas is crucial for policymakers, business leaders, and society as a whole, as they navigate the complexities of AI adoption and its implications for employment and economic stability.
- Job Displacement: The rise of AI technologies threatens to displace a significant number of jobs, particularly in sectors reliant on routine tasks.
- Skill Gaps: As AI systems become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for a workforce skilled in AI management, data analysis, and technology integration.
- Economic Inequality: The benefits of AI may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating existing economic inequalities as certain sectors thrive while others decline.
Addressing these moral dilemmas requires a multifaceted approach that considers the ethical implications of AI deployment. It is essential to foster an environment where workers are supported through retraining and upskilling initiatives, ensuring they can adapt to the changing job landscape.
The challenge lies not only in technological advancement but also in ensuring that the workforce is prepared to meet the demands of an AI-driven economy, says a leading expert in workforce development.
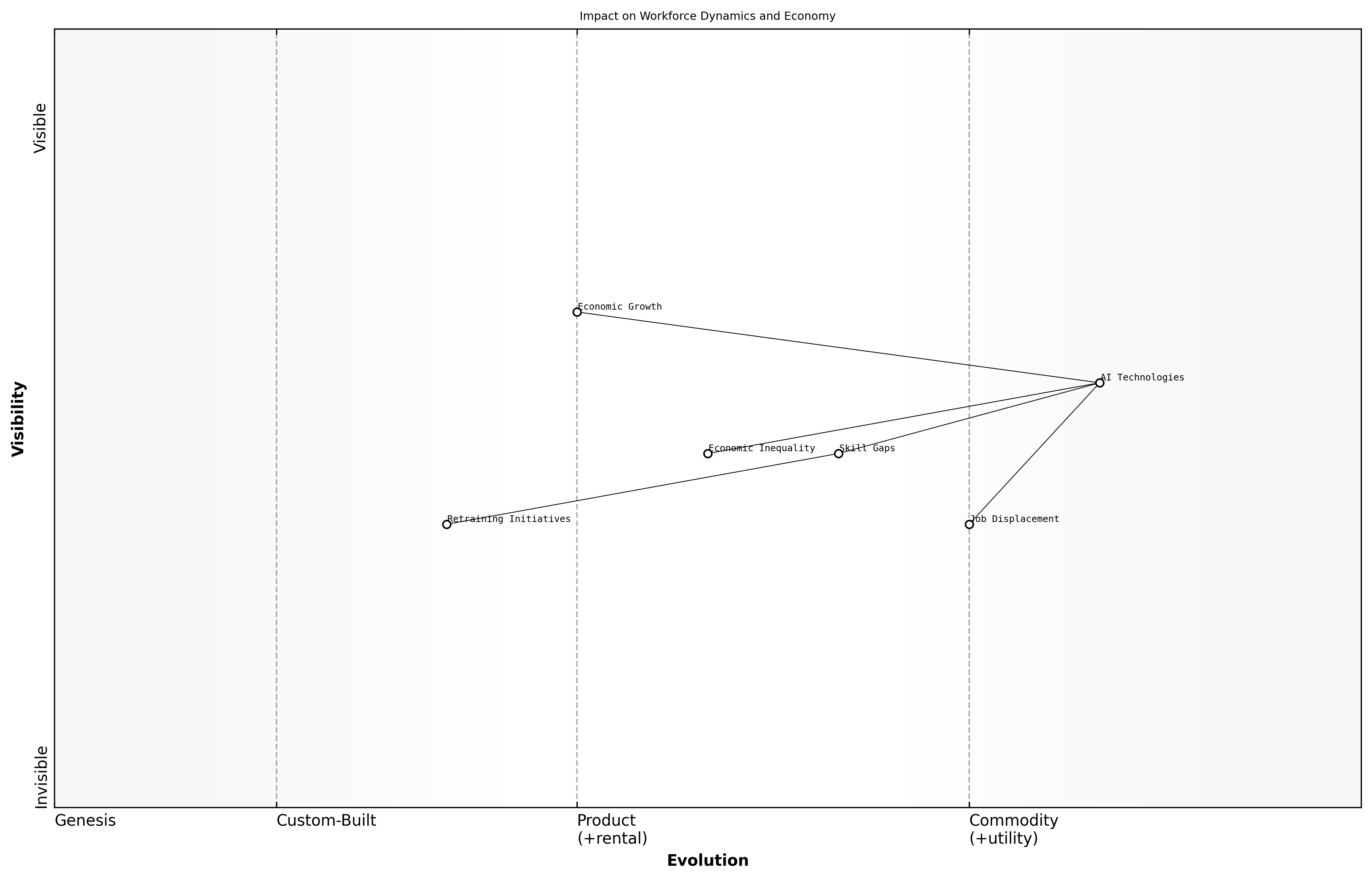
Furthermore, the economic implications of AI extend beyond job displacement. The introduction of AI can lead to increased productivity and efficiency, potentially driving economic growth. However, this growth must be managed carefully to ensure that it benefits all segments of society and does not lead to further disparities.
Societal Impacts
Public Perception of AI
Public perception of artificial intelligence (AI) is a critical factor influencing its adoption and integration into society. As AI technologies become more prevalent, understanding how the public views these innovations is essential for policymakers, developers, and stakeholders. The societal impacts of AI are multifaceted, encompassing both positive and negative perceptions that can shape the future of AI development and deployment.
- Increased awareness of AI capabilities and limitations
- Concerns about job displacement and economic impact
- Fears regarding privacy and surveillance
The rise of AI has led to a growing awareness among the public regarding its capabilities and limitations. While many individuals are excited about the potential benefits of AI, such as improved efficiency and enhanced decision-making, there is also a significant level of skepticism and concern. This duality in perception can be attributed to various factors, including media portrayals, personal experiences, and the influence of social networks.
The public's understanding of AI is often shaped by sensationalist media coverage, which can lead to misconceptions about the technology, says a leading expert in the field.
Concerns about job displacement are prevalent, with many fearing that AI will render certain professions obsolete. This anxiety is particularly pronounced in sectors such as manufacturing, customer service, and transportation, where automation is already transforming job landscapes. Policymakers must address these concerns by promoting workforce retraining and upskilling initiatives to help individuals transition to new roles in an AI-driven economy.
- Promoting transparency in AI systems
- Engaging with communities to understand their concerns
- Implementing ethical guidelines to govern AI use
Privacy and surveillance concerns also play a significant role in shaping public perception of AI. As AI systems increasingly rely on vast amounts of data, individuals worry about how their personal information is collected, stored, and used. This has led to calls for greater transparency in AI systems, as well as the implementation of robust data protection measures. Engaging with communities to understand their concerns and incorporating their feedback into AI development can help build trust and alleviate fears.
Building public trust in AI requires a commitment to ethical practices and transparency, says a senior government official.
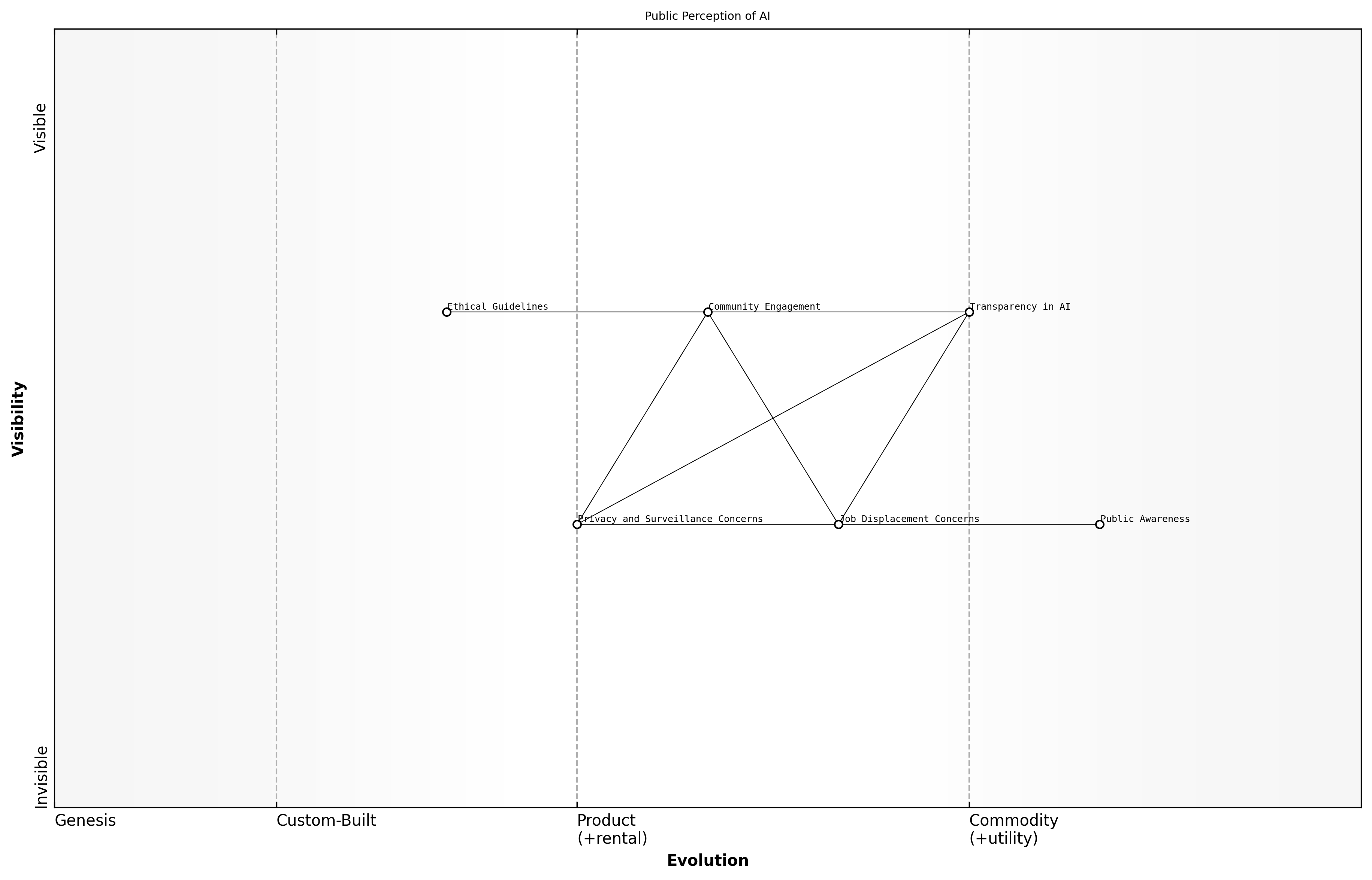
Regulatory Challenges
Regulatory challenges in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) are becoming increasingly prominent as governments and public sector organisations grapple with the rapid advancements in technology. The societal impacts of these challenges are multifaceted, affecting not only the development and deployment of AI systems but also the ethical considerations that underpin their use. As AI technologies evolve, so too must the frameworks that govern them, ensuring they align with societal values and public interests.
- The need for comprehensive regulatory frameworks that address the unique characteristics of AI technologies.
- Balancing innovation with the protection of individual rights and societal norms.
- Ensuring transparency and accountability in AI decision-making processes.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by the global nature of AI development. Different countries are adopting varying approaches to regulation, leading to potential conflicts and challenges for multinational organisations. A senior government official noted that a cohesive international regulatory framework is essential to foster collaboration while safeguarding ethical standards.
Regulatory frameworks must evolve to keep pace with technological advancements, ensuring that AI serves the public good, says a leading expert in the field.
One of the most pressing concerns is the potential for bias and discrimination in AI systems, which can have significant societal implications. Regulatory bodies must ensure that AI technologies are developed and deployed in ways that promote fairness and equity, addressing the risks of perpetuating existing inequalities.
- Implementing standards for data collection and usage to prevent bias.
- Establishing oversight mechanisms to monitor AI systems post-deployment.
- Encouraging public engagement in the regulatory process to reflect diverse societal perspectives.
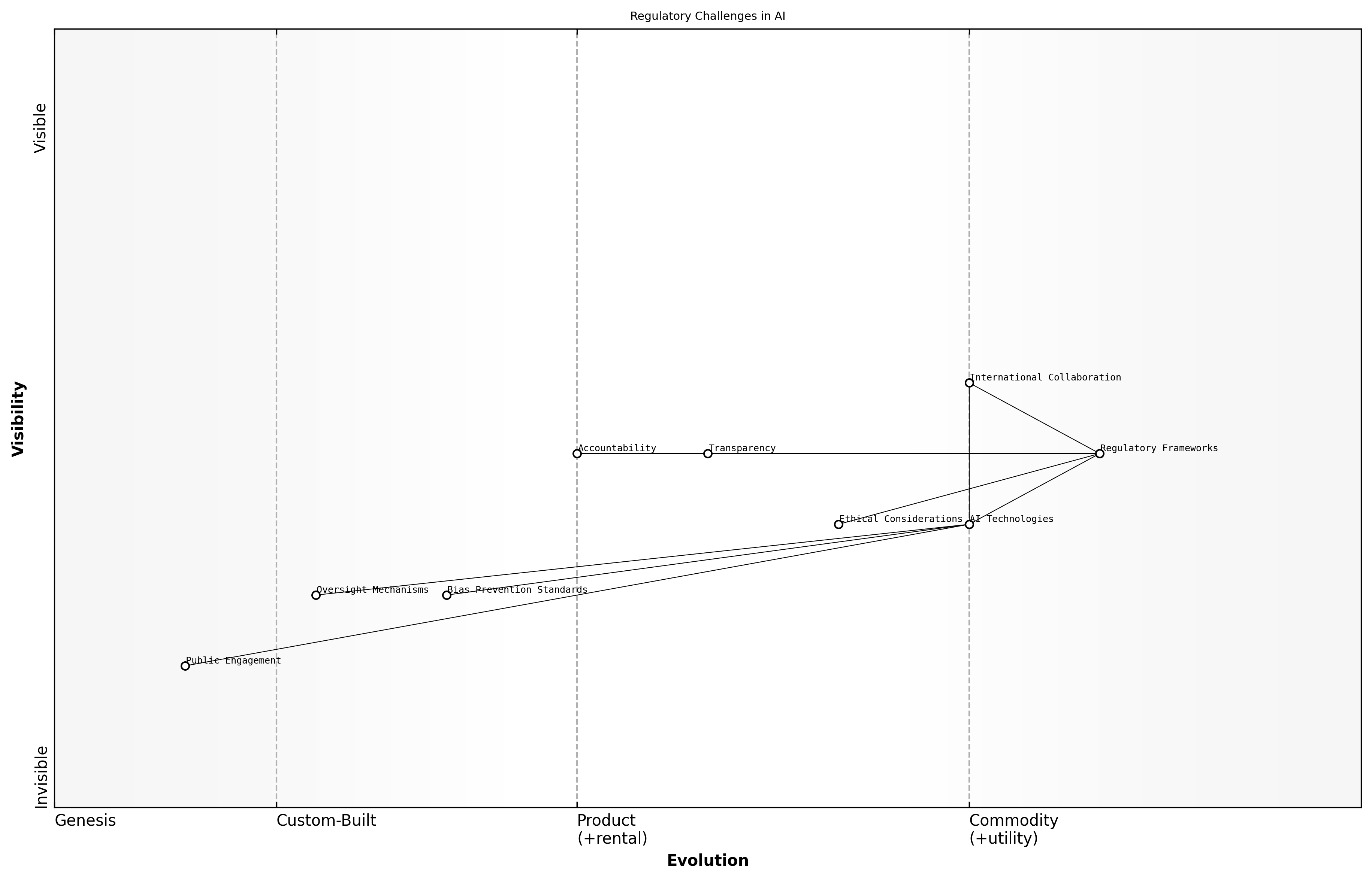
As AI continues to permeate various aspects of society, the urgency for effective regulatory measures cannot be overstated. Policymakers must engage with technologists, ethicists, and the public to craft regulations that not only mitigate risks but also harness the transformative potential of AI for societal benefit.
Ethical Frameworks in AI Development
The societal impacts of AI development are profound and multifaceted, influencing various aspects of daily life, governance, and economic structures. As AI technologies become more integrated into society, understanding these impacts is crucial for ensuring ethical frameworks guide their development and deployment.
- Transformation of job markets and workforce dynamics
- Changes in social interactions and communication patterns
- Implications for privacy and personal data security
One of the most significant societal impacts of AI is the transformation of job markets. As automation and AI systems take on tasks traditionally performed by humans, there is a growing concern about job displacement and the need for reskilling the workforce. A senior government official noted that the challenge lies not only in creating new jobs but also in ensuring that the workforce is equipped with the necessary skills to thrive in an AI-driven economy.
Moreover, AI technologies are reshaping social interactions and communication patterns. With the rise of social media algorithms and AI-driven content curation, individuals are increasingly exposed to echo chambers that reinforce their existing beliefs. This phenomenon raises ethical questions about the role of AI in shaping public discourse and societal cohesion.
The implications for privacy and personal data security cannot be overstated, as AI systems often rely on vast amounts of personal data to function effectively, says a leading expert in the field.
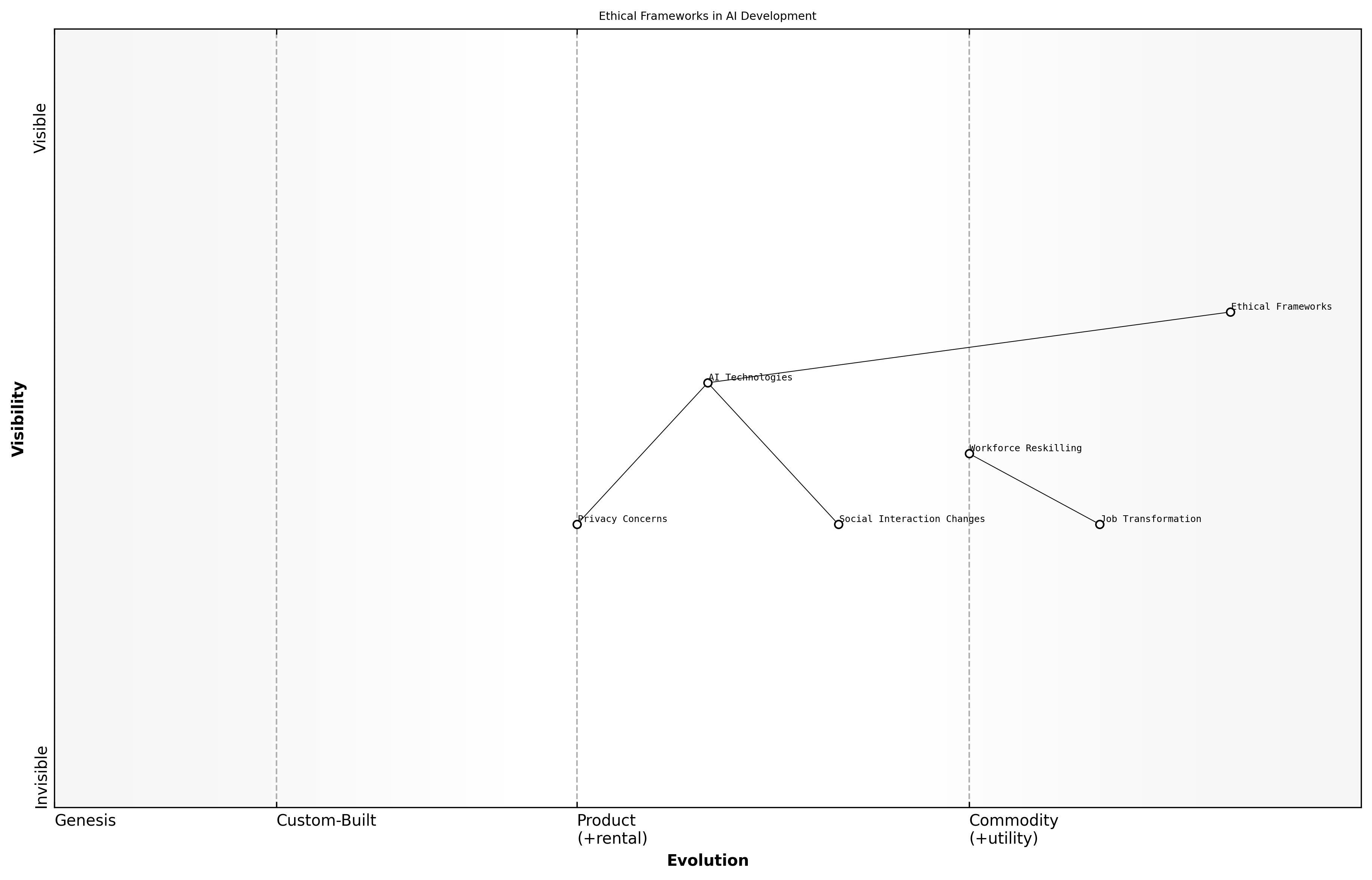
In conclusion, the societal impacts of AI development necessitate a comprehensive ethical framework that addresses the challenges posed by these technologies. Policymakers and industry leaders must collaborate to ensure that AI serves the public good while mitigating potential harms.
Future Trends in AI
Emerging Trends
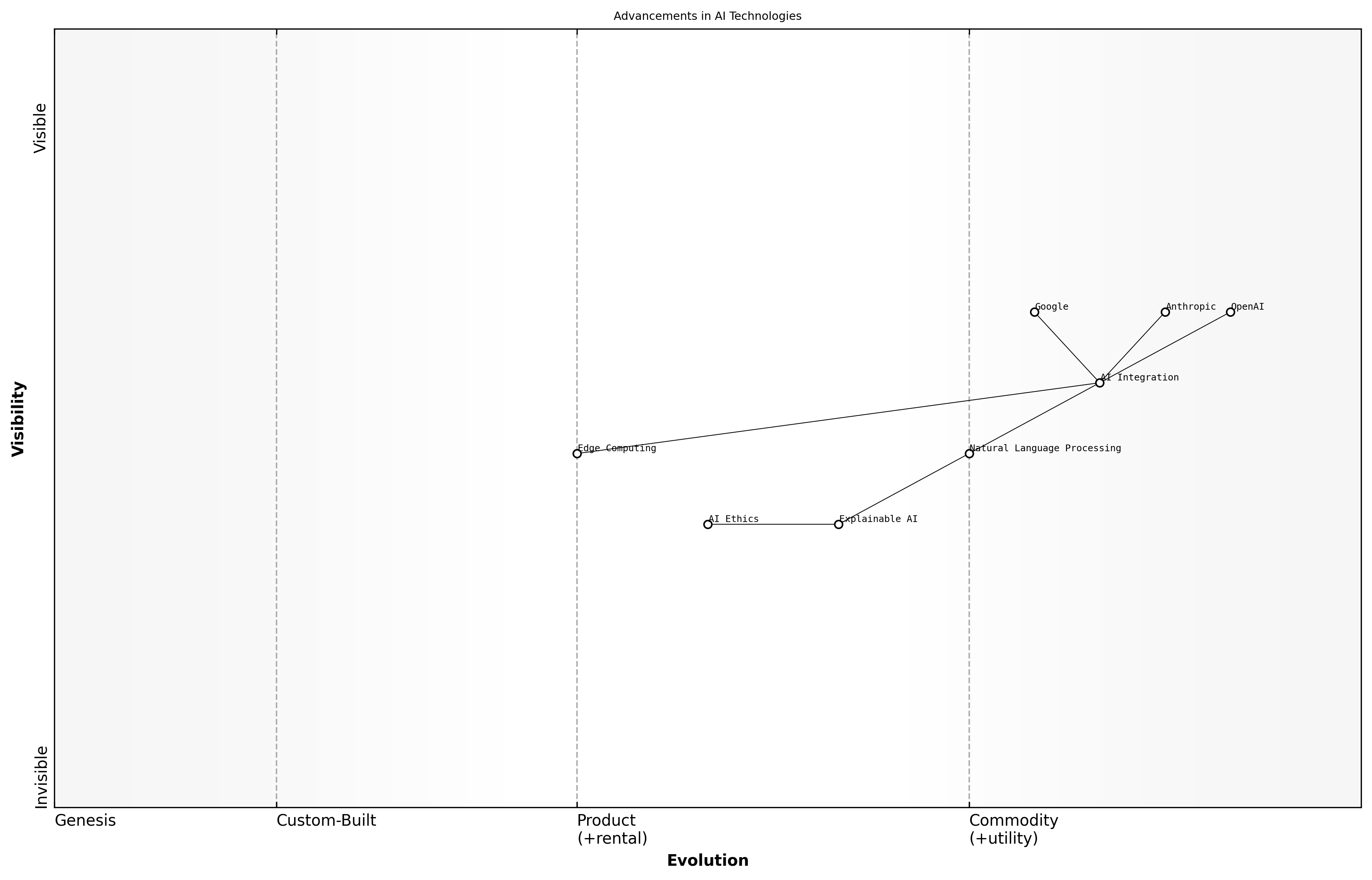
Advancements in AI Technologies
The landscape of artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving, with advancements that are reshaping industries and redefining the capabilities of technology. As OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google vie for supremacy, several key trends are emerging that will significantly influence the future of AI.
- Increased Integration of AI in Everyday Applications
- Advancements in Natural Language Processing and Understanding
- Growth of Explainable AI and Transparency in Algorithms
- Enhanced Focus on AI Ethics and Responsible AI Development
- Expansion of AI in Edge Computing and IoT Devices
These trends not only highlight the technological advancements but also underscore the importance of ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks that must evolve alongside AI technologies. The collaboration between government entities and AI companies will be crucial in addressing these challenges.
The future of AI will be defined not just by technological prowess but by our ability to integrate ethical considerations into every layer of development, says a leading expert in the field.
Shifts in Regulatory Frameworks
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, regulatory frameworks are also undergoing significant transformations. The need for effective governance in AI is paramount, particularly as governments and organisations grapple with the ethical implications and societal impacts of these technologies. This section explores the emerging trends in regulatory frameworks that are shaping the landscape of AI development and deployment.
- Increased focus on transparency and accountability in AI systems
- Development of international standards for AI ethics and safety
- Greater collaboration between governments, industry leaders, and civil society
One of the most significant shifts is the move towards more stringent regulations that require AI systems to be explainable and auditable. This trend reflects a growing recognition of the potential risks associated with opaque algorithms and the need for stakeholders to understand how AI decisions are made.
The future of AI regulation will hinge on balancing innovation with the protection of public interest, says a leading expert in the field.
Another emerging trend is the establishment of regulatory sandboxes, which allow companies to test AI technologies in a controlled environment. This approach enables regulators to better understand the implications of AI while fostering innovation and ensuring compliance with existing laws.
- Keeping pace with rapid technological advancements
- Addressing cross-border regulatory issues
- Ensuring inclusivity and fairness in AI governance
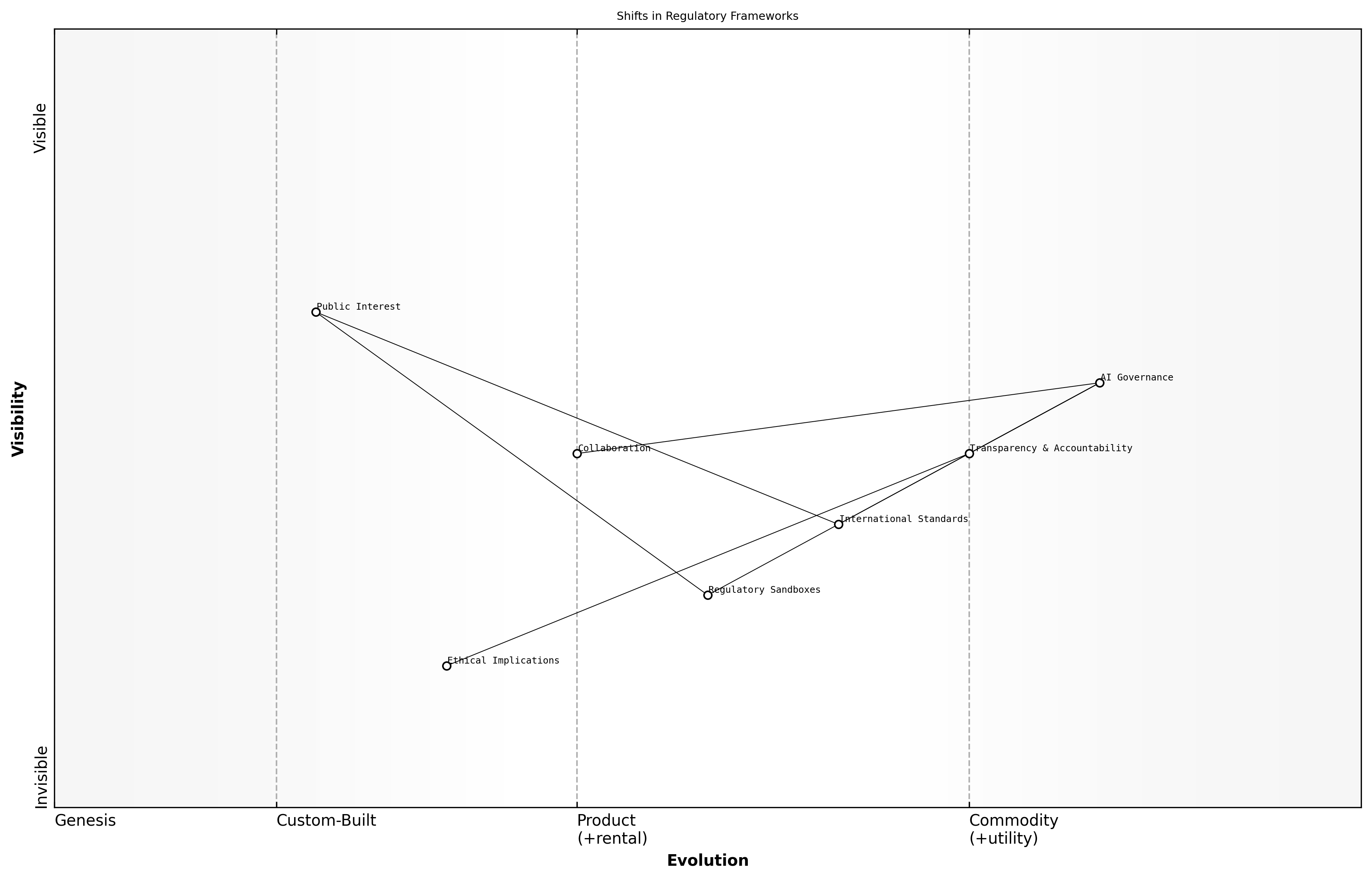
In conclusion, the shifts in regulatory frameworks are indicative of a broader recognition of the importance of responsible AI development. As these trends continue to unfold, it will be crucial for stakeholders to engage in dialogue and collaboration to shape a regulatory environment that supports innovation while safeguarding public interests.
Collaboration vs. Competition
The landscape of artificial intelligence is increasingly characterised by a complex interplay between collaboration and competition. As organisations like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google strive for supremacy, they are also recognising the potential benefits of working together in certain areas. This duality is shaping the future of AI development, influencing everything from technological advancements to ethical considerations.
- Shared Research Initiatives: Companies are beginning to collaborate on research projects that address common challenges, such as bias in AI systems and the ethical implications of AI deployment.
- Open Source Contributions: There is a growing trend towards open-source AI tools and frameworks, allowing organisations to build upon each other's work and accelerate innovation.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Governments and private sector entities are increasingly partnering to leverage AI for public good, such as improving healthcare outcomes or enhancing public safety.
The balance between collaboration and competition is not merely a strategic choice; it is also a necessity in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by AI. As a leading expert in the field notes, the future of AI will depend on how well organisations can navigate this balance, fostering an environment where innovation thrives while ensuring ethical standards are upheld.
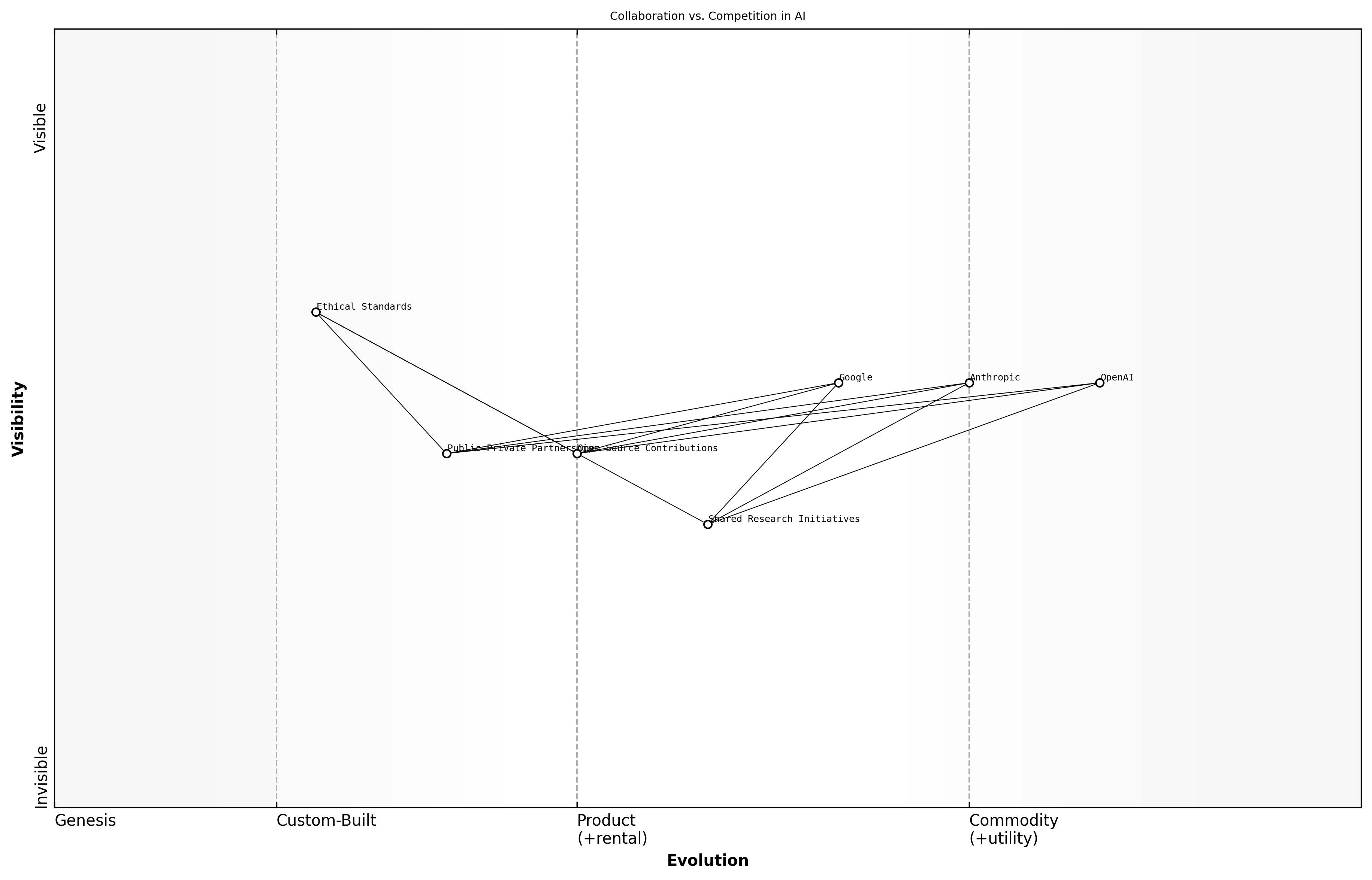
The most successful AI advancements will come from a blend of competitive drive and collaborative spirit, says a senior government official.
Predictions for the Future
Potential Scenarios for AI Development
As we look towards the future of AI development, several potential scenarios emerge that could shape the trajectory of the industry. These scenarios are influenced by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and societal attitudes towards AI. Understanding these possibilities is crucial for stakeholders in the public sector and beyond, as they navigate the complexities of AI integration into their operations.
- Increased Collaboration Between AI Entities: As competition intensifies, companies may seek partnerships to leverage shared resources and expertise, leading to innovative solutions that address complex societal challenges.
- Regulatory Frameworks Evolving: Governments may implement more stringent regulations to ensure ethical AI development, which could either stifle innovation or create a more trustworthy environment for AI applications.
- AI Democratization: Advances in technology may lead to more accessible AI tools, enabling smaller organisations and governments to harness AI capabilities, thus broadening the competitive landscape.
The implications of these scenarios are profound. For instance, increased collaboration could foster a culture of shared knowledge and ethical standards, while evolving regulations might necessitate a shift in how AI companies operate. Furthermore, the democratization of AI could empower underrepresented sectors, ensuring a more equitable distribution of AI benefits.
The future of AI will not be defined solely by competition, but by how well we can collaborate to address the pressing challenges of our time, says a leading expert in the field.
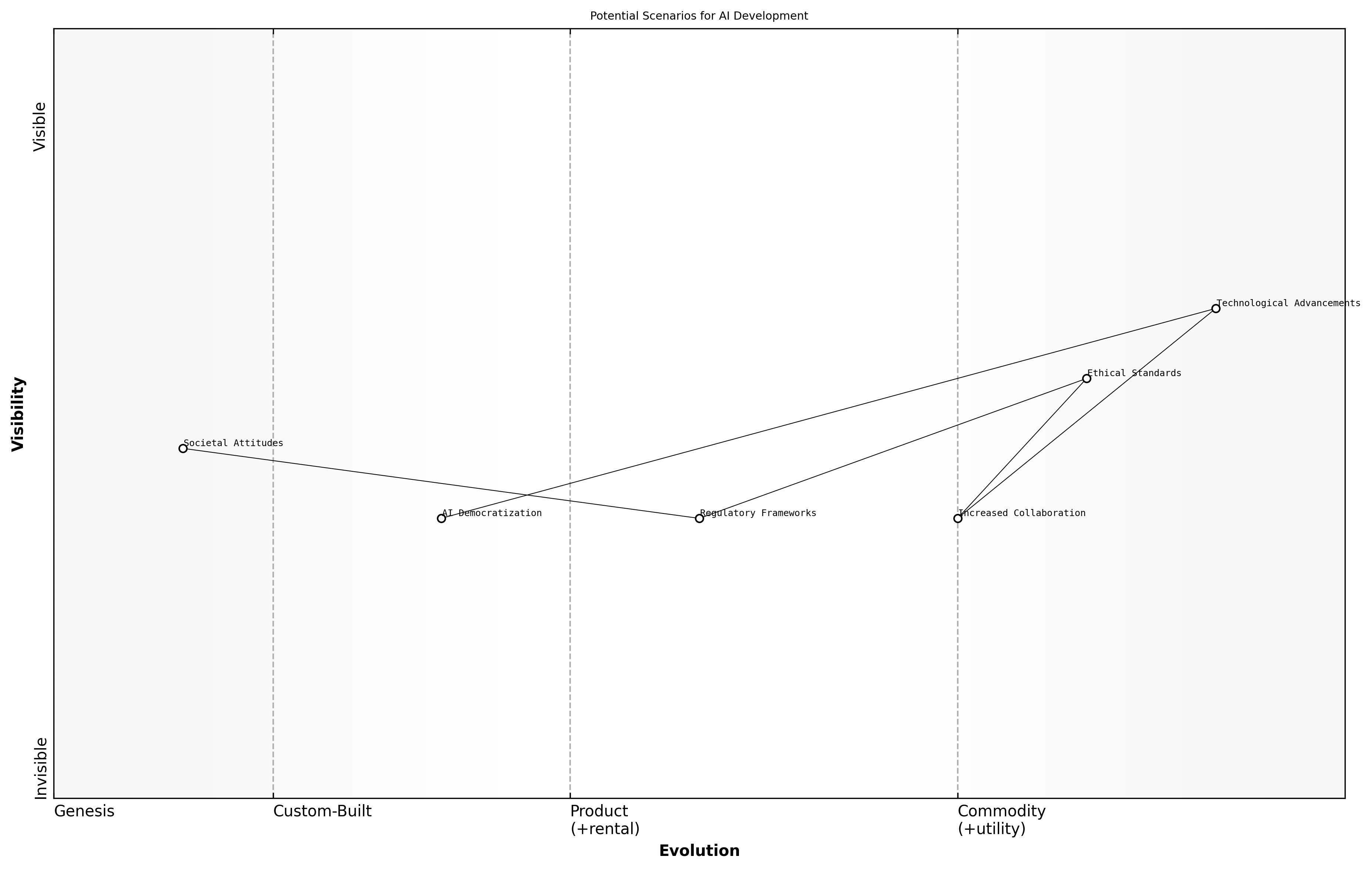
Ultimately, the future of AI development will hinge on the decisions made today by industry leaders, policymakers, and society at large. By anticipating these scenarios, stakeholders can better prepare for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Impact on Global Economy
As we look towards the future, the impact of AI on the global economy is poised to be profound, reshaping industries, labour markets, and economic structures. The integration of AI technologies is expected to drive productivity gains, enhance decision-making processes, and create new economic opportunities. However, these advancements also bring challenges that must be navigated carefully, particularly in terms of workforce displacement and economic inequality.
- Increased Productivity: AI technologies are anticipated to automate routine tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex and creative endeavours, thereby boosting overall productivity.
- Job Transformation: While AI may displace certain jobs, it will also create new roles that require different skill sets, necessitating a shift in workforce training and education.
- Economic Disparities: The benefits of AI may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating existing economic inequalities between regions and sectors.
The future of AI will redefine the global economy, creating both opportunities and challenges that require proactive policy responses, says a leading economist in the field.
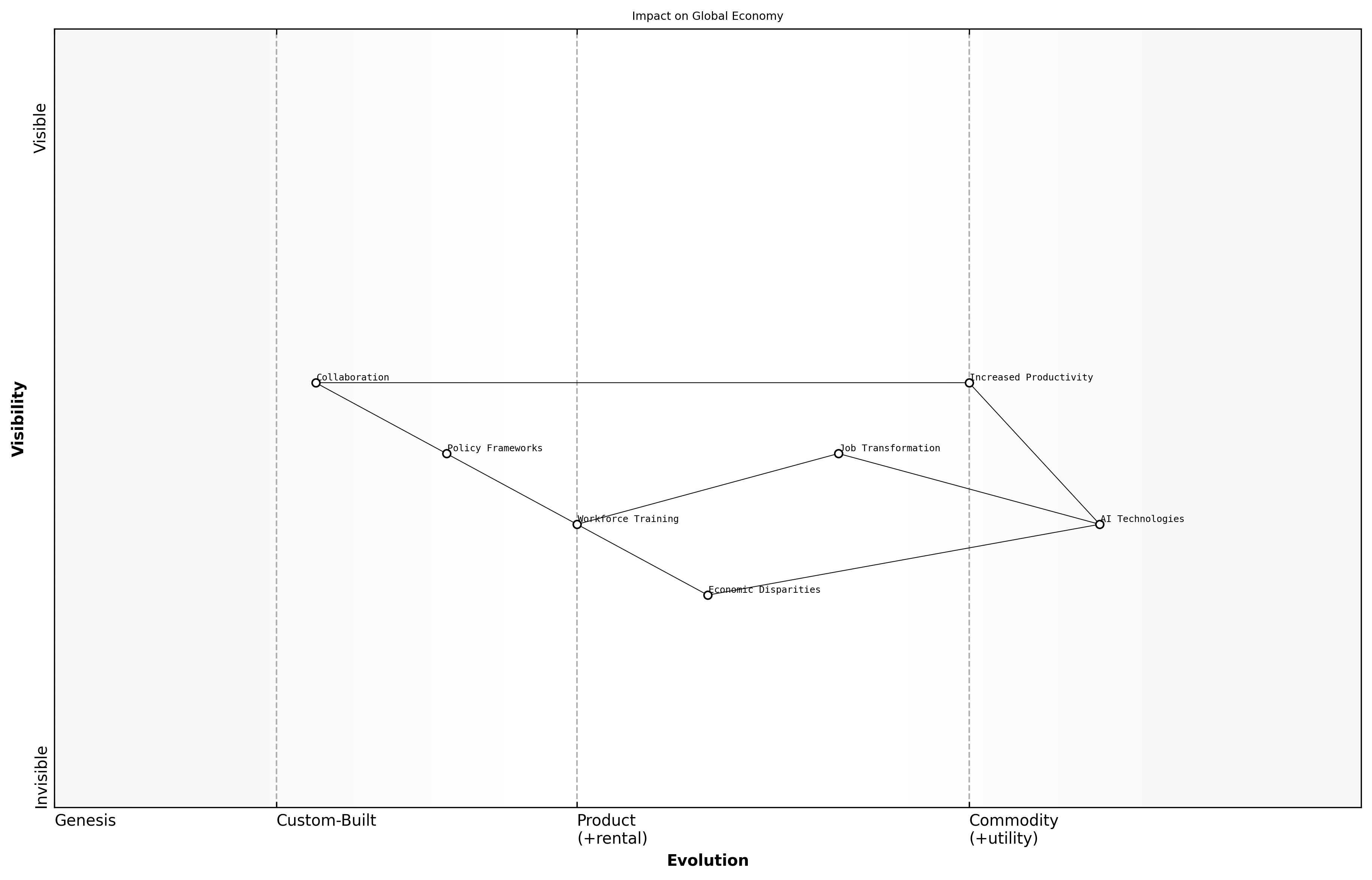
To harness the potential of AI for economic growth, collaboration between governments, businesses, and educational institutions will be essential. Policymakers must develop frameworks that encourage innovation while addressing the ethical and social implications of AI deployment.
Role of AI in Society
The role of AI in society is poised for transformative changes as we look towards the future. The integration of AI technologies into various sectors will not only enhance efficiency but also redefine the way we interact with technology and each other. As AI systems become more sophisticated, their influence will permeate everyday life, shaping social norms, economic structures, and even ethical considerations.
- Increased Automation: AI will drive further automation across industries, leading to significant changes in job roles and the nature of work.
- Enhanced Personalisation: AI systems will provide more tailored experiences in sectors such as healthcare, education, and retail, improving user satisfaction and outcomes.
- Ethical and Regulatory Evolution: As AI becomes more embedded in society, there will be a growing need for ethical frameworks and regulations to govern its use, ensuring accountability and fairness.
Moreover, the societal implications of AI will extend to issues of equity and access. A leading expert in the field notes that the digital divide could widen if access to AI technologies is not equitably distributed, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities.
The future of AI in society will depend on our collective ability to harness its potential while addressing the ethical dilemmas it presents, says a senior government official.
- Collaboration Between Humans and AI: Future AI systems will increasingly work alongside humans, augmenting capabilities rather than replacing them.
- Global AI Governance: International cooperation will be essential to establish norms and standards for AI deployment, ensuring that advancements benefit all of humanity.
- Sustainability Focus: AI will play a critical role in addressing global challenges such as climate change, helping to optimise resource use and reduce waste.
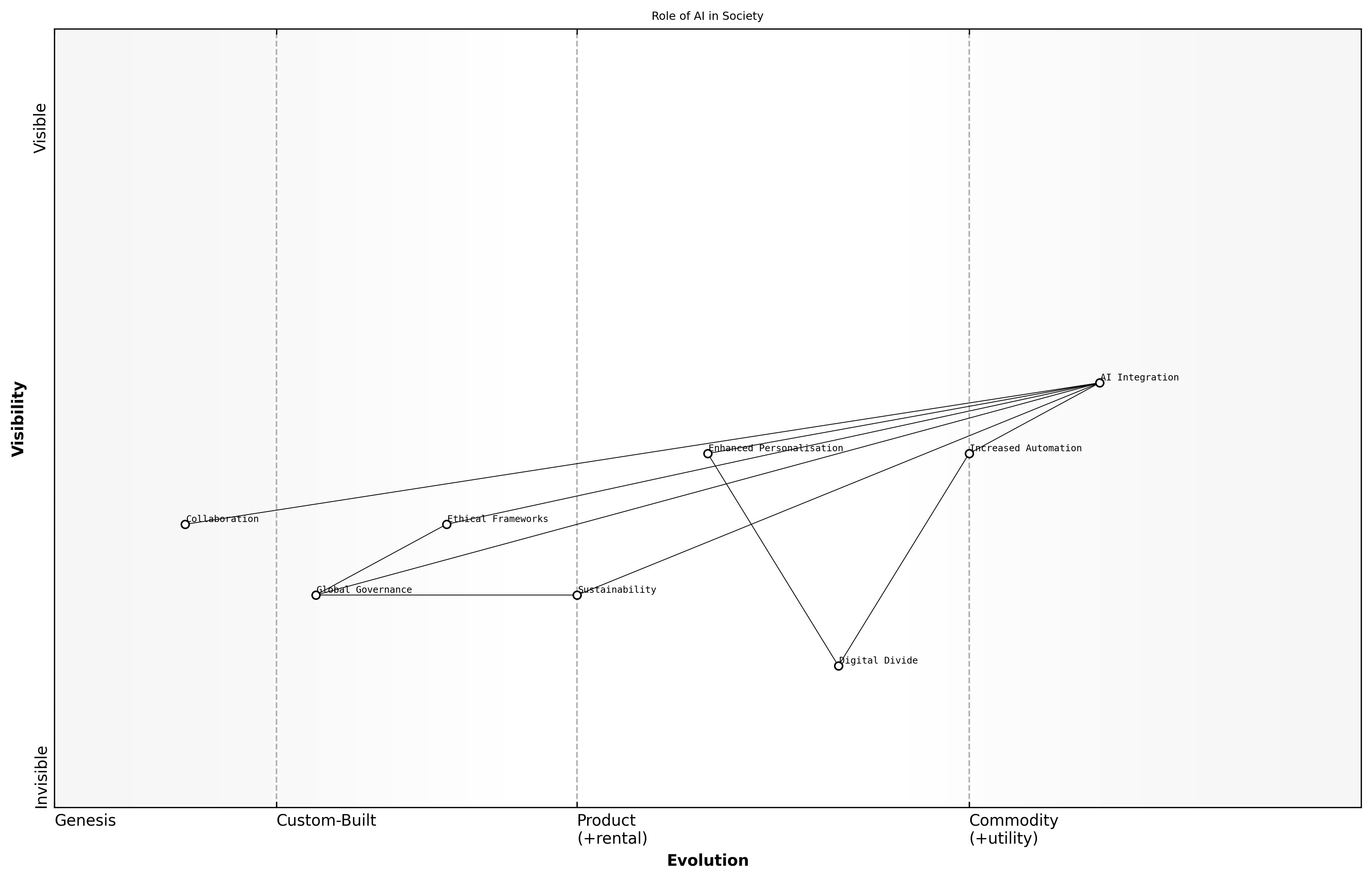
Case Studies
Success Stories
OpenAI's ChatGPT in Customer Service
The integration of OpenAI's ChatGPT into customer service has revolutionised the way organisations interact with their clients. By leveraging natural language processing capabilities, ChatGPT has enabled companies to provide timely, accurate, and personalised responses to customer inquiries, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- 24/7 Availability: ChatGPT can handle customer queries at any time, ensuring that support is always accessible.
- Cost Efficiency: Automating responses reduces the need for extensive human resources, leading to significant cost savings.
- Scalability: ChatGPT can manage a high volume of inquiries simultaneously, allowing businesses to scale their customer service operations without compromising quality.
Several organisations have successfully implemented ChatGPT in their customer service frameworks, demonstrating its effectiveness in real-world scenarios. These success stories highlight the versatility and adaptability of AI in enhancing customer interactions.
ChatGPT has transformed our customer service approach, allowing us to respond to inquiries faster and more efficiently, says a senior customer service manager.
One notable case involved a leading telecommunications company that integrated ChatGPT into its customer support system. By doing so, they achieved a 30% reduction in response times and a 20% increase in customer satisfaction ratings within the first three months of deployment.
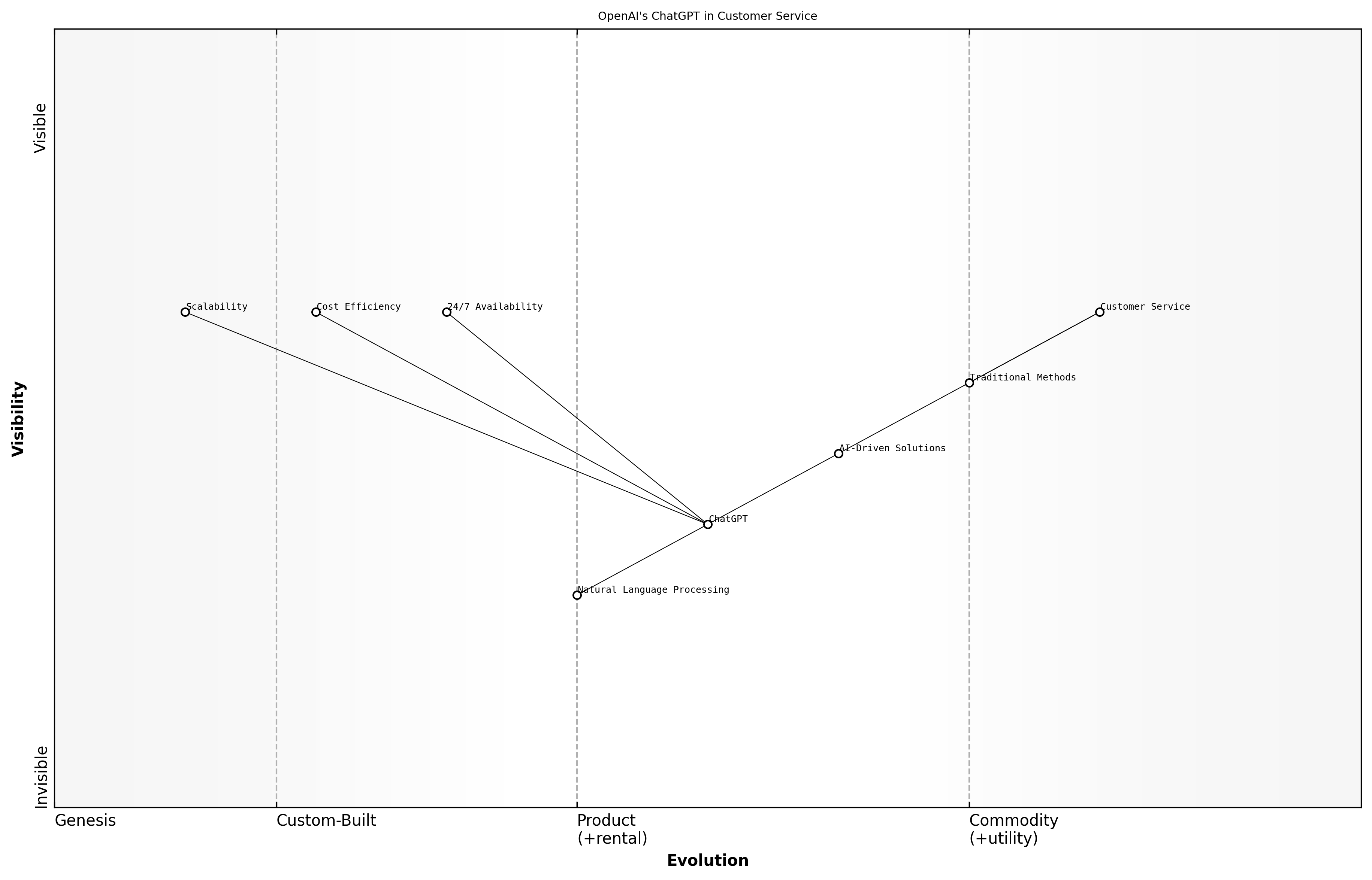
Another example is a major retail chain that utilised ChatGPT to handle online inquiries during peak shopping seasons. The AI was able to manage thousands of simultaneous interactions, providing customers with instant support and freeing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
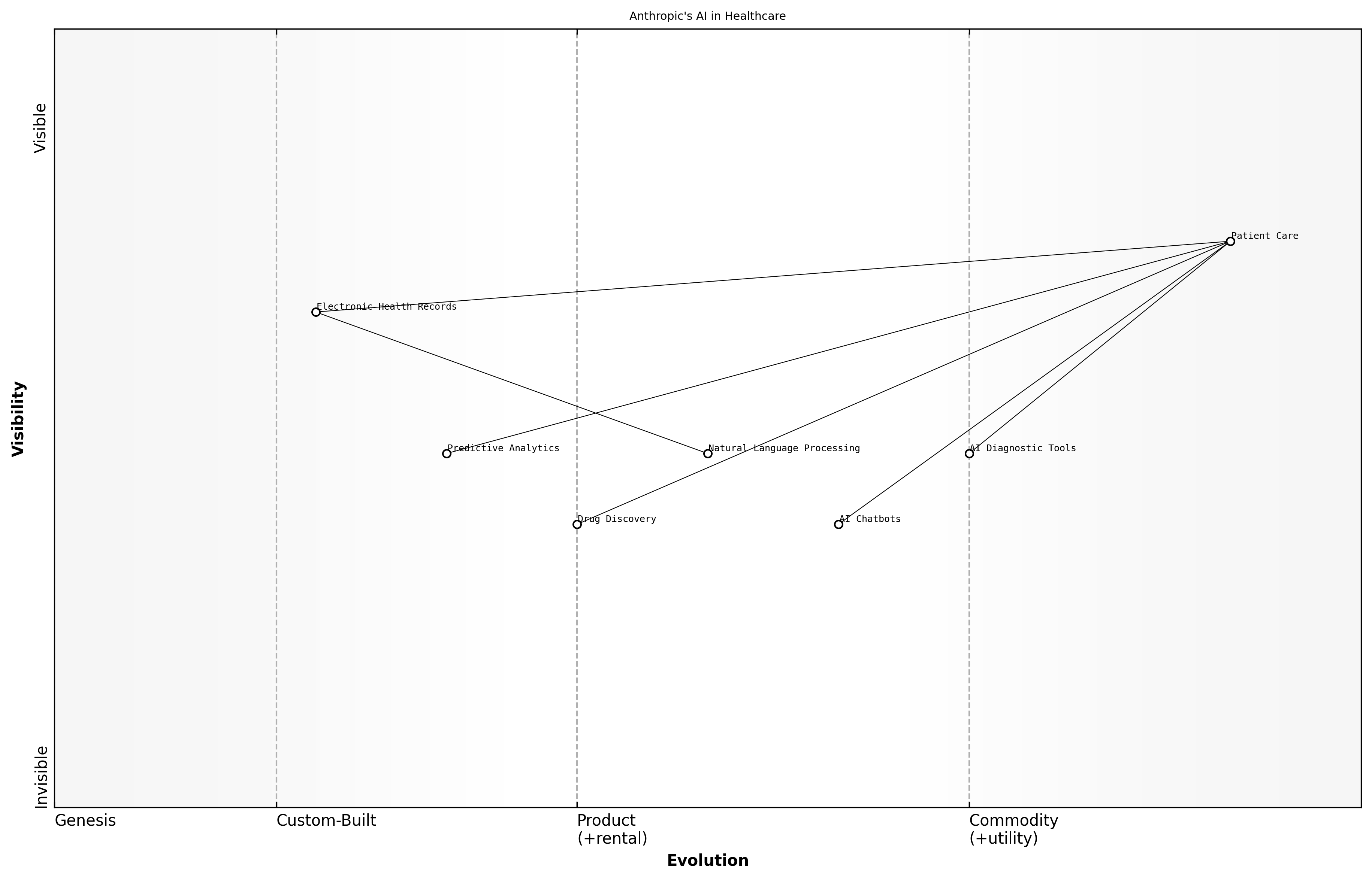
Anthropic's AI in Healthcare
Anthropic has made significant strides in the healthcare sector, leveraging its AI capabilities to enhance patient care, streamline operations, and improve diagnostic accuracy. These advancements not only demonstrate the potential of AI in transforming healthcare but also highlight the ethical considerations that guide Anthropic's approach.
- AI-driven diagnostic tools that assist healthcare professionals in identifying diseases at earlier stages.
- Natural language processing applications that help in managing patient records and extracting relevant information efficiently.
- Predictive analytics models that forecast patient outcomes and optimise treatment plans.
One notable success story involves the implementation of an AI diagnostic tool in a major hospital network. This tool, developed by Anthropic, utilises advanced machine learning algorithms to analyse medical imaging data, significantly reducing the time required for radiologists to interpret scans.
The integration of AI in healthcare not only enhances efficiency but also empowers clinicians to make more informed decisions, says a leading expert in the field.
In another instance, Anthropic's natural language processing technology was deployed in a large-scale electronic health record system. This application enabled healthcare providers to quickly access patient histories and treatment plans, thereby improving the quality of care delivered.
- Enhanced patient engagement through AI-driven chatbots that provide 24/7 support.
- Reduction in administrative burdens, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Improved drug discovery processes by analysing vast datasets to identify potential new treatments.
AI is not just a tool; it is a partner in healthcare that can help us navigate complex challenges, says a senior government official.
These success stories illustrate how Anthropic's commitment to ethical AI development is not only beneficial for healthcare providers but also for patients, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and more efficient healthcare systems.
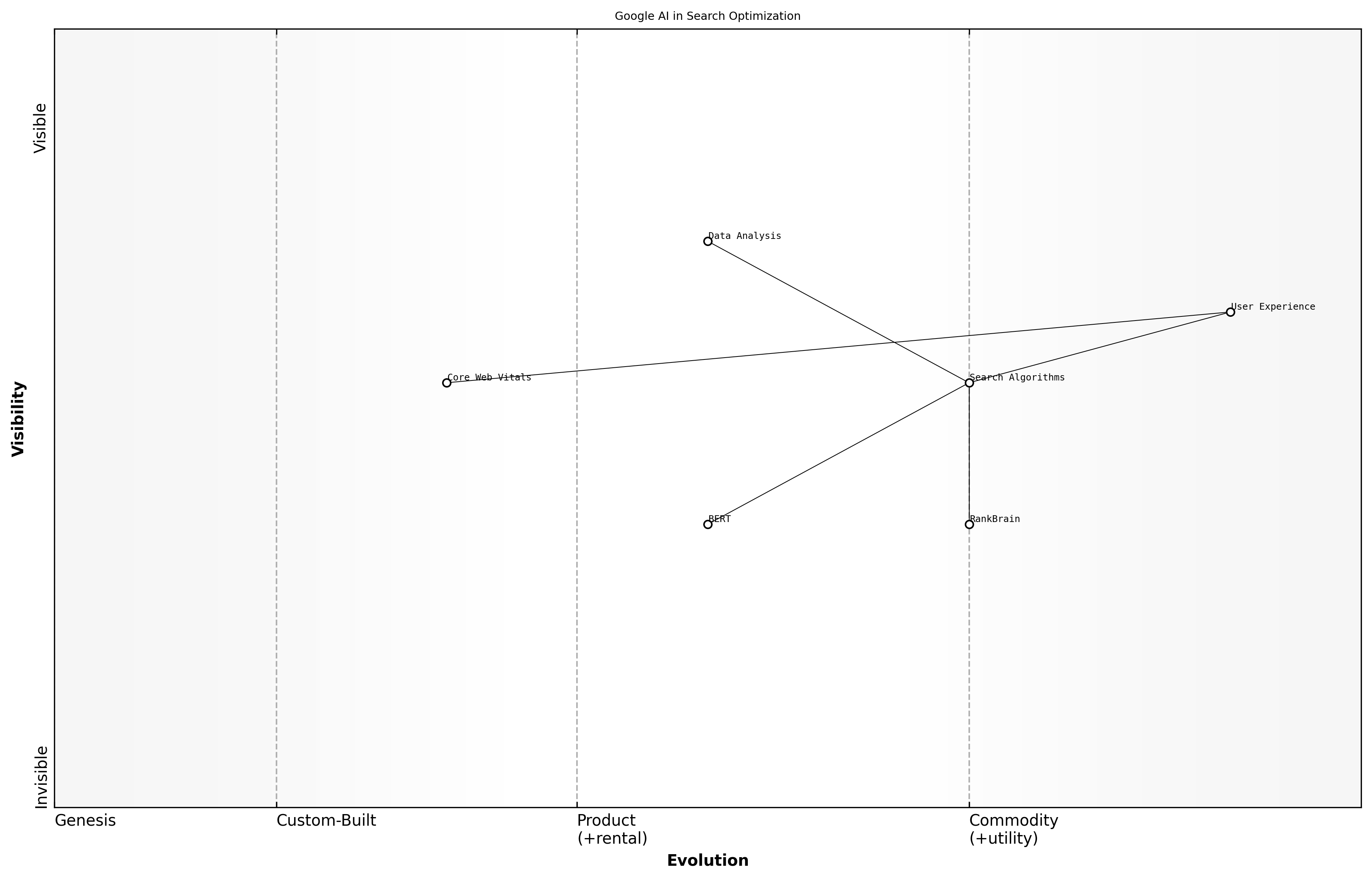
Google's AI in Search Optimization
Google has long been at the forefront of search optimization, leveraging artificial intelligence to enhance user experience and improve the relevance of search results. The integration of AI technologies into Google's search algorithms has transformed how information is retrieved and presented, making it more intuitive and efficient for users.
- RankBrain: An AI-based system that helps Google process search queries and deliver more relevant results by understanding the context and intent behind the words used.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): A groundbreaking model that allows Google to understand the nuances of language, improving the search engine's ability to comprehend the meaning of queries in a more human-like manner.
- Core Web Vitals: A set of metrics introduced by Google that focuses on user experience, measuring loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability, which are now critical factors in search rankings.
These innovations have not only improved the accuracy of search results but have also enhanced the overall user experience. By utilising AI, Google can analyse vast amounts of data in real-time, allowing for more dynamic and responsive search capabilities.
The integration of AI into search optimization has fundamentally changed how users interact with information, making it more accessible and relevant, says a leading expert in the field.
A notable success story is the implementation of BERT, which significantly improved the understanding of natural language queries. Following its introduction, Google reported a marked increase in user satisfaction and engagement, demonstrating the effectiveness of AI in enhancing search capabilities.
Lessons from Failures
OpenAI's Missteps in Public Perception
OpenAI's journey has been marked by significant achievements, but it has also faced notable missteps that have shaped public perception. Understanding these failures is crucial for both the organisation and the broader AI community, as they provide valuable lessons on the importance of transparency, communication, and ethical considerations in AI development.
- Inadequate communication regarding the limitations of AI models, leading to inflated public expectations.
- Failure to address biases in AI outputs, which raised concerns about fairness and discrimination.
- Controversial partnerships that sparked debates about the ethical implications of AI deployment.
These missteps highlight the necessity for organisations like OpenAI to engage in proactive communication strategies. A leading expert in the field notes that transparency in AI capabilities and limitations is essential for fostering trust among users and stakeholders.
The public's understanding of AI is often shaped by sensational narratives rather than factual information, which can lead to misunderstandings and mistrust, says a senior government official.
To mitigate the impact of these failures, OpenAI must adopt a more robust ethical framework that prioritises accountability and inclusivity. This involves not only refining their AI technologies but also ensuring that diverse perspectives are integrated into the development process.
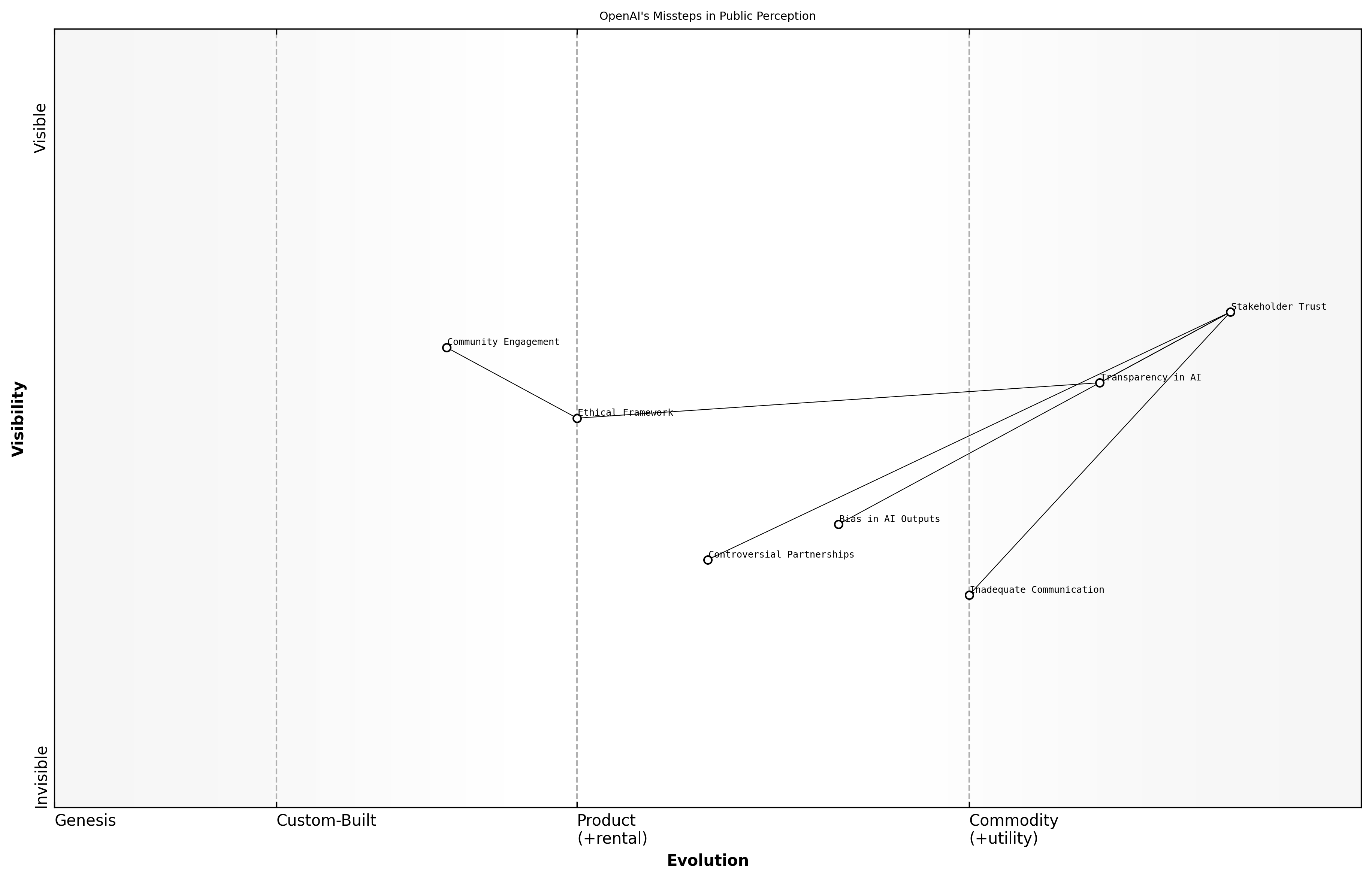
- Enhancing transparency about AI capabilities and limitations.
- Implementing rigorous bias detection and mitigation strategies.
- Engaging with diverse communities to gather feedback and address concerns.
By learning from past mistakes and implementing these strategies, OpenAI can work towards rebuilding its reputation and ensuring that its innovations are perceived positively by the public and stakeholders alike.
Anthropic's Challenges in Scaling
Anthropic, despite its ambitious goals and ethical focus, has faced significant challenges in scaling its operations effectively. These challenges provide critical lessons for both the company and the broader AI community, particularly in understanding the complexities of growth in a rapidly evolving sector.
- Underestimating the complexity of AI alignment and safety, which has slowed down product development.
- Struggling to attract and retain top talent in a competitive market, leading to resource constraints.
- Facing difficulties in establishing robust partnerships that could facilitate scaling efforts.
These challenges highlight the importance of strategic foresight and adaptability in the AI landscape. Companies must not only focus on technological advancements but also on building a sustainable organisational structure that can support growth.
Scaling in AI is not just about technology; it's about aligning your mission with operational capabilities, says a leading expert in the field.
Anthropic's experience serves as a cautionary tale for emerging AI firms. It underscores the necessity of balancing innovation with practical considerations of scalability, ensuring that ethical commitments do not hinder operational effectiveness.
Google's Controversies in AI Ethics
Google's journey in the realm of artificial intelligence has not been without its share of controversies, particularly regarding ethical considerations. These controversies have often stemmed from the company's rapid advancements in AI technologies, which sometimes outpaced the development of corresponding ethical frameworks. Understanding these failures provides valuable lessons for both Google and the broader AI community.
- The importance of transparency in AI development processes to build public trust.
- The need for robust ethical guidelines that evolve alongside technological advancements.
- The significance of stakeholder engagement, including diverse voices in the decision-making process.
One prominent example of Google's ethical missteps occurred with the launch of its AI ethics board, which was disbanded shortly after its formation due to backlash over the inclusion of certain members. This incident highlighted the necessity of carefully considering the composition of ethical oversight bodies and ensuring they reflect a wide range of perspectives.
Ethics in AI is not just about compliance; it's about fostering a culture of responsibility and accountability, says a leading expert in the field.
Another critical lesson emerged from the controversy surrounding Google's Project Maven, which involved the use of AI in military applications. The backlash from employees and the public underscored the need for companies to align their AI initiatives with societal values and ethical standards.
- Establishing clear communication channels to address public concerns about AI applications.
- Implementing continuous ethical training for employees involved in AI projects.
- Creating mechanisms for accountability to ensure that ethical guidelines are followed.
In conclusion, the lessons learned from Google's controversies in AI ethics serve as a crucial reminder that ethical considerations must be integral to the development and deployment of AI technologies. By addressing these challenges head-on, Google and other AI leaders can work towards a future where technology serves the greater good.
Methodologies for Analysis
Strategic Frameworks
Introduction to Wardley Mapping
Wardley Mapping is a strategic framework that provides a visual representation of the competitive landscape, helping organisations understand their position relative to others in the market. It allows leaders to identify opportunities, anticipate changes, and make informed decisions about their strategic direction. In the context of AI supremacy, where companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google are vying for dominance, Wardley Mapping becomes an essential tool for analysing the evolving dynamics of the industry.
- Visualisation of the value chain: Wardley Maps illustrate the components of a business model and how they interact to deliver value to customers.
- Understanding evolution: The framework categorises components into stages of evolution, from genesis to commodity, helping organisations assess where they stand in the lifecycle of their offerings.
- Strategic foresight: By mapping the landscape, organisations can identify potential disruptions, emerging trends, and areas for innovation.
The application of Wardley Mapping in the AI sector highlights the importance of strategic thinking in an environment characterised by rapid technological advancements and shifting market dynamics. It encourages organisations to not only focus on their immediate competitors but also to consider the broader ecosystem in which they operate.
Wardley Mapping empowers organisations to visualise their strategic landscape, enabling them to navigate complexities and make informed decisions, says a leading expert in strategic frameworks.
Applying Wardley Mapping to AI Companies
Wardley Mapping is a strategic framework that provides a visual representation of the landscape in which an organisation operates. It helps identify the components of a business model, their maturity, and the competitive dynamics at play. In the context of AI companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, applying Wardley Mapping can illuminate their strategic positioning and reveal opportunities for innovation and collaboration.
- Understanding the components of AI technology and their evolution
- Identifying user needs and how they drive the development of AI solutions
- Mapping the competitive landscape to assess strengths and weaknesses
The first step in applying Wardley Mapping to AI companies involves identifying the components that make up their technology stack. This includes everything from foundational algorithms to user-facing applications. By understanding how these components evolve over time, organisations can better anticipate shifts in the market and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Next, it is crucial to identify user needs, which serve as the driving force behind AI development. By mapping these needs against the technological components, companies can prioritise their efforts and ensure that they are addressing the most pressing challenges faced by their users.
Finally, mapping the competitive landscape allows AI companies to assess their strengths and weaknesses relative to their competitors. This analysis can highlight areas where a company may have a competitive advantage, as well as potential threats from emerging players in the market.
Wardley Mapping enables organisations to visualise their strategic landscape, making it easier to identify where to focus resources and how to leverage their unique capabilities, says a leading expert in strategic frameworks.
Visualising Competitive Landscapes
Visualising competitive landscapes is crucial for understanding the dynamics between key players in the AI sector, particularly in the context of OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. By employing strategic frameworks, organisations can map out their competitive positioning, identify opportunities for collaboration or differentiation, and anticipate market shifts. This section will delve into various strategic frameworks that can be utilised to visualise these competitive landscapes effectively.
- Wardley Mapping
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter's Five Forces
- PESTLE Analysis
- Value Chain Analysis
Wardley Mapping is particularly effective in the AI landscape as it allows organisations to visualise their capabilities in relation to user needs and the evolution of technology. This method highlights the strategic position of a company and helps in identifying areas for innovation and improvement.
Strategic frameworks provide a structured approach to understanding competitive dynamics, enabling organisations to make informed decisions about their positioning and strategy, says a leading expert in the field.
In addition to Wardley Mapping, SWOT analysis can be employed to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats faced by AI companies. This framework encourages a thorough examination of internal capabilities and external market conditions, which is essential for strategic planning.
- Strengths: Unique technologies, strong brand recognition
- Weaknesses: Limited market presence, ethical concerns
- Opportunities: Emerging markets, partnerships
- Threats: Regulatory challenges, competitive pressures
Porter's Five Forces framework can also be applied to analyse the competitive forces at play in the AI sector. This model examines the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of competitive rivalry. Understanding these forces can help organisations navigate the complexities of the AI marketplace.
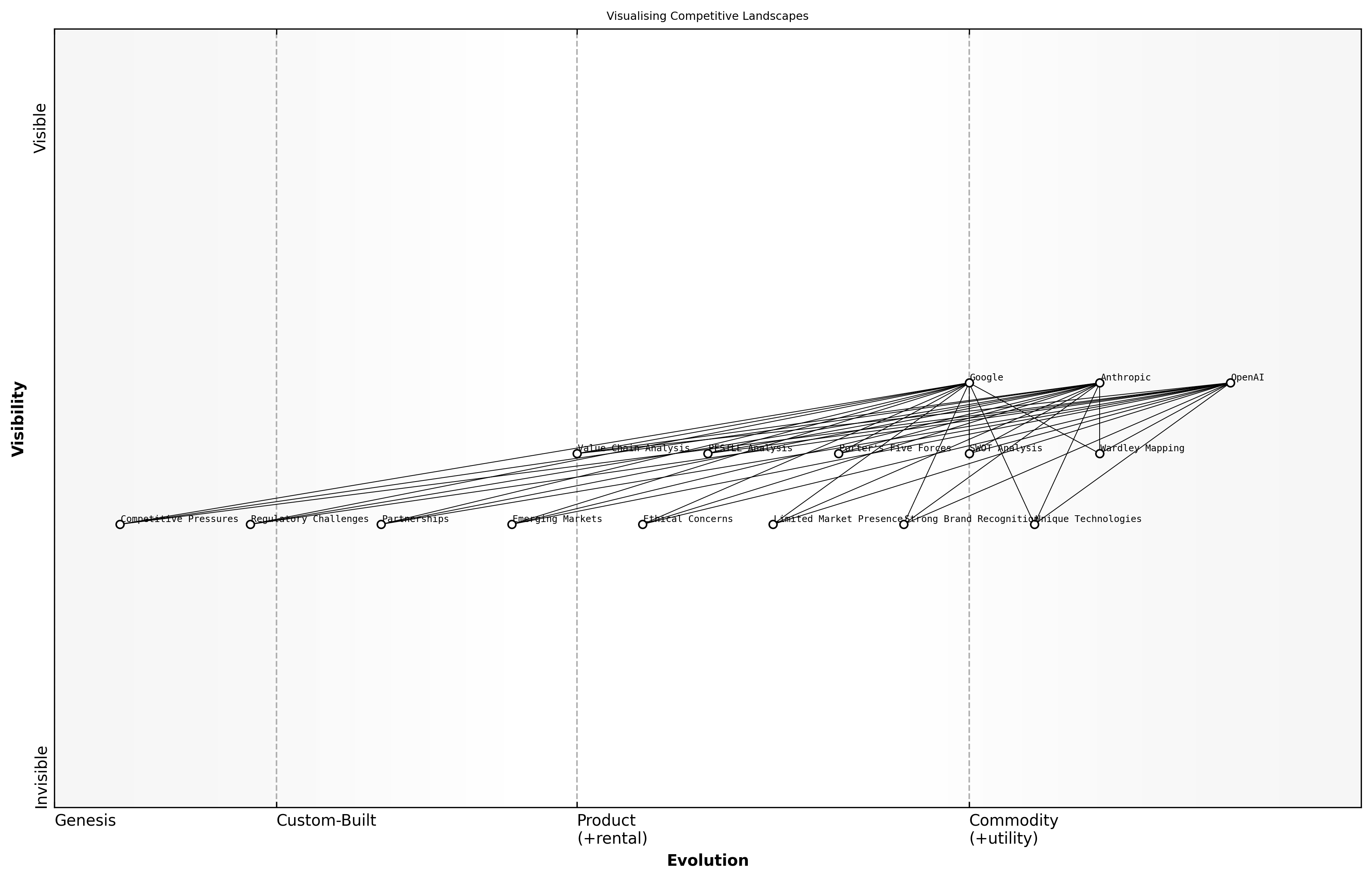
Finally, PESTLE analysis allows organisations to consider the broader political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that may impact their strategic positioning. This holistic view is vital for anticipating changes in the competitive landscape and adapting strategies accordingly.
Analytical Tools
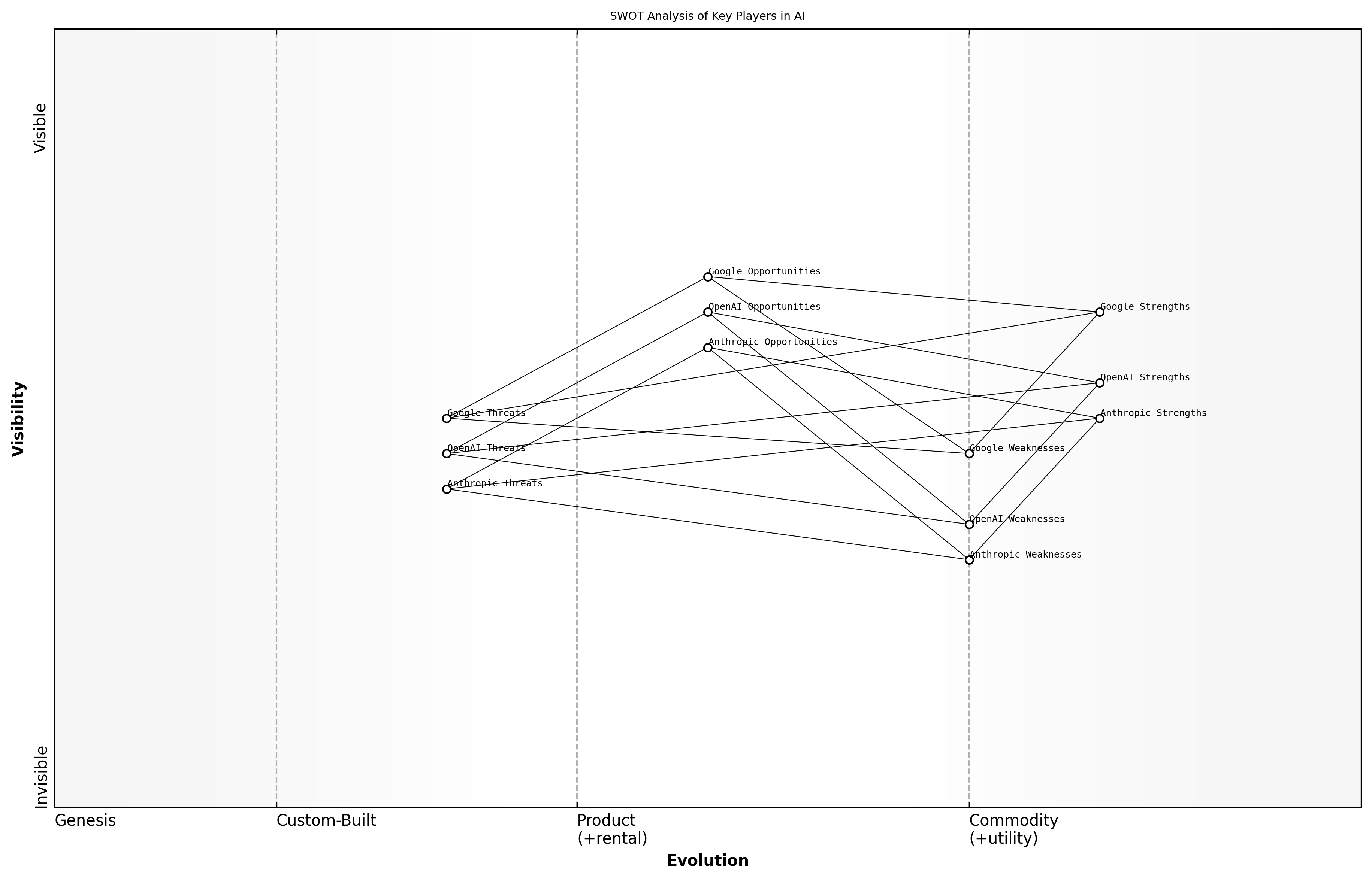
SWOT Analysis of Key Players
The SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps organisations identify their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. In the context of the competitive landscape of AI, particularly among OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, conducting a SWOT analysis provides valuable insights into each company's position and strategic direction. This analysis not only highlights internal capabilities and challenges but also external factors that could impact their market standing and innovation trajectories.
- Strengths: Internal attributes and resources that support a successful outcome.
- Weaknesses: Internal factors that may hinder performance or competitiveness.
- Opportunities: External conditions that could be leveraged for growth or advantage.
- Threats: External challenges that could jeopardise success or market position.
When applying SWOT analysis to the key players in AI, it is essential to consider the unique aspects of each company. For instance, OpenAI's strengths may lie in its innovative models and research capabilities, while its weaknesses could stem from public perception issues. Conversely, Google may have significant technological dominance but faces threats related to regulatory scrutiny.
A comprehensive SWOT analysis can illuminate the strategic paths that AI companies might pursue, enabling them to harness their strengths and mitigate weaknesses, says a leading expert in the field.
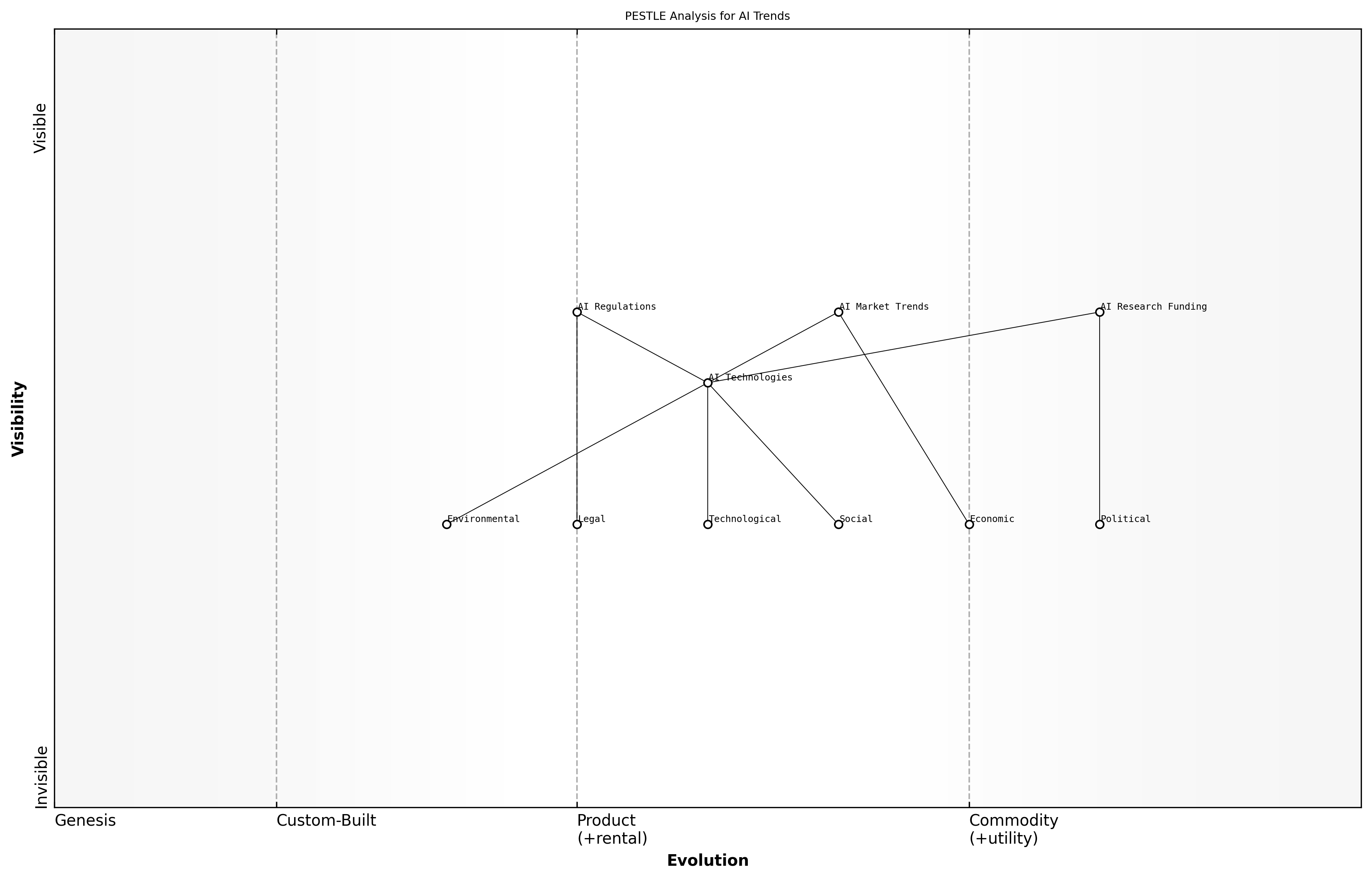
PESTLE Analysis for AI Trends
PESTLE analysis is a strategic tool used to understand the external environment in which an organisation operates. In the context of AI, this analysis helps stakeholders identify the various factors influencing the development and deployment of AI technologies. By examining Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors, professionals can gain insights into the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead in the competitive landscape of AI.
- Political: Government policies, funding for AI research, and international relations affecting AI collaboration.
- Economic: Market trends, investment in AI startups, and the economic impact of AI on various sectors.
- Social: Public perception of AI, ethical considerations, and the societal implications of AI technologies.
- Technological: Advancements in AI algorithms, hardware capabilities, and the integration of AI into existing systems.
- Legal: Regulations governing AI use, data protection laws, and intellectual property issues related to AI innovations.
- Environmental: The sustainability of AI technologies, energy consumption of AI systems, and the impact of AI on environmental conservation.
By employing PESTLE analysis, organisations can strategically position themselves to leverage AI advancements while mitigating risks associated with external factors. This analytical tool not only aids in understanding the current landscape but also assists in forecasting future trends, making it an invaluable resource for policymakers and technology leaders.
Understanding the external environment through PESTLE analysis is crucial for navigating the complexities of AI development and ensuring responsible innovation, says a leading expert in the field.
Scenario Planning for Future Developments
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI, scenario planning serves as a crucial analytical tool for anticipating future developments. This method allows organisations to explore various potential futures based on different assumptions and variables, enabling them to prepare strategically for uncertainty. By employing scenario planning, stakeholders can better understand the implications of their decisions and the competitive dynamics among key players like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google.
- SWOT Analysis: Evaluates strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to identify strategic advantages.
- PESTLE Analysis: Assesses political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors influencing AI developments.
- Scenario Frameworks: Structures narratives around plausible future scenarios to guide strategic decision-making.
Utilising these tools in tandem can provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape, allowing organisations to identify potential risks and opportunities. For instance, a leading expert in the field notes that effective scenario planning can help organisations navigate the complexities of AI governance and ethical considerations, which are increasingly critical in the public sector.
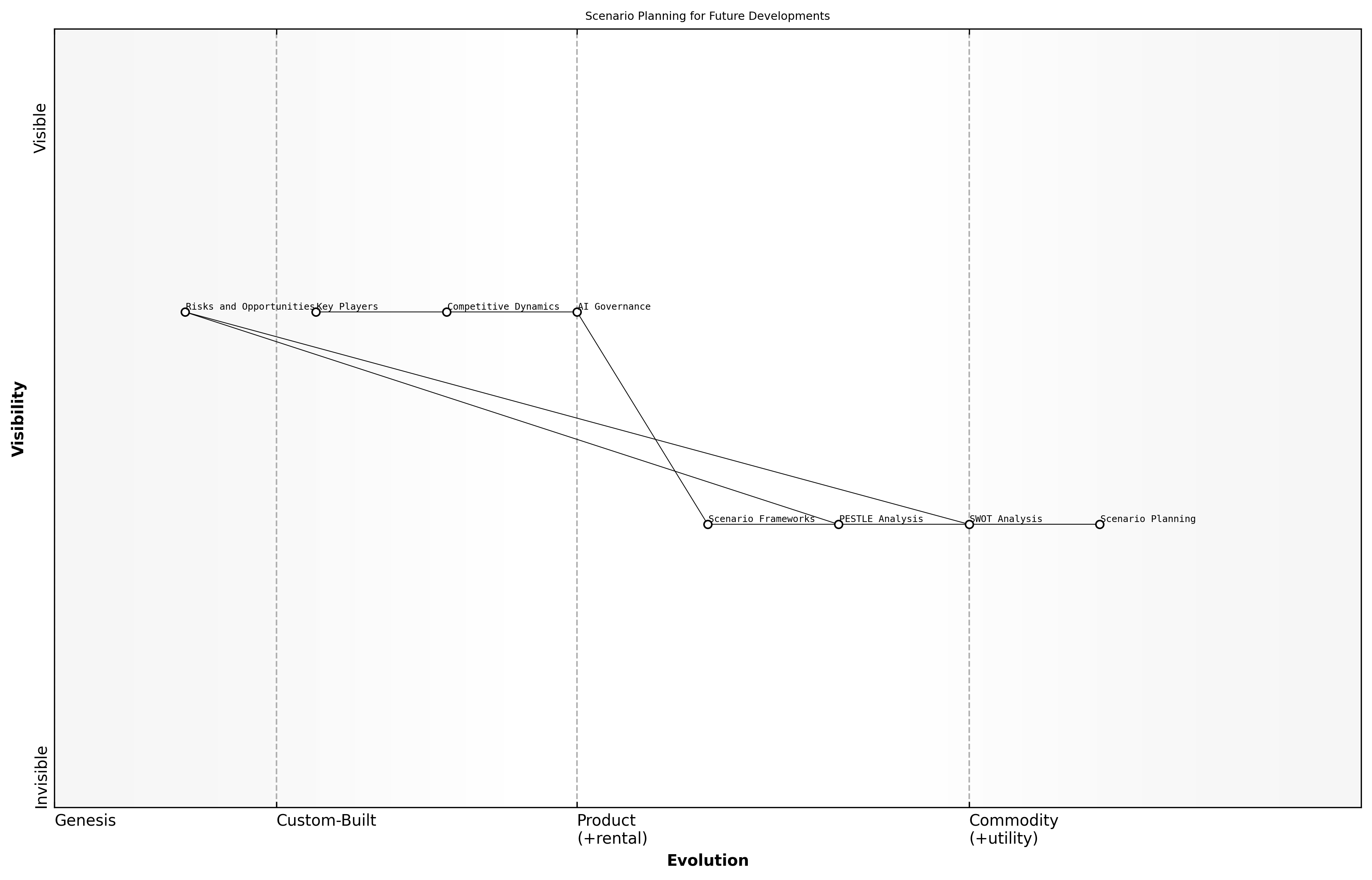
Scenario planning is essential for organisations to remain agile and responsive in a landscape characterised by rapid technological advancements and shifting regulatory environments, says a senior government official.
Conclusion: The Future of AI Supremacy
Key Takeaways
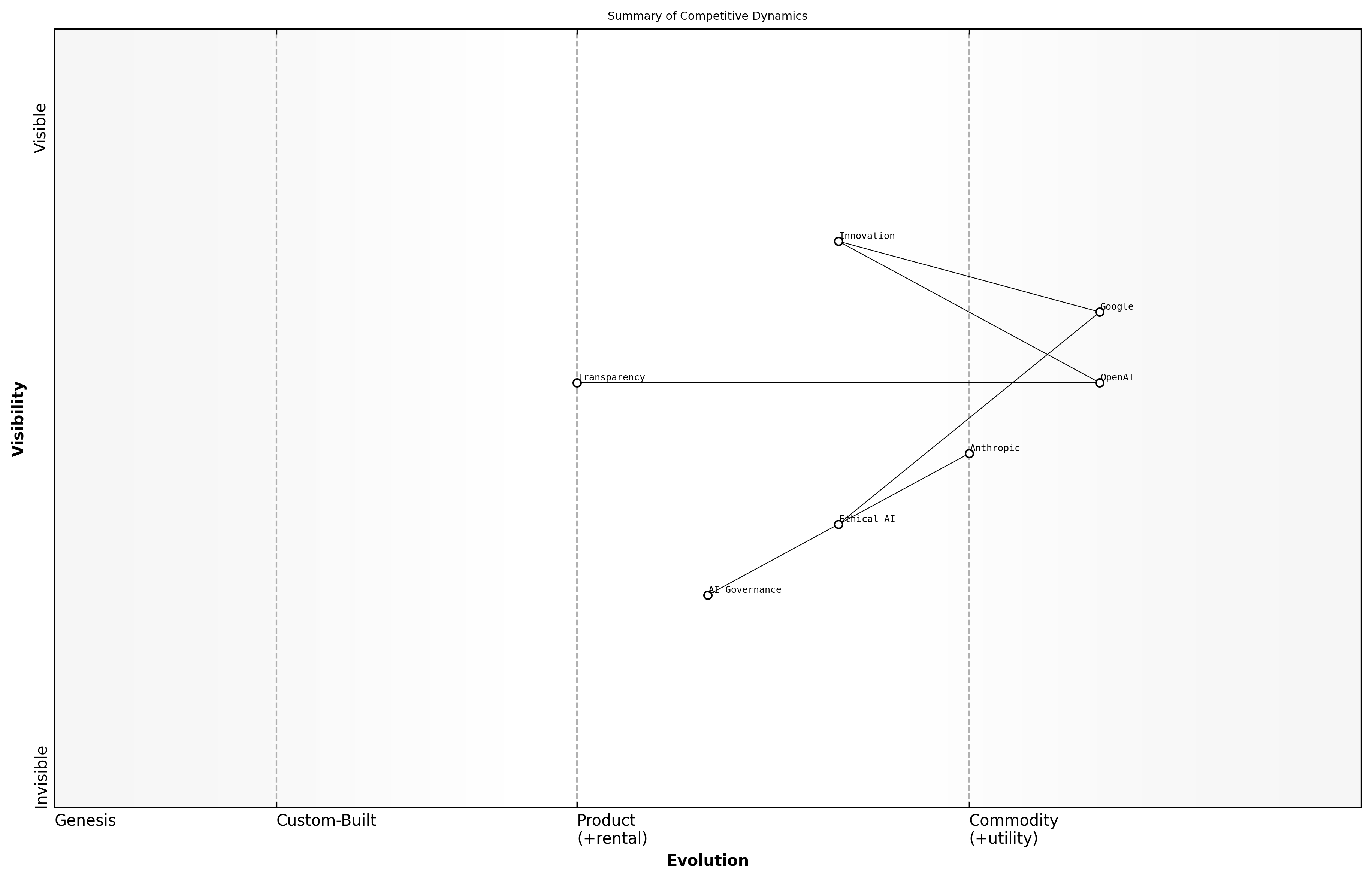
Summary of Competitive Dynamics
The competitive dynamics between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google have shaped the landscape of artificial intelligence, influencing not only technological advancements but also ethical considerations and market strategies.
- OpenAI's commitment to transparency and collaboration has established it as a leader in AI research and application.
- Anthropic's focus on ethical AI development positions it uniquely in a market increasingly concerned with the implications of AI technologies.
- Google's technological dominance and vast resources allow it to innovate rapidly, but it faces scrutiny over ethical practices and data privacy.
As these companies continue to evolve, their strategies will likely impact global AI governance, regulatory frameworks, and public perception, necessitating ongoing dialogue among stakeholders.
The future of AI supremacy will depend on how well these companies navigate the balance between innovation and ethical responsibility, says a leading expert in the field.
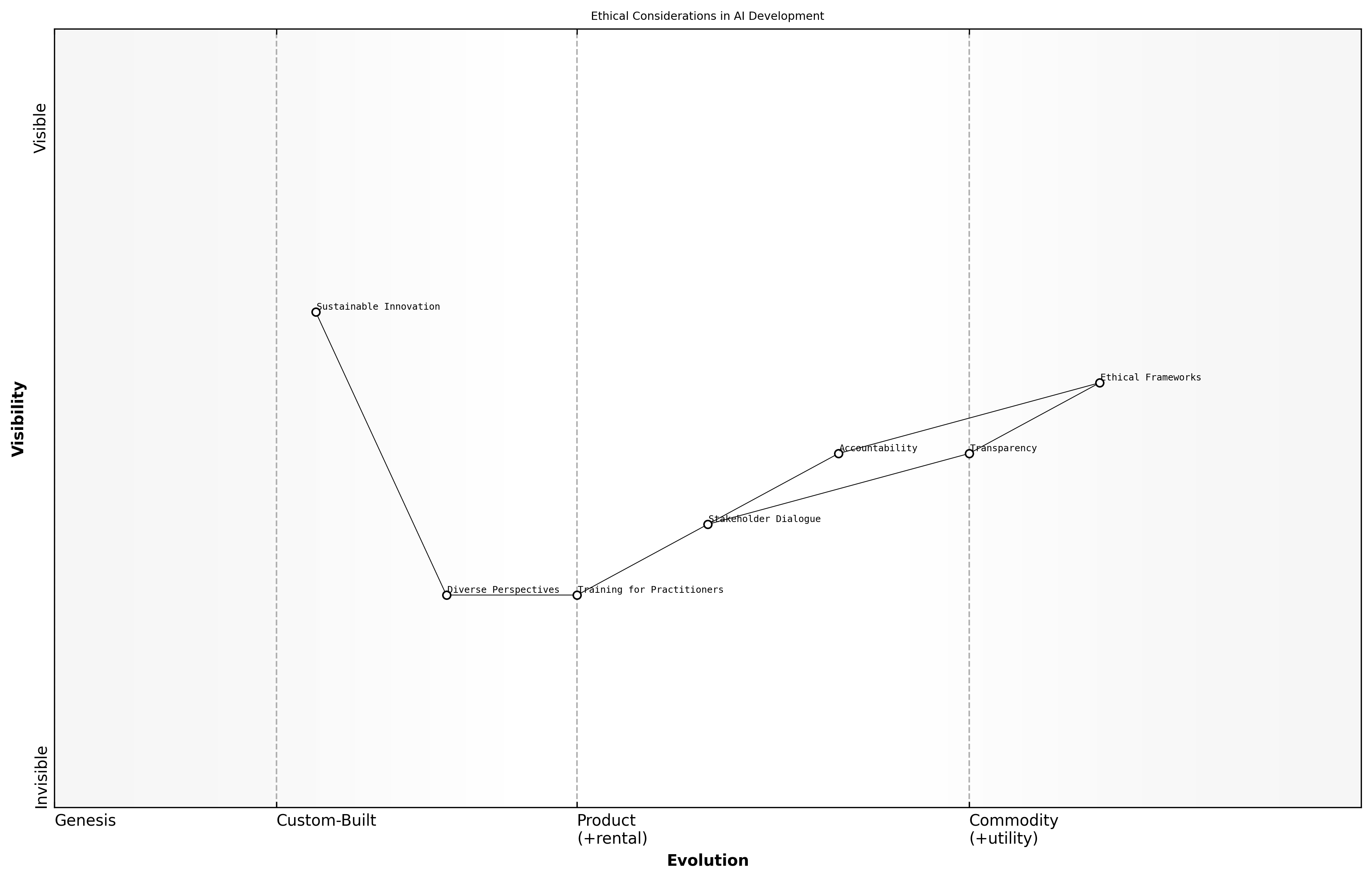
Ethical Considerations Moving Forward
As we conclude our exploration of ethical considerations in the context of AI supremacy, it is imperative to reflect on the critical insights that have emerged. The ethical landscape surrounding AI is complex and multifaceted, necessitating a proactive approach to governance and development.
- The importance of establishing robust ethical frameworks that guide AI development and deployment.
- The need for transparency and accountability in AI systems to foster public trust.
- The necessity of ongoing dialogue among stakeholders, including technologists, policymakers, and the public, to address ethical dilemmas.
Ethical AI is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a foundational pillar for sustainable innovation in technology, says a leading expert in the field.
Moving forward, it is essential that organisations prioritise ethical considerations in their AI strategies. This includes investing in training for AI practitioners on ethical implications and ensuring diverse perspectives are included in the design and implementation of AI systems.
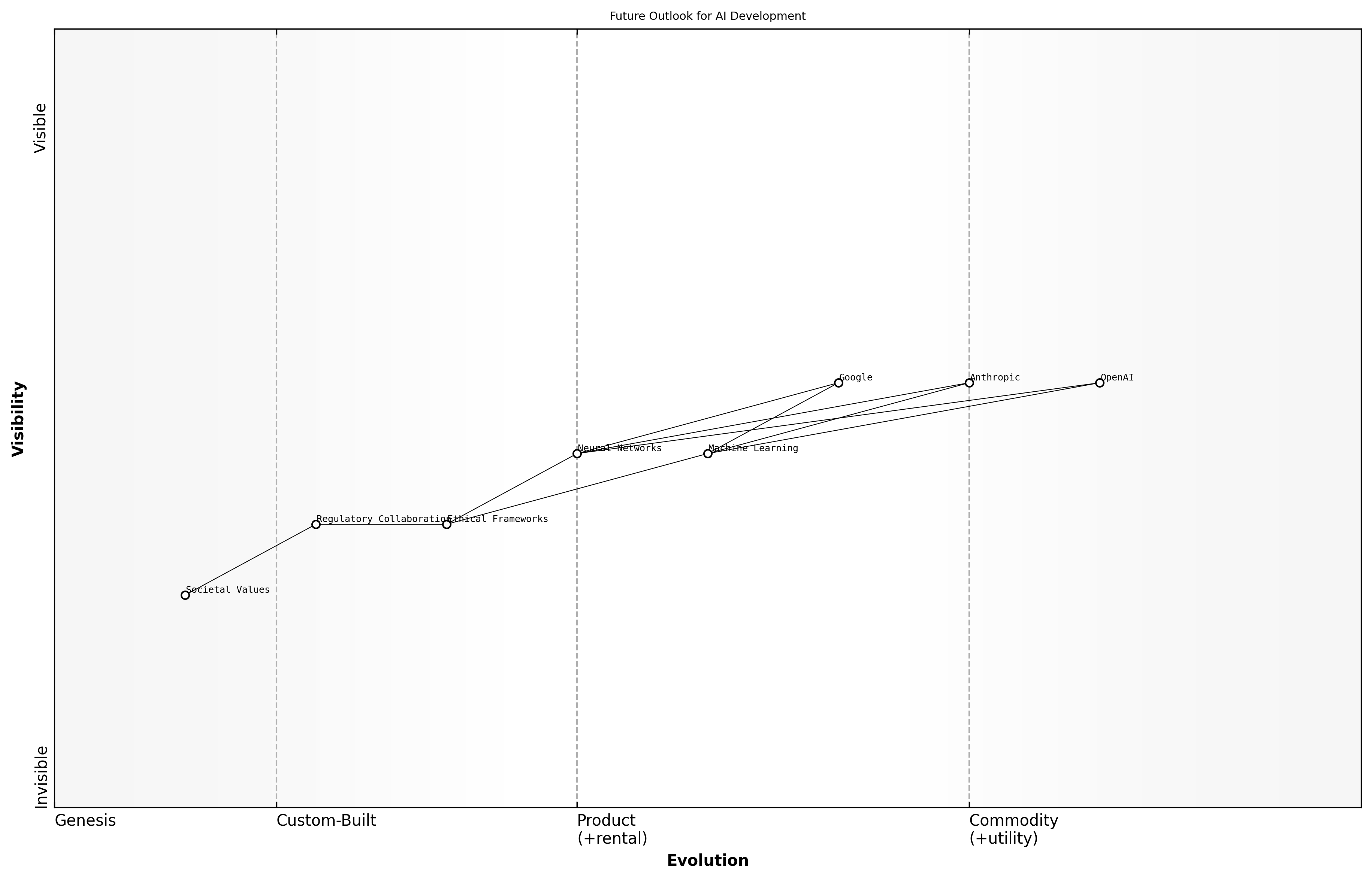
Future Outlook for AI Development
As we conclude our exploration of the competitive landscape in AI, it is essential to synthesise the insights gained regarding the future outlook for AI development. The dynamics between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google not only highlight the technological advancements but also the ethical considerations that must be addressed moving forward.
- AI will continue to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in machine learning and neural networks.
- Ethical frameworks will become increasingly important as AI systems are integrated into various sectors, necessitating collaboration between tech companies and regulatory bodies.
- The competition among major players will spur innovation, but it will also require vigilance to ensure that AI development aligns with societal values and public interest.
The future of AI is not just about technological supremacy; it is about ensuring that these technologies serve humanity responsibly, says a leading expert in AI ethics.
Call to Action
Encouraging Responsible AI Development
As the landscape of artificial intelligence continues to evolve, the need for responsible AI development has never been more critical. The competitive dynamics between OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google highlight the importance of ethical considerations in AI deployment, particularly in government and public sector contexts. Encouraging responsible AI development is not merely a regulatory requirement but a moral imperative that can shape the future of technology and society.
- Establish clear ethical guidelines for AI development that prioritise transparency and accountability.
- Foster collaboration between AI companies, governments, and civil society to create a shared understanding of ethical AI.
- Invest in education and training programs that equip professionals with the skills to develop AI responsibly.
Incorporating ethical frameworks into AI development processes can mitigate risks associated with bias, privacy concerns, and societal impacts. A leading expert in the field emphasises that the integration of ethical considerations must be a foundational aspect of AI strategy rather than an afterthought.
The future of AI depends on our ability to develop technologies that are not only innovative but also aligned with the values of society, says a senior government official.
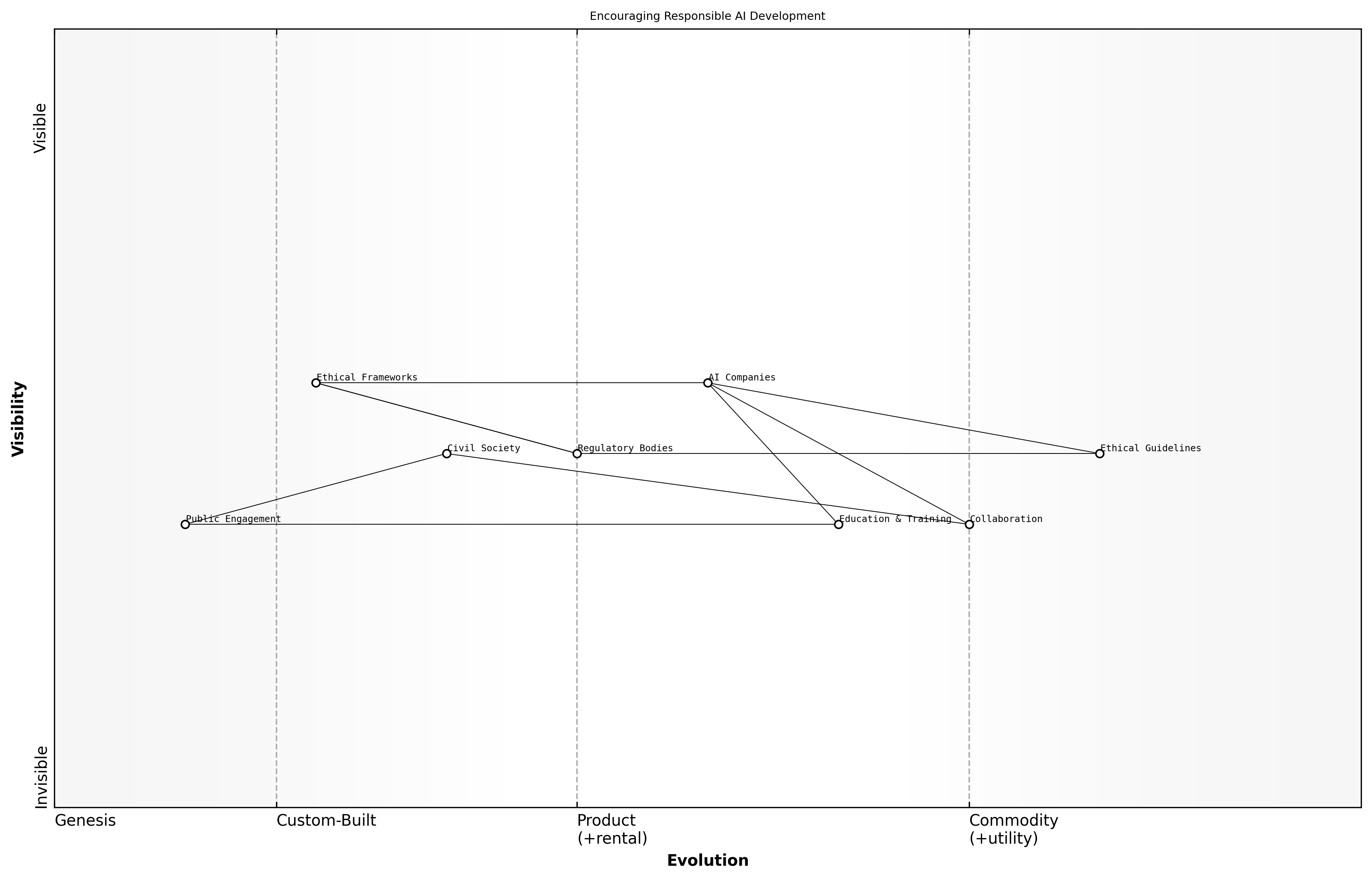
Encouraging responsible AI development requires a multi-faceted approach that includes regulatory frameworks, industry standards, and public engagement. Policymakers must play an active role in shaping the narrative around AI, ensuring that ethical considerations are at the forefront of discussions about technological advancement.
Promoting Collaboration in the AI Community
As the competition for AI supremacy intensifies among leading players like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, it is imperative to foster a culture of collaboration within the AI community. This collaboration is essential not only for the advancement of technology but also for addressing the ethical and societal challenges that arise from AI deployment.
- Encourage open-source initiatives that allow for shared learning and innovation.
- Facilitate cross-industry partnerships to leverage diverse expertise and resources.
- Establish forums and conferences that bring together stakeholders from academia, industry, and government to discuss best practices and ethical considerations.
Collaboration is not just beneficial; it is necessary for the responsible development of AI technologies, says a leading expert in the field.
In practical terms, promoting collaboration can take many forms. For instance, joint research projects can lead to breakthroughs that individual entities might not achieve alone. Additionally, collaborative efforts can enhance transparency and trust in AI systems, which is crucial for public acceptance.
Ultimately, the future of AI supremacy will not be defined solely by competition but by the ability of organisations to work together towards common goals. By prioritising collaboration, the AI community can ensure that advancements are made responsibly and ethically, benefiting society as a whole.
Engaging Policymakers and Stakeholders
Engaging policymakers and stakeholders is critical in shaping the future of AI development and ensuring that it aligns with societal needs and ethical standards. As AI technologies evolve, the role of government and public sector leaders becomes increasingly significant in guiding responsible innovation and addressing the challenges posed by AI. This engagement is essential not only for fostering collaboration but also for establishing frameworks that govern AI use effectively.
- Establish regular communication channels between AI developers and policymakers to facilitate dialogue and understanding.
- Create collaborative platforms where stakeholders can share insights, concerns, and best practices regarding AI implementation.
- Encourage public consultations to gather diverse perspectives on AI policies and their societal implications.
The future of AI will depend on how well we can engage with those who create the policies that govern its use, says a leading expert in technology policy.
To effectively engage policymakers and stakeholders, it is vital to present clear, evidence-based insights into the benefits and risks associated with AI technologies. This involves not only educating decision-makers about the technical aspects of AI but also highlighting its potential impact on various sectors, including healthcare, education, and public safety.
- Provide training sessions for policymakers to enhance their understanding of AI technologies and their implications.
- Develop comprehensive reports that outline the current state of AI, its applications, and the ethical considerations involved.
- Foster partnerships between AI companies and government agencies to pilot innovative solutions that address public sector challenges.
Collaboration between the public and private sectors is essential for harnessing the full potential of AI while ensuring ethical standards are met, says a senior government official.
In conclusion, engaging policymakers and stakeholders is not merely a strategic necessity; it is a moral imperative. As AI continues to permeate various aspects of life, the responsibility lies with both industry leaders and government officials to work together in crafting policies that promote innovation while safeguarding public interests.
Appendix: Further Reading on Wardley Mapping
The following books, primarily authored by Mark Craddock, offer comprehensive insights into various aspects of Wardley Mapping:
Core Wardley Mapping Series
-
Wardley Mapping, The Knowledge: Part One, Topographical Intelligence in Business
- Author: Simon Wardley
- Editor: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This foundational text introduces readers to the Wardley Mapping approach:
- Covers key principles, core concepts, and techniques for creating situational maps
- Teaches how to anchor mapping in user needs and trace value chains
- Explores anticipating disruptions and determining strategic gameplay
- Introduces the foundational doctrine of strategic thinking
- Provides a framework for assessing strategic plays
- Includes concrete examples and scenarios for practical application
The book aims to equip readers with:
- A strategic compass for navigating rapidly shifting competitive landscapes
- Tools for systematic situational awareness
- Confidence in creating strategic plays and products
- An entrepreneurial mindset for continual learning and improvement
-
Wardley Mapping Doctrine: Universal Principles and Best Practices that Guide Strategic Decision-Making
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This book explores how doctrine supports organizational learning and adaptation:
- Standardisation: Enhances efficiency through consistent application of best practices
- Shared Understanding: Fosters better communication and alignment within teams
- Guidance for Decision-Making: Offers clear guidelines for navigating complexity
- Adaptability: Encourages continuous evaluation and refinement of practices
Key features:
- In-depth analysis of doctrine's role in strategic thinking
- Case studies demonstrating successful application of doctrine
- Practical frameworks for implementing doctrine in various organizational contexts
- Exploration of the balance between stability and flexibility in strategic planning
Ideal for:
- Business leaders and executives
- Strategic planners and consultants
- Organizational development professionals
- Anyone interested in enhancing their strategic decision-making capabilities
-
Wardley Mapping Gameplays: Transforming Insights into Strategic Actions
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This book delves into gameplays, a crucial component of Wardley Mapping:
- Gameplays are context-specific patterns of strategic action derived from Wardley Maps
- Types of gameplays include:
- User Perception plays (e.g., education, bundling)
- Accelerator plays (e.g., open approaches, exploiting network effects)
- De-accelerator plays (e.g., creating constraints, exploiting IPR)
- Market plays (e.g., differentiation, pricing policy)
- Defensive plays (e.g., raising barriers to entry, managing inertia)
- Attacking plays (e.g., directed investment, undermining barriers to entry)
- Ecosystem plays (e.g., alliances, sensing engines)
Gameplays enhance strategic decision-making by:
- Providing contextual actions tailored to specific situations
- Enabling anticipation of competitors' moves
- Inspiring innovative approaches to challenges and opportunities
- Assisting in risk management
- Optimizing resource allocation based on strategic positioning
The book includes:
- Detailed explanations of each gameplay type
- Real-world examples of successful gameplay implementation
- Frameworks for selecting and combining gameplays
- Strategies for adapting gameplays to different industries and contexts
-
Navigating Inertia: Understanding Resistance to Change in Organisations
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This comprehensive guide explores organizational inertia and strategies to overcome it:
Key Features:
- In-depth exploration of inertia in organizational contexts
- Historical perspective on inertia's role in business evolution
- Practical strategies for overcoming resistance to change
- Integration of Wardley Mapping as a diagnostic tool
The book is structured into six parts:
- Understanding Inertia: Foundational concepts and historical context
- Causes and Effects of Inertia: Internal and external factors contributing to inertia
- Diagnosing Inertia: Tools and techniques, including Wardley Mapping
- Strategies to Overcome Inertia: Interventions for cultural, behavioral, structural, and process improvements
- Case Studies and Practical Applications: Real-world examples and implementation frameworks
- The Future of Inertia Management: Emerging trends and building adaptive capabilities
This book is invaluable for:
- Organizational leaders and managers
- Change management professionals
- Business strategists and consultants
- Researchers in organizational behavior and management
-
Wardley Mapping Climate: Decoding Business Evolution
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This comprehensive guide explores climatic patterns in business landscapes:
Key Features:
- In-depth exploration of 31 climatic patterns across six domains: Components, Financial, Speed, Inertia, Competitors, and Prediction
- Real-world examples from industry leaders and disruptions
- Practical exercises and worksheets for applying concepts
- Strategies for navigating uncertainty and driving innovation
- Comprehensive glossary and additional resources
The book enables readers to:
- Anticipate market changes with greater accuracy
- Develop more resilient and adaptive strategies
- Identify emerging opportunities before competitors
- Navigate complexities of evolving business ecosystems
It covers topics from basic Wardley Mapping to advanced concepts like the Red Queen Effect and Jevon's Paradox, offering a complete toolkit for strategic foresight.
Perfect for:
- Business strategists and consultants
- C-suite executives and business leaders
- Entrepreneurs and startup founders
- Product managers and innovation teams
- Anyone interested in cutting-edge strategic thinking
Practical Resources
-
Wardley Mapping Cheat Sheets & Notebook
- Author: Mark Craddock
- 100 pages of Wardley Mapping design templates and cheat sheets
- Available in paperback format
- Amazon Link
This practical resource includes:
- Ready-to-use Wardley Mapping templates
- Quick reference guides for key Wardley Mapping concepts
- Space for notes and brainstorming
- Visual aids for understanding mapping principles
Ideal for:
- Practitioners looking to quickly apply Wardley Mapping techniques
- Workshop facilitators and educators
- Anyone wanting to practice and refine their mapping skills
Specialized Applications
-
UN Global Platform Handbook on Information Technology Strategy: Wardley Mapping The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Explores the use of Wardley Mapping in the context of sustainable development
- Available for free with Kindle Unlimited or for purchase
- Amazon Link
This specialized guide:
- Applies Wardley Mapping to the UN's Sustainable Development Goals
- Provides strategies for technology-driven sustainable development
- Offers case studies of successful SDG implementations
- Includes practical frameworks for policy makers and development professionals
-
AIconomics: The Business Value of Artificial Intelligence
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Applies Wardley Mapping concepts to the field of artificial intelligence in business
- Amazon Link
This book explores:
- The impact of AI on business landscapes
- Strategies for integrating AI into business models
- Wardley Mapping techniques for AI implementation
- Future trends in AI and their potential business implications
Suitable for:
- Business leaders considering AI adoption
- AI strategists and consultants
- Technology managers and CIOs
- Researchers in AI and business strategy
These resources offer a range of perspectives and applications of Wardley Mapping, from foundational principles to specific use cases. Readers are encouraged to explore these works to enhance their understanding and application of Wardley Mapping techniques.
Note: Amazon links are subject to change. If a link doesn't work, try searching for the book title on Amazon directly.