Mastering Modern Bid and Tender Consultancy: A Digital-Era Guide to Strategic Supply Market Management
TechnologyMastering Modern Bid and Tender Consultancy: A Digital-Era Guide to Strategic Supply Market Management
Table of Contents
- Mastering Modern Bid and Tender Consultancy: A Digital-Era Guide to Strategic Supply Market Management
- Introduction: The Evolution of Bid and Tender Management
- Digital Transformation in Bid Management
- Strategic Supply Market Analysis and Relationship Management
- ESG and Risk Management in Modern Bidding
- Practical Applications and Case Studies
- Practical Resources
- Specialized Applications
Introduction: The Evolution of Bid and Tender Management
The Modern Bid Management Landscape
Current Market Dynamics and Trends
The bid and tender consultancy market has undergone significant transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancement, regulatory changes, and evolving procurement practices. As we navigate through the 2020s, the landscape continues to shift dramatically, presenting both challenges and opportunities for organisations engaging in public and private sector procurement.
The convergence of digital technologies and traditional procurement processes has fundamentally altered how we approach bid management, creating a new paradigm that demands both technical expertise and strategic insight, notes a leading procurement strategist.
- Increased emphasis on digital submission platforms and e-procurement solutions
- Growing focus on sustainability and social value requirements in bid evaluation
- Rise of data-driven decision making and predictive analytics
- Enhanced scrutiny of supply chain resilience and risk management
- Greater importance of collaborative supplier relationships and innovation partnerships
The public sector, in particular, has witnessed a substantial shift towards more sophisticated procurement methodologies. Government bodies are increasingly adopting outcome-based specifications and moving away from purely price-driven evaluations. This evolution requires bid consultants to develop deeper expertise in value proposition development and social impact assessment.
Market consolidation has become a notable trend, with larger consultancies acquiring specialist bid firms to create comprehensive service offerings. This consolidation is driving the need for more integrated approaches to bid management, combining technical expertise with strategic advisory services and digital capabilities.
- Emergence of specialist bid technology providers and platforms
- Integration of artificial intelligence in bid analysis and development
- Growing importance of cybersecurity and data protection compliance
- Increased focus on post-award contract management capabilities
- Rise of agile procurement methodologies and flexible contracting models
The most successful organisations in today's market are those that can seamlessly blend traditional bid writing expertise with digital innovation and strategic thinking, observes a senior public sector procurement advisor.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated many of these trends, particularly the adoption of digital solutions and the emphasis on supply chain resilience. Procurement teams are now expected to demonstrate adaptability and maintain effective bid management processes in remote working environments, leading to the rapid adoption of collaborative tools and digital workflows.
Impact of Digital Transformation
The digital transformation has fundamentally revolutionised the bid and tender consultancy landscape, creating a paradigm shift in how organisations approach, develop, and submit bids. As a seasoned bid consultant who has witnessed this evolution firsthand, I can attest that the impact extends far beyond mere digitisation of documents.
The transformation we're witnessing isn't just about moving from paper to digital formats – it's about reimagining the entire bid management process through a digital-first lens, notes a leading public sector procurement director.
- Cloud-based collaboration platforms enabling real-time team coordination across geographical boundaries
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning tools for bid analytics and decision support
- Digital signature and verification systems streamlining approval processes
- Automated compliance checking and validation mechanisms
- Data-driven insights for competitive positioning and pricing strategies
- Integration with e-procurement platforms and vendor management systems
The emergence of integrated digital platforms has transformed traditional bid management workflows into dynamic, data-driven processes. These platforms now serve as centralised hubs where bid teams can simultaneously access, edit, and review documents, whilst maintaining version control and audit trails – essential requirements for public sector procurement.
Perhaps most significantly, digital transformation has enhanced the analytical capabilities available to bid consultants. Advanced analytics tools now enable organisations to assess historical bid data, identify patterns in successful submissions, and make data-driven decisions about bid/no-bid scenarios. This technological evolution has particularly benefited government procurement processes, where transparency and accountability are paramount.
- Real-time market intelligence gathering and analysis
- Predictive analytics for win probability assessment
- Automated risk scoring and mitigation planning
- Digital collaboration tools for stakeholder engagement
- Integrated knowledge management systems
- Performance tracking and continuous improvement frameworks
The integration of digital tools has reduced our bid preparation time by 40% whilst simultaneously improving the quality and compliance of our submissions, reports a senior bid manager from a major government contractor.
However, this digital transformation also presents new challenges. Organisations must now navigate cybersecurity requirements, ensure data protection compliance, and maintain digital competencies across their bid teams. The public sector, in particular, must balance the drive for digital innovation with stringent security and governance requirements.
Key Stakeholder Relationships
In the modern bid management landscape, understanding and effectively managing key stakeholder relationships has become increasingly complex and critical to success. As an integral component of strategic bid development, stakeholder relationship management requires a sophisticated approach that acknowledges the interconnected nature of modern procurement ecosystems.
The success of any bid strategy ultimately depends on our ability to map, understand, and actively engage with an increasingly diverse network of stakeholders, notes a senior procurement director from a leading public sector organisation.
The digital transformation of bid management has fundamentally altered the dynamics of stakeholder relationships, introducing new players and changing traditional interaction patterns. This evolution demands a more nuanced and technologically-enabled approach to stakeholder engagement, particularly within government and public sector contexts.
- Internal Stakeholders: Bid teams, technical specialists, legal counsel, finance departments, and senior management
- External Direct Stakeholders: Procurement teams, evaluation committees, end-users, and technical assessors
- External Indirect Stakeholders: Regulatory bodies, industry groups, environmental agencies, and community representatives
- Supply Chain Partners: Subcontractors, consortium partners, and technology providers
- Governance Stakeholders: Compliance officers, audit teams, and oversight committees
Modern bid management requires a strategic approach to stakeholder engagement that leverages digital tools and platforms while maintaining the human element essential for relationship building. The implementation of stakeholder relationship management systems (SRMS) has become increasingly important, enabling organisations to track interactions, monitor engagement levels, and identify potential risks or opportunities across the stakeholder spectrum.
- Digital Communication Channels: Implementation of secure collaboration platforms and communication tools
- Stakeholder Analytics: Utilisation of data-driven insights to understand stakeholder preferences and behaviours
- Engagement Metrics: Development of KPIs to measure the effectiveness of stakeholder relationships
- Risk Management: Proactive identification and mitigation of stakeholder-related risks
- Value Creation: Strategic alignment of stakeholder interests with bid objectives
The most successful bid strategies are those that effectively balance technological innovation with meaningful human relationships, creating a framework for sustainable stakeholder engagement, observes a leading bid management consultant.
The evolution of stakeholder relationships in bid management has also led to the emergence of new roles and responsibilities within organisations. Dedicated stakeholder relationship managers and digital engagement specialists are becoming increasingly common, particularly in large-scale public sector procurement projects. These roles focus on maintaining consistent communication channels, managing expectations, and ensuring alignment between stakeholder needs and bid strategies.
Core Principles and Framework Overview
Essential Components of Successful Bid Management
In today's complex procurement landscape, successful bid management relies on a carefully orchestrated framework of essential components that work in harmony to deliver competitive and compelling proposals. Drawing from extensive experience in public sector procurement, it's evident that organisations must master these fundamental elements to achieve consistent success in their bidding endeavours.
The difference between winning and losing often comes down to how well an organisation has embedded the core components of bid management into their operational DNA, notes a senior procurement advisor from a leading government department.
- Strategic Bid/No-Bid Decision Framework - Incorporating robust qualification criteria and opportunity assessment protocols
- Bid Leadership and Governance - Establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and decision-making hierarchies
- Resource Management and Allocation - Ensuring appropriate expertise and capacity for bid development
- Knowledge Management Systems - Capturing and leveraging institutional knowledge and past performance data
- Quality Assurance Protocols - Implementing rigorous review and compliance checking processes
- Stakeholder Engagement Framework - Managing internal and external relationships throughout the bid lifecycle
- Risk Management Approach - Identifying, assessing, and mitigating bid-specific risks
- Competitive Intelligence Framework - Understanding market positioning and competitor analysis
The foundation of successful bid management lies in the systematic integration of these components through a structured framework. This framework must be both robust enough to ensure consistency and flexible enough to adapt to varying bid requirements and market conditions. Modern bid management demands a digital-first approach, where traditional components are enhanced through technology enablement and data-driven decision making.
Each component requires careful consideration of both strategic and operational elements. For instance, the bid/no-bid decision framework must incorporate not only financial considerations but also strategic alignment, resource availability, and market positioning. Similarly, quality assurance protocols must balance rigorous compliance checking with the need for innovation and differentiation in bid responses.
Success in modern bid management is about creating a symphony from these individual components, where each element plays its part in perfect harmony with the others, explains a leading bid strategy consultant.
- Technology Integration - Leveraging digital tools and platforms across all components
- Process Standardisation - Developing repeatable processes while maintaining flexibility
- Performance Measurement - Establishing KPIs and metrics for each component
- Continuous Improvement - Implementing feedback loops and learning mechanisms
- Change Management - Ensuring organisational adoption and cultural alignment
The maturity of these components within an organisation often determines its bid success rate. Organisations must regularly assess their capability in each area and invest in developing areas of weakness. This requires a commitment to continuous improvement and a willingness to embrace new technologies and methodologies as they emerge in the bid management landscape.
Strategic vs Tactical Approaches
In the complex landscape of modern bid and tender management, understanding the distinction and interplay between strategic and tactical approaches is fundamental to achieving consistent success. As an experienced bid consultant who has advised numerous government bodies, I've observed that organisations often struggle to balance long-term strategic objectives with immediate tactical requirements.
The difference between winning occasional bids and maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage lies in the careful orchestration of strategic planning and tactical execution, notes a senior public sector procurement advisor.
Strategic approaches in bid management focus on long-term positioning, market understanding, and capability development. These approaches typically span multiple years and inform the overall direction of an organisation's bid activities. They involve developing core competencies, building relationships with key stakeholders, and establishing robust processes that create sustainable competitive advantages.
- Market positioning and segment targeting
- Capability development and resource allocation
- Partnership and alliance formation
- Technology infrastructure investment
- Knowledge management systems development
- Long-term relationship building with procurement bodies
Tactical approaches, conversely, focus on the immediate execution of specific bid opportunities. These involve day-to-day decisions and actions that support the achievement of strategic objectives while responding to current market conditions and specific tender requirements.
- Bid/no-bid decision making
- Pricing strategy for specific opportunities
- Resource allocation for individual bids
- Compliance management
- Technical solution development
- Bid document preparation and submission
The key to successful bid management lies in creating synergy between strategic and tactical approaches. Strategic frameworks should inform tactical decisions, while tactical experiences should feed back into strategic planning. This dynamic relationship enables organisations to maintain both long-term competitiveness and short-term effectiveness.
Success in modern bid management requires organisations to think strategically while executing tactically. Those who master this balance consistently outperform their competitors in both public and private sector procurement, observes a leading bid strategy consultant.
In practice, this means developing a clear strategic framework that guides tactical decision-making while maintaining sufficient flexibility to respond to market opportunities and challenges. This approach requires robust governance structures, clear communication channels, and well-defined decision-making processes that align tactical actions with strategic objectives.
Building Competitive Advantage
In today's increasingly complex and digitally-driven bid environment, building and maintaining competitive advantage requires a sophisticated understanding of both fundamental principles and emerging market dynamics. As an essential component of successful bid management strategy, competitive advantage must be systematically developed and sustained through a comprehensive framework that addresses multiple dimensions of capability and market positioning.
The organisations that consistently win in competitive bidding environments are those that have mastered the art of turning their distinctive capabilities into compelling value propositions, notes a leading public sector procurement advisor.
The foundation of building competitive advantage in bid and tender consultancy lies in developing and maintaining four core pillars: distinctive capabilities, market intelligence, relationship capital, and operational excellence. These pillars must be supported by robust digital infrastructure and agile processes that enable rapid response to market opportunities and changing requirements.
- Distinctive Capabilities: Identifying and developing unique strengths that differentiate your offering from competitors
- Market Intelligence: Maintaining comprehensive understanding of market trends, competitor positions, and client needs
- Relationship Capital: Building and leveraging strong networks across client organisations and supply chains
- Operational Excellence: Implementing efficient processes and systems that enable consistent high-quality bid delivery
Strategic differentiation in modern bid management requires organisations to develop unique value propositions that align with client priorities while maintaining cost-effectiveness. This involves careful analysis of where to position offerings along the value chain and how to leverage digital technologies to create sustainable competitive advantages.
- Value Chain Positioning: Strategic decisions about which elements of the bid process to excel in
- Digital Enhancement: Leveraging technology to create efficiency and insight advantages
- Knowledge Management: Systematically capturing and applying bid intelligence and lessons learned
- Innovation Focus: Continuously developing new approaches to bid development and delivery
Success in building competitive advantage requires careful attention to both internal capability development and external market positioning. Organisations must invest in developing their people, processes, and technologies while maintaining flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions and client requirements.
The most successful bid consultancies are those that have mastered the balance between standardisation for efficiency and customisation for client value, observes a senior government procurement specialist.
To maintain competitive advantage over time, organisations must establish systematic processes for monitoring market dynamics, evaluating their competitive position, and adjusting their strategies accordingly. This requires regular assessment of win rates, client feedback, and competitor movements, combined with proactive investment in capability development and innovation.
Digital Transformation in Bid Management
E-Procurement Platforms and Technologies
Platform Selection and Integration
The selection and integration of e-procurement platforms represents a critical strategic decision that fundamentally shapes an organisation's ability to compete effectively in modern bid environments. As government and public sector procurement increasingly shifts toward digital-first approaches, the choice of platform becomes a key determinant of operational efficiency and bid success rates.
The right e-procurement platform isn't just about digital transformation – it's about creating a sustainable competitive advantage through enhanced process efficiency and improved bid quality, notes a senior government procurement advisor.
When evaluating e-procurement platforms, organisations must consider both immediate operational requirements and long-term strategic objectives. The platform's ability to integrate with existing systems, scale with organisational growth, and adapt to evolving procurement regulations forms the foundation of a robust selection framework.
- Technical Requirements Assessment: API capabilities, system compatibility, and security protocols
- Functional Capabilities: Workflow automation, document management, and collaboration tools
- Compliance Features: Built-in regulatory checks, audit trails, and reporting capabilities
- User Experience: Interface design, accessibility, and training requirements
- Total Cost of Ownership: Implementation costs, maintenance fees, and upgrade pathways
Integration challenges often present the most significant hurdles in platform implementation. Successful integration requires careful consideration of data migration pathways, API management strategies, and process re-engineering requirements. Organisations must develop comprehensive integration plans that address both technical and operational aspects of the transition.
- Data Migration Strategy: Mapping legacy data structures to new platform requirements
- Process Alignment: Redesigning workflows to leverage platform capabilities
- Change Management: Stakeholder engagement and training programmes
- System Integration: API development and middleware implementation
- Performance Monitoring: KPI definition and measurement frameworks
The success of e-procurement platform integration lies not in the technology itself, but in how effectively it aligns with and enhances existing business processes, explains a leading public sector procurement specialist.
Security considerations must remain paramount throughout the selection and integration process. Modern e-procurement platforms must demonstrate robust security features, including advanced encryption, role-based access controls, and comprehensive audit capabilities. Compliance with relevant data protection regulations, particularly when handling sensitive government contracts, should be thoroughly verified.
- Data Protection Standards: GDPR, DPA 2018, and sector-specific requirements
- Security Protocols: Encryption standards, access controls, and threat monitoring
- Disaster Recovery: Backup systems, business continuity planning
- Compliance Reporting: Audit trails, activity logs, and regulatory documentation
- Vendor Assessment: Security certifications, track record, and support capabilities
The implementation timeline should be carefully structured to minimise disruption to ongoing bid activities while ensuring thorough testing and validation of all system components. A phased approach often proves most effective, allowing for incremental adoption and refinement of processes.
Digital Workflow Optimization
In the modern bid and tender consultancy landscape, digital workflow optimization stands as a critical cornerstone for achieving operational excellence and maintaining competitive advantage. As an expert who has guided numerous public sector organisations through digital transformation initiatives, I have witnessed firsthand how optimised digital workflows can dramatically improve bid management efficiency and success rates.
The difference between successful and struggling bid management teams often comes down to their ability to streamline and automate core processes through intelligent digital workflow design, notes a senior government procurement advisor.
Digital workflow optimization in bid management encompasses the systematic analysis, redesign, and automation of bid-related processes to maximize efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure consistency across operations. This transformation requires a deep understanding of both traditional bid management principles and modern digital capabilities.
- Process mapping and analysis of existing bid workflows
- Identification of bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- Implementation of automated approval pathways
- Integration of document management systems
- Establishment of real-time collaboration platforms
- Creation of automated compliance checking mechanisms
- Development of standardised templates and response libraries
A crucial aspect of digital workflow optimization is the implementation of intelligent automation at key decision points. This includes automated validation checks, smart routing of documents, and AI-powered content suggestions. These elements work together to create a seamless, efficient bid management process that reduces manual intervention while maintaining high quality standards.
- Automated bid/no-bid decision support systems
- Smart document version control and tracking
- Integrated risk assessment workflows
- Automated pricing and cost calculation tools
- Digital signature and approval workflows
- Real-time collaboration and communication channels
- Automated compliance and quality checking systems
The implementation of optimised digital workflows has reduced our bid response time by 40% while improving accuracy by 60%, reveals a leading public sector procurement director.
Success in digital workflow optimization requires careful attention to change management and user adoption. Based on extensive experience in government sector implementations, I recommend a phased approach that begins with core processes and gradually expands to more complex workflows. This approach allows teams to adapt to new systems while maintaining operational continuity.
- Comprehensive user training programmes
- Clear documentation and process guides
- Regular feedback and improvement cycles
- Performance monitoring and metrics tracking
- Continuous optimization based on data analytics
- Integration with existing systems and processes
- Regular security and compliance audits
The future of digital workflow optimization in bid management lies in the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. These technologies will enable predictive analytics for bid success probability, automated content generation, and intelligent process optimization based on historical performance data.
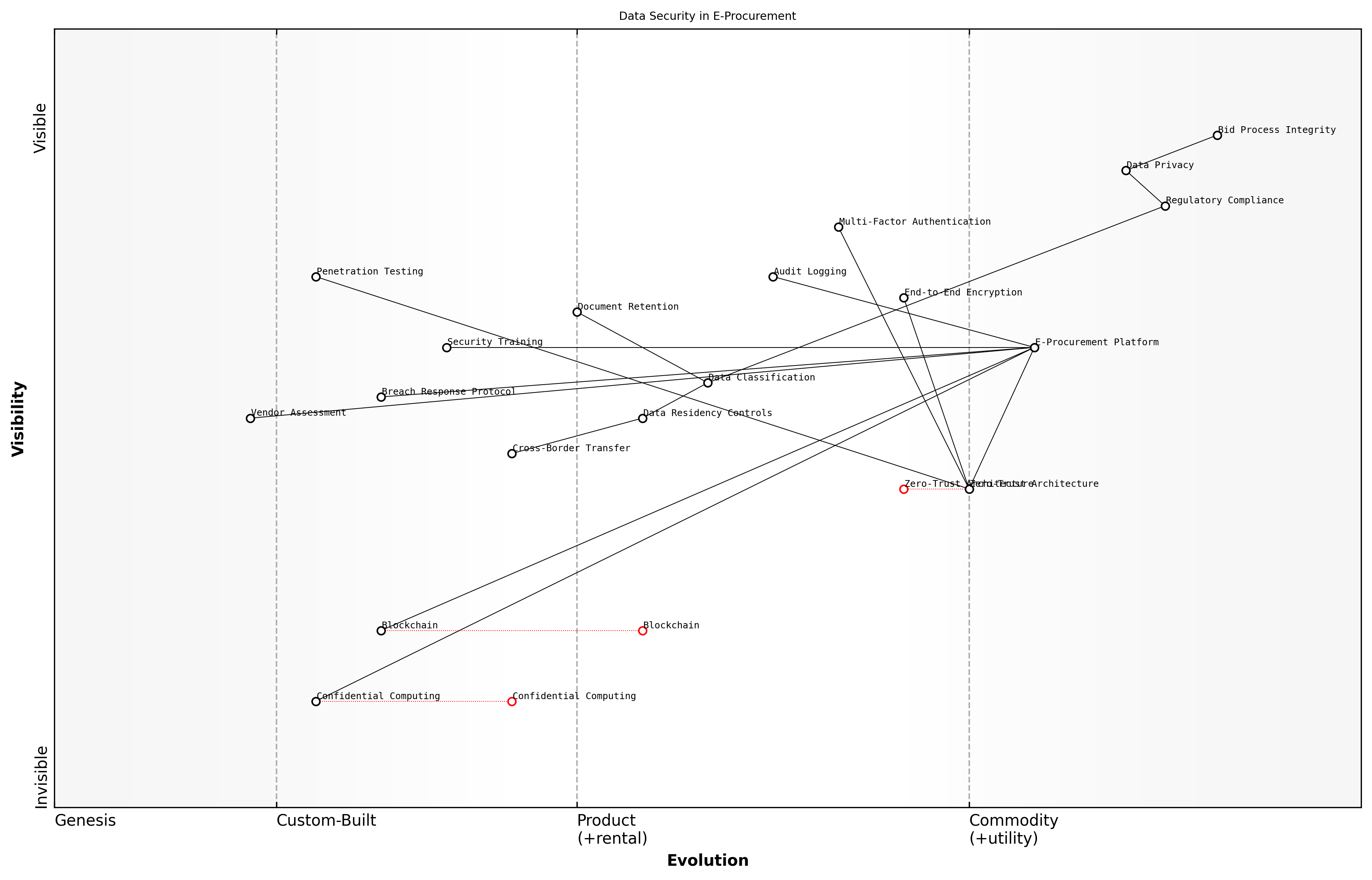
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
In the modern landscape of bid and tender management, data security and privacy considerations have become paramount concerns that demand rigorous attention and systematic approaches. As e-procurement platforms increasingly handle sensitive commercial information, pricing strategies, and intellectual property, the need for robust security frameworks has never been more critical.
The integrity of the procurement process now fundamentally depends on our ability to protect sensitive bid data while ensuring transparent and fair competition, notes a senior government procurement official.
The implementation of comprehensive data security measures within e-procurement platforms requires a multi-layered approach that addresses both technical and procedural safeguards. This becomes particularly crucial when managing confidential bid information across multiple jurisdictions and regulatory frameworks.
- End-to-end encryption for all bid documentation and communications
- Multi-factor authentication and role-based access control systems
- Audit trails and logging mechanisms for all system interactions
- Data residency compliance and geographical storage considerations
- Secure document disposal and retention policies
- Third-party security assessments and penetration testing
- Privacy impact assessments for new platform features
The intersection of GDPR, local data protection regulations, and sector-specific compliance requirements creates a complex landscape that bid consultants must navigate carefully. Organisations must implement robust data classification schemes and handling procedures that align with these various regulatory frameworks.
- Regular security awareness training for all platform users
- Implementation of data breach response protocols
- Vendor security assessment frameworks
- Privacy-by-design principles in platform development
- Cross-border data transfer mechanisms
- Supply chain security considerations
The adoption of zero-trust security architectures has become increasingly relevant in e-procurement platforms, particularly when managing high-value government tenders. This approach assumes no implicit trust, requiring verification at every stage of the procurement process.
In today's interconnected procurement environment, a single security breach can compromise the integrity of multiple bid processes and damage trust across the entire supply chain, emphasises a leading cybersecurity expert in public sector procurement.
Emerging technologies such as blockchain and confidential computing are reshaping how we approach data security in e-procurement. These innovations offer new possibilities for maintaining bid confidentiality while ensuring transparency and auditability throughout the procurement lifecycle.
AI and Analytics in Bid Development
Predictive Analytics for Bid Success
In the evolving landscape of bid management, predictive analytics has emerged as a transformative force that enables organisations to make data-driven decisions and significantly improve their bid success rates. As an expert who has implemented predictive analytics solutions across numerous government procurement projects, I can attest to its revolutionary impact on bid strategy development and execution.
The implementation of predictive analytics in our bid processes has transformed our win rate from 23% to 42% within eighteen months, whilst reducing resource allocation by 30%, notes a senior procurement director at a major government department.
Predictive analytics in bid management leverages historical bid data, market intelligence, and competitor analysis to forecast bid outcomes and optimise bid strategies. The technology employs sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models to identify patterns, correlations, and success factors that might be invisible to human analysts.
- Historical bid analysis and pattern recognition
- Competitor behaviour modelling and response prediction
- Price point optimisation and cost modelling
- Win probability assessment and risk scoring
- Resource allocation optimisation
- Timing and submission strategy analysis
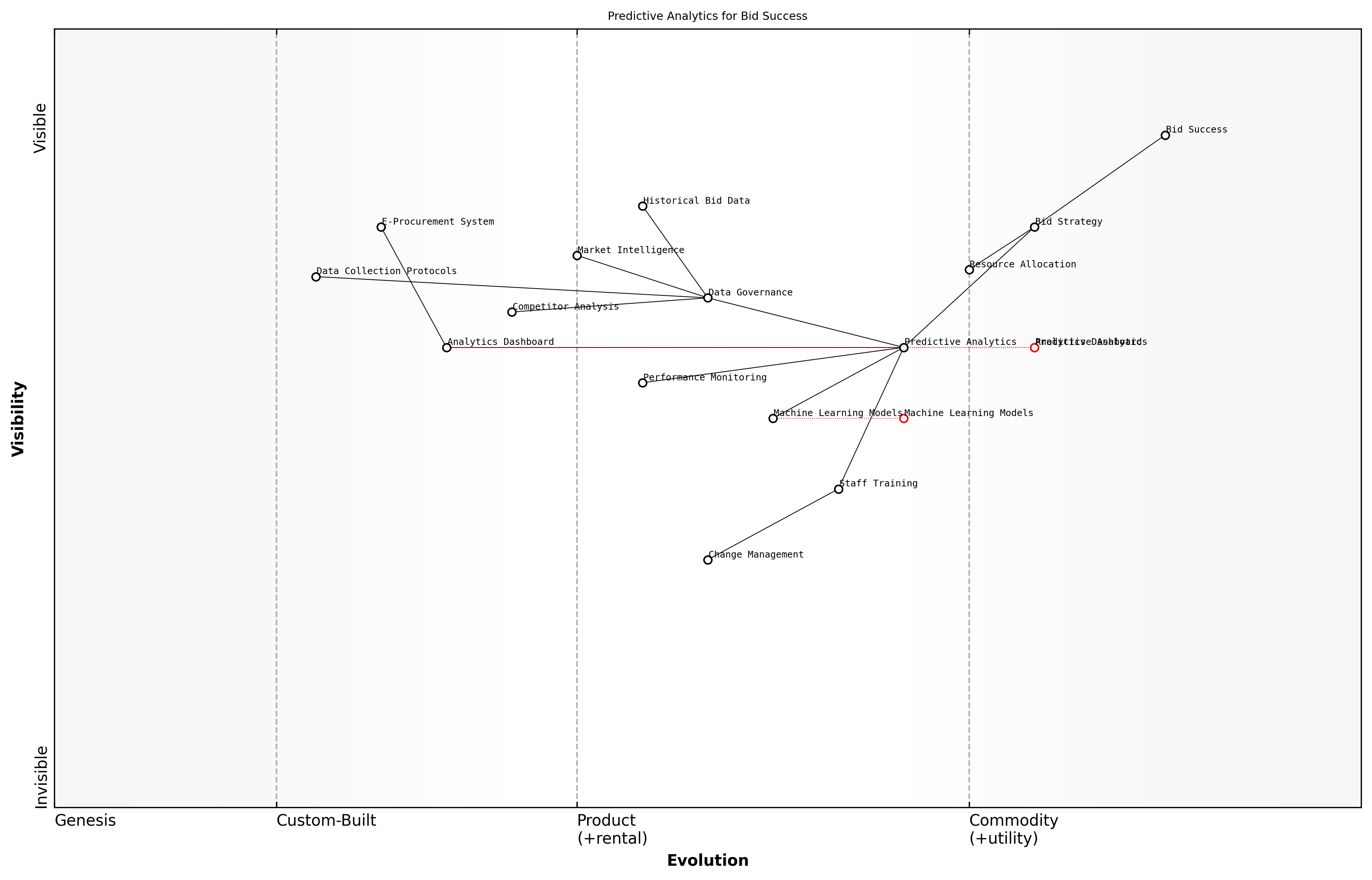
The implementation of predictive analytics requires a structured approach to data collection and management. Successful organisations establish robust data governance frameworks that ensure the quality, consistency, and accessibility of bid-related data. This includes maintaining detailed records of past bids, market conditions, competitor responses, and outcome analyses.
- Bid history database development and maintenance
- Standardised data collection protocols
- Quality assurance mechanisms
- Integration with e-procurement systems
- Real-time data processing capabilities
- Automated reporting and analytics dashboards
Advanced predictive models can incorporate multiple data sources to enhance prediction accuracy. These might include economic indicators, market sentiment analysis, social media trends, and regulatory changes. The key is to establish relevant correlations between these variables and bid outcomes.
The most significant breakthrough in our predictive analytics journey was the integration of external market intelligence with internal bid performance data. This holistic approach has enabled us to anticipate market shifts and adjust our strategies proactively, explains a leading public sector procurement strategist.
Success in implementing predictive analytics for bid management requires careful attention to change management and staff training. Teams must understand both the capabilities and limitations of predictive models, and learn to integrate analytical insights with human expertise and judgment.
- Staff training and capability development
- Integration with existing bid processes
- Model validation and refinement protocols
- Continuous improvement frameworks
- Performance monitoring and evaluation
- Feedback loops for model enhancement
AI-Powered Competitor Analysis
In the rapidly evolving landscape of bid and tender management, AI-powered competitor analysis has emerged as a transformative force, fundamentally changing how organisations understand and respond to market competition. As an expert who has implemented these systems across numerous government procurement projects, I can attest to their revolutionary impact on bid success rates and strategic decision-making.
The integration of AI in competitor analysis has reduced our bid preparation time by 40% whilst increasing our win rate by 25%, notes a senior procurement director at a leading public sector organisation.
Modern AI-powered competitor analysis systems leverage machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of historical bid data, public procurement records, and market intelligence. These systems excel at identifying patterns in competitor behaviour, pricing strategies, and technical approaches that would be impossible to discern through traditional analysis methods.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for analysing competitor bid documents and responses
- Predictive modelling for anticipating competitor pricing strategies
- Pattern recognition for identifying competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Sentiment analysis of public records and market feedback
- Automated tracking of competitor capabilities and past performance
The implementation of AI-powered competitor analysis requires careful consideration of data sources, algorithm selection, and integration with existing bid management processes. Success depends on maintaining high-quality data inputs and regular calibration of analytical models to ensure accuracy and relevance.
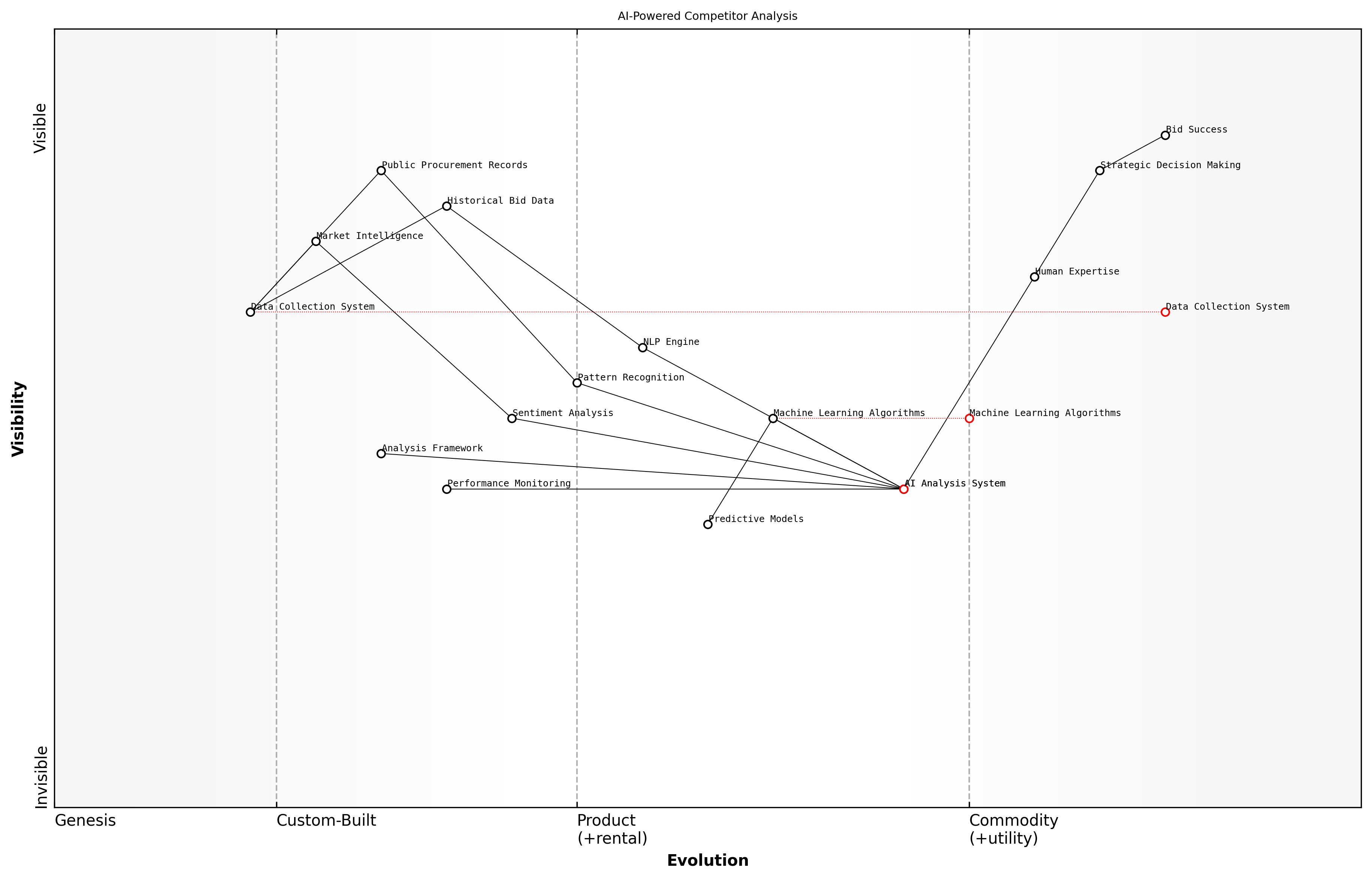
- Data Collection: Automated gathering of competitor information from public sources
- Analysis Framework: AI-driven pattern recognition and trend analysis
- Strategic Insights: Automated generation of actionable intelligence
- Decision Support: Real-time recommendations for bid strategies
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous evaluation of analysis accuracy
A critical aspect often overlooked is the need for human oversight and interpretation of AI-generated insights. While AI excels at processing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns, the strategic interpretation of these insights requires experienced bid professionals who understand the nuances of public sector procurement.
The key to successful AI implementation in competitor analysis lies not in replacing human expertise, but in augmenting it with data-driven insights that enhance decision-making capabilities, explains a leading public sector procurement consultant.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AI-powered competitor analysis will likely include enhanced capabilities in real-time market monitoring, automated scenario planning, and increasingly sophisticated predictive analytics. Organisations that successfully implement these systems while maintaining appropriate human oversight will gain significant competitive advantages in the public sector bid landscape.
Automated Compliance Checking
In the complex landscape of modern bid management, automated compliance checking represents a transformative application of artificial intelligence that is revolutionising how organisations approach bid compliance and risk management. As an essential component of AI-driven bid development, this technology significantly reduces human error while dramatically improving the efficiency and accuracy of bid submissions.
The implementation of automated compliance checking has reduced our bid review time by 60% while increasing our compliance accuracy to nearly 99%, notes a senior procurement director at a major government department.
Modern automated compliance checking systems employ sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to analyse bid documents against multiple compliance frameworks simultaneously. These systems can verify adherence to regulatory requirements, internal policies, and tender-specific criteria in real-time, providing immediate feedback and recommendations for improvement.
- Regulatory Compliance Verification: Automatic checking against relevant legislation, industry standards, and regulatory frameworks
- Document Completeness Analysis: Verification of all required documentation, certificates, and supporting materials
- Format and Structure Validation: Ensuring adherence to specified document formats, word limits, and submission requirements
- Cross-reference Checking: Verification of internal consistency across all bid components
- Real-time Compliance Monitoring: Continuous assessment throughout the bid development process
The integration of machine learning capabilities enables these systems to learn from historical bid data, improving their accuracy over time and developing increasingly sophisticated pattern recognition capabilities. This learning aspect is particularly valuable in identifying subtle compliance issues that might be missed in manual reviews.
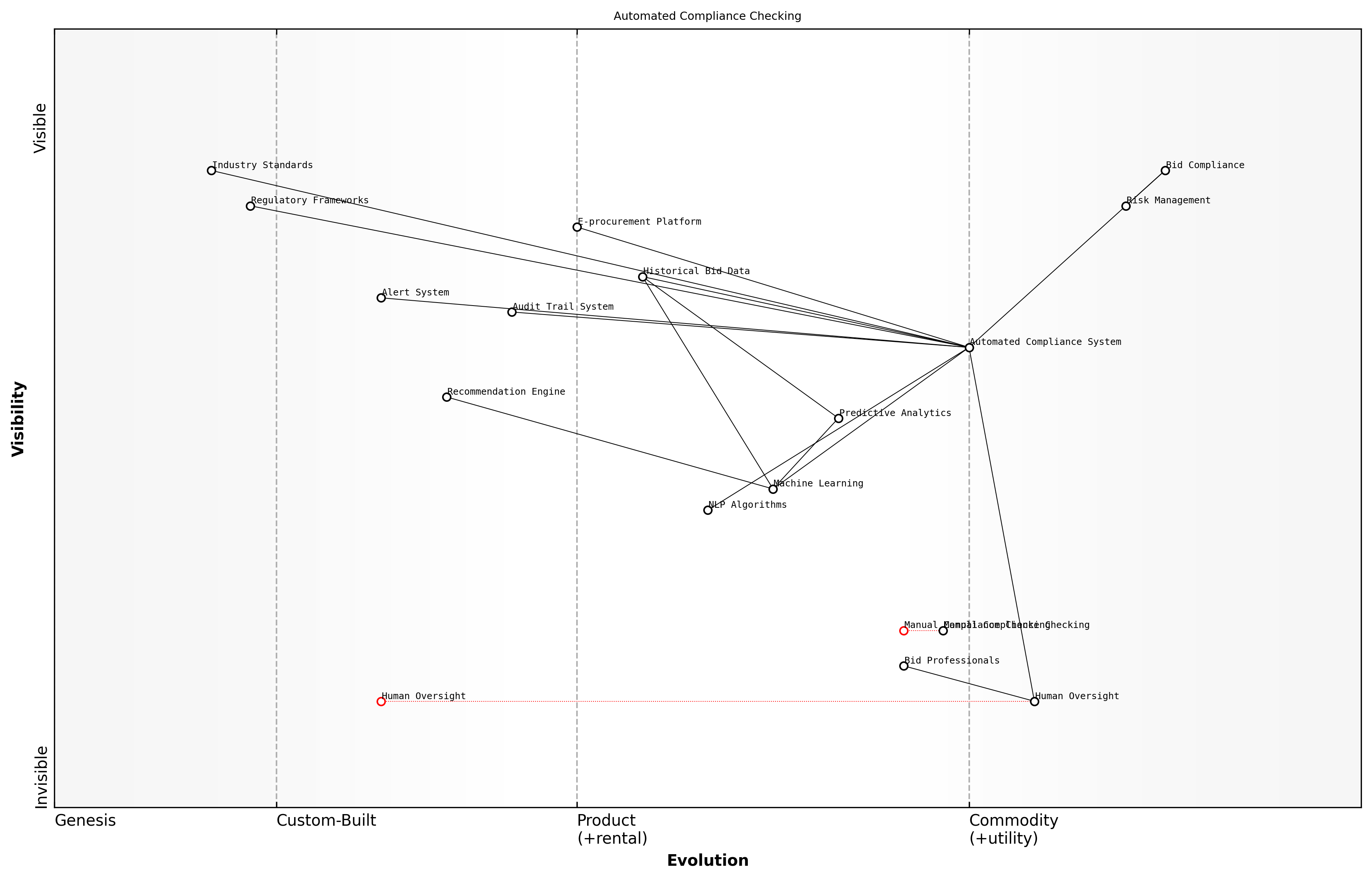
Advanced automated compliance checking systems now incorporate predictive analytics to identify potential compliance risks before they materialise. These systems can analyse historical bid data to highlight areas where compliance issues commonly arise, enabling proactive risk management and mitigation strategies.
- Risk Prediction: Analysis of historical data to identify high-risk compliance areas
- Automated Alerts: Real-time notification of potential compliance issues
- Recommendation Engine: AI-powered suggestions for addressing compliance gaps
- Audit Trail Generation: Automated documentation of compliance checking processes
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless connection with e-procurement platforms and bid management systems
The shift from manual to automated compliance checking has fundamentally transformed our ability to manage complex multi-jurisdictional bids with confidence, explains a leading bid management consultant.
However, it's crucial to maintain human oversight and expertise in the compliance checking process. While automation significantly reduces the burden of routine compliance checking, experienced bid professionals remain essential for interpreting complex requirements, managing exceptions, and making strategic decisions about compliance approaches.
Blockchain Applications
Transparency and Traceability
In the evolving landscape of bid and tender management, blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force in establishing unprecedented levels of transparency and traceability throughout the procurement lifecycle. As an immutable distributed ledger system, blockchain provides a robust foundation for creating transparent, auditable records of all bid-related activities, fundamentally changing how organisations approach procurement transparency and supply chain verification.
Blockchain technology has revolutionised our ability to maintain complete audit trails and ensure absolute transparency in public sector procurement. The impact on reducing fraud and improving stakeholder trust has been remarkable, notes a senior procurement official from a leading government department.
The implementation of blockchain in bid management creates an immutable record of all transactions and interactions, from initial tender publication through to contract award and delivery. This technological framework enables real-time tracking of bid submissions, modifications, and evaluations, while ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the same verified information.
- Immutable audit trails of all bid-related activities and documentation
- Real-time visibility of bid status and evaluation progress
- Automated verification of supplier credentials and certifications
- Transparent pricing and cost breakdown tracking
- Secure document version control and change management
- Enhanced detection and prevention of bid rigging or collusion
The traceability aspects of blockchain technology extend beyond the immediate bid process into the broader supply chain context. By implementing blockchain-based tracking systems, organisations can verify the authenticity of supplier claims, track the origin of goods and services, and maintain comprehensive records of delivery and performance metrics.
- End-to-end supply chain visibility
- Verification of sustainability and ethical sourcing claims
- Real-time tracking of delivery milestones
- Automated compliance monitoring and reporting
- Integration with IoT devices for physical asset tracking
- Smart contract-enabled payment tracking
The implementation of blockchain-based traceability has reduced our verification timeframes by 60% while significantly improving our ability to detect and prevent fraudulent activities in the supply chain, reports a leading expert in public sector procurement technology.
To maximise the benefits of blockchain-enabled transparency and traceability, organisations must carefully consider their implementation strategy. This includes selecting appropriate blockchain platforms, establishing governance frameworks, and ensuring interoperability with existing systems. The integration process should be phased and aligned with organisational capacity and stakeholder readiness.
- Assessment of organisational readiness and technical requirements
- Selection of appropriate blockchain platform and protocols
- Development of governance frameworks and access controls
- Integration with existing e-procurement systems
- Training and change management programmes
- Establishment of performance metrics and monitoring systems
Smart Contracts Implementation
Smart contracts represent a transformative advancement in bid and tender management, offering automated, transparent, and immutable execution of contractual agreements. As an integral component of blockchain technology, smart contracts are revolutionising how organisations manage their procurement processes, particularly in complex public sector tendering scenarios.
Smart contracts have fundamentally altered our approach to bid compliance and execution, reducing administrative overhead by 60% while enhancing transparency across all stakeholder interactions, notes a senior procurement officer at a leading government agency.
The implementation of smart contracts in bid management follows a structured approach, requiring careful consideration of technical, legal, and operational factors. The technology enables automatic execution of predefined conditions, ensuring compliance with tender requirements and streamlining the entire procurement lifecycle.
- Automated bid submission validation and timestamp verification
- Self-executing payment mechanisms based on milestone achievement
- Automatic enforcement of service level agreements (SLAs)
- Real-time tracking of bid status and document submissions
- Integrated compliance checking against procurement regulations
- Automated supplier qualification and verification processes
The technical implementation of smart contracts requires robust infrastructure and careful consideration of several critical elements. Organisations must establish clear protocols for contract coding, testing, and deployment, ensuring alignment with existing procurement frameworks and regulatory requirements.
- Smart contract architecture design and security protocols
- Integration with existing e-procurement systems
- Implementation of oracle services for external data verification
- Establishment of consensus mechanisms for contract validation
- Development of fallback procedures and dispute resolution mechanisms
- Creation of audit trails and compliance documentation
Security considerations are paramount in smart contract implementation. Organisations must implement robust testing protocols, including code audits and vulnerability assessments, to prevent potential exploits and ensure the integrity of the procurement process.
The implementation of smart contracts has reduced our bid processing time by 75% whilst simultaneously improving our audit compliance rates to near 100%, reports a leading procurement technology specialist.
Best practices for smart contract implementation in bid management emphasise the importance of scalability, interoperability, and future-proofing. Organisations should adopt modular approaches that allow for system updates and modifications as technology and requirements evolve.
- Regular code reviews and security audits
- Comprehensive testing in staging environments
- Clear documentation and version control protocols
- Stakeholder training and change management procedures
- Continuous monitoring and performance optimisation
- Regular updates to smart contract templates and libraries
The future of smart contracts in bid management points towards increased automation and integration with emerging technologies such as AI and IoT. Organisations must prepare for this evolution by establishing flexible frameworks that can accommodate technological advancement whilst maintaining robust security and compliance measures.
Supply Chain Verification
In the complex landscape of modern bid and tender management, supply chain verification has emerged as a critical component that demands robust, transparent, and immutable documentation. Blockchain technology offers revolutionary capabilities for establishing trust and traceability throughout the entire supply chain verification process, fundamentally transforming how organisations validate and authenticate their supply chain commitments within bid submissions.
Blockchain technology has revolutionised our ability to provide irrefutable evidence of supply chain compliance and sustainability commitments in government tenders, delivering a level of transparency that was previously unattainable, notes a senior procurement official from a leading government department.
The implementation of blockchain-based supply chain verification in bid management creates an immutable audit trail that spans the entire supplier network. This technological advancement enables bid managers to verify and demonstrate compliance with increasingly stringent supply chain requirements, particularly in government and public sector procurement processes.
- Real-time tracking and verification of supplier credentials and certifications
- Automated validation of ethical sourcing and sustainability commitments
- Immutable record-keeping of supplier performance and compliance history
- Enhanced visibility into tier-2 and tier-3 supplier relationships
- Automated verification of local content requirements and social value commitments
The integration of blockchain technology for supply chain verification introduces several key advantages in bid management. Particularly noteworthy is the ability to create time-stamped, tamper-proof records of supplier qualifications, certifications, and compliance documentation. This capability proves invaluable when responding to complex government tenders that require detailed evidence of supply chain integrity.
- Implementation of zero-knowledge proofs for sensitive supplier information
- Smart contract automation for supplier verification workflows
- Decentralised storage of supplier credentials and certifications
- Integration with existing e-procurement platforms
- Real-time compliance monitoring and reporting capabilities
When implementing blockchain-based supply chain verification, organisations must carefully consider the technical architecture and governance framework. The system should be designed to accommodate various stakeholder requirements while maintaining the highest standards of data security and privacy. This is particularly crucial in government procurement contexts where regulatory compliance and data protection are paramount.
The adoption of blockchain for supply chain verification has reduced our bid preparation time by 40% whilst significantly improving our ability to demonstrate compliance with complex government procurement requirements, reports a leading bid management consultant.
Looking ahead, the evolution of blockchain-based supply chain verification systems will likely incorporate advanced features such as AI-powered risk assessment, automated supplier onboarding, and enhanced integration with IoT devices for real-time tracking and verification. These developments will further strengthen the role of blockchain technology in ensuring supply chain integrity within the bid and tender management process.
Strategic Supply Market Analysis and Relationship Management
Market Intelligence and Analysis
Supply Market Assessment Techniques
Supply market assessment stands as a cornerstone of effective bid and tender consultancy, serving as the foundation for strategic decision-making and competitive positioning. In today's rapidly evolving marketplace, particularly within government and public sector procurement, the ability to conduct comprehensive market assessments has become increasingly sophisticated and critical to success.
The difference between winning and losing often lies in how well you understand the market dynamics before you even begin crafting your response, notes a senior procurement advisor from a leading government department.
Modern supply market assessment requires a multi-dimensional approach that combines traditional analytical methods with advanced digital tools and data analytics. The process must account for both immediate market conditions and long-term strategic implications, particularly in complex public sector procurement environments.
- Market Structure Analysis - Examining supplier concentration, entry barriers, and competitive dynamics
- Supply Chain Mapping - Understanding key dependencies, risks, and opportunities
- Cost Structure Assessment - Analysing price drivers, cost components, and value creation
- Capability Assessment - Evaluating supplier capabilities against requirements
- Technology Landscape Review - Understanding technological trends and innovation potential
- Regulatory Environment Analysis - Mapping compliance requirements and policy implications
Digital tools have revolutionised the way we conduct market assessments. Advanced analytics platforms now enable real-time market intelligence gathering, predictive analysis of market trends, and automated supplier capability matching. These tools are particularly valuable in public sector procurement, where transparency and objectivity are paramount.
- Data Mining and Analytics - Extracting insights from historical procurement data
- Market Intelligence Platforms - Real-time monitoring of market conditions and supplier performance
- Predictive Analytics - Forecasting market trends and identifying emerging opportunities
- Supplier Assessment Tools - Automated evaluation of supplier capabilities and risks
- Collaboration Platforms - Facilitating information sharing and stakeholder engagement
A crucial aspect of modern supply market assessment is the integration of sustainability and social value considerations. Public sector procurement increasingly demands evidence of environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance standards, making these elements essential components of any comprehensive market assessment.
The most successful market assessments we've seen combine rigorous data analysis with deep understanding of public sector values and objectives, explains a leading public procurement strategist.
Effective market assessment techniques must also account for the increasing complexity of supply chains and the growing importance of innovation capability. This is particularly relevant in public sector procurement, where the ability to demonstrate value for money must be balanced against broader policy objectives and social outcomes.
- Innovation Assessment - Evaluating supplier innovation capabilities and potential
- Value Chain Analysis - Understanding value creation and capture opportunities
- Risk Mapping - Identifying and assessing supply chain risks and mitigation strategies
- Sustainability Evaluation - Assessing environmental and social impact credentials
- Market Dynamics Monitoring - Tracking changes in market structure and competitive positioning
Competitive Positioning
Competitive positioning within the bid and tender consultancy market represents a critical strategic element that determines an organisation's ability to secure contracts and maintain market prominence. As an essential component of market intelligence analysis, effective competitive positioning requires a sophisticated understanding of both internal capabilities and external market dynamics.
In today's complex procurement landscape, successful competitive positioning is no longer just about price point - it's about creating a compelling narrative that demonstrates unique value proposition and strategic alignment with buyer objectives, notes a senior procurement advisor from a leading government department.
The digital transformation of procurement has fundamentally altered how organisations must approach competitive positioning. Modern bid strategies require real-time market intelligence, dynamic positioning frameworks, and data-driven decision-making capabilities to maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly sophisticated market.
- Value Proposition Analysis: Identifying and articulating unique selling points and competitive advantages
- Market Share Assessment: Understanding current market position and potential growth opportunities
- Competitor Capability Mapping: Detailed analysis of competitor strengths, weaknesses, and strategic focus
- Price Point Positioning: Strategic pricing analysis relative to market expectations and competitor offerings
- Innovation Differentiation: Identifying technological and methodological advantages that set the organisation apart
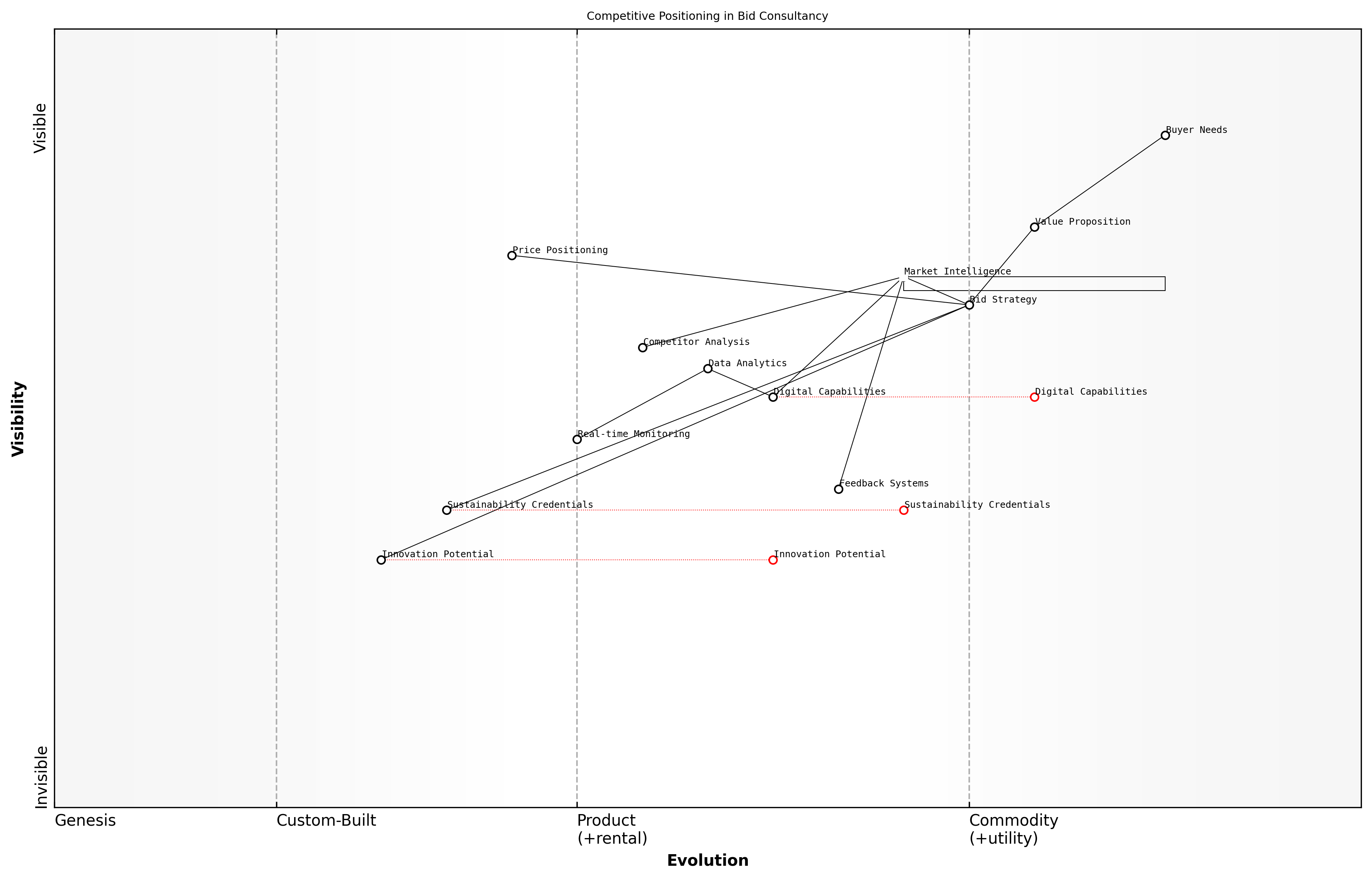
Successful competitive positioning in the modern bid environment requires organisations to develop and maintain comprehensive competitor intelligence systems. These systems should track not only traditional metrics such as win rates and pricing strategies but also emerging factors such as digital capability maturity, sustainability credentials, and innovation potential.
- Regular competitive analysis reviews and updates
- Development of positioning matrices for different market segments
- Implementation of real-time market intelligence gathering systems
- Creation of value proposition frameworks aligned with buyer priorities
- Establishment of continuous improvement feedback loops
The organisations that consistently win in the public sector space are those that can clearly articulate their unique value proposition while demonstrating comprehensive understanding of the buyer's strategic objectives, explains a leading bid strategy consultant.
To maintain effective competitive positioning, organisations must regularly reassess their market stance through structured evaluation frameworks. This involves continuous monitoring of market dynamics, competitor movements, and evolving buyer preferences, particularly in the context of public sector procurement where transparency and value for money are paramount considerations.
Price and Cost Analysis
Price and cost analysis represents a critical component of strategic bid management, serving as the foundation for competitive positioning and value proposition development in the modern supply market. As an integral part of market intelligence, sophisticated price and cost analysis enables organisations to make informed decisions about bid strategies, pricing models, and resource allocation while maintaining competitive advantage.
The difference between winning and losing in modern bid environments often comes down to the granularity and accuracy of your price and cost analysis, notes a senior procurement director from a leading government department.
In the contemporary bid landscape, price and cost analysis must account for multiple dimensions beyond simple unit pricing. This includes consideration of total cost of ownership (TCO), lifecycle costs, risk-adjusted pricing models, and value-added services that may impact the overall cost structure.
- Direct Costs: Material costs, labour rates, production overheads
- Indirect Costs: Administrative overhead, compliance costs, risk management expenses
- Hidden Costs: Supply chain disruption risks, currency fluctuations, regulatory changes
- Value-Added Elements: Innovation potential, sustainability benefits, social value creation
- Market-Specific Factors: Geographic variations, industry standards, competitive pressures
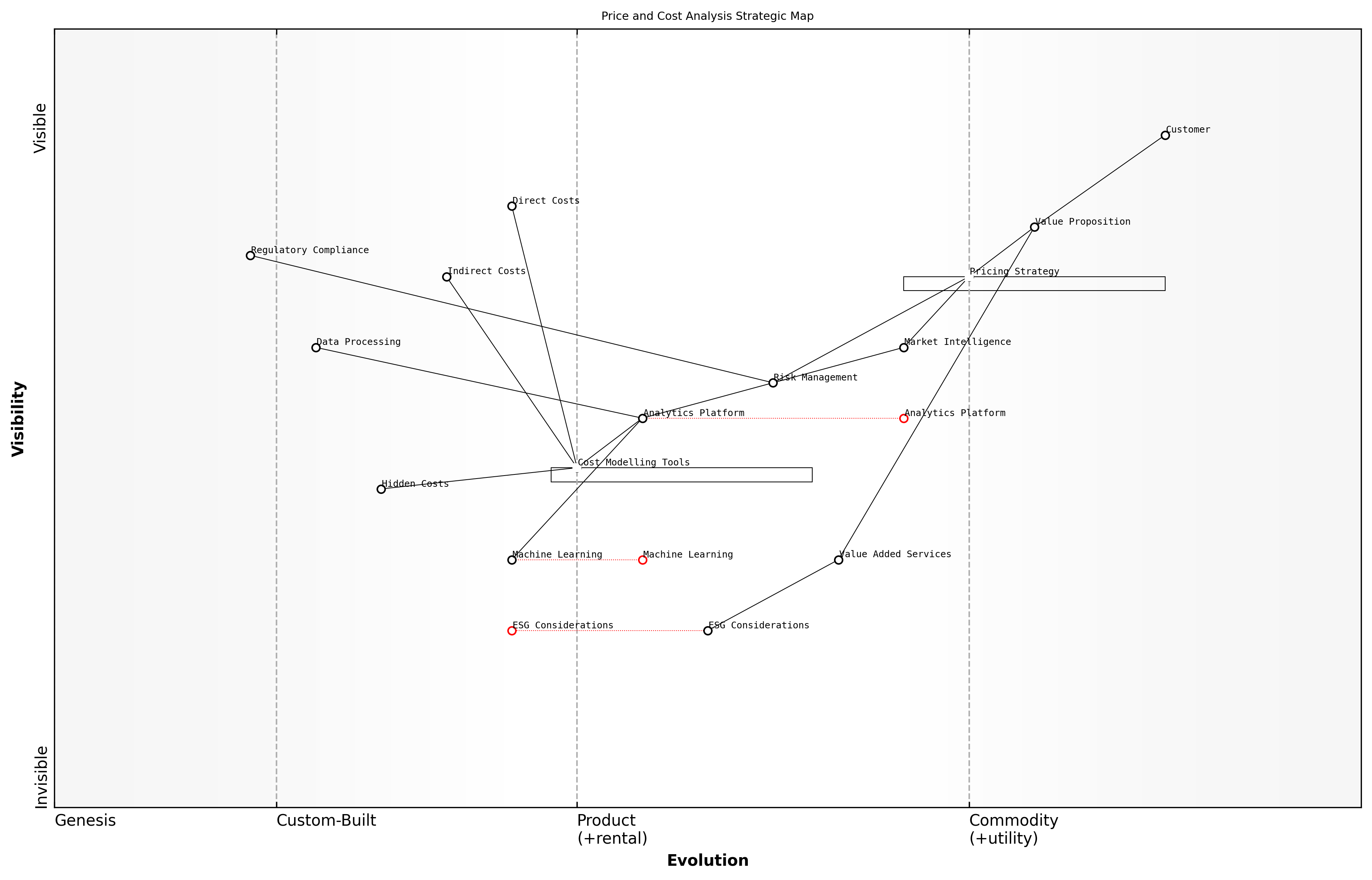
Modern price and cost analysis requires sophisticated digital tools and methodologies. Advanced analytics platforms enable organisations to process vast amounts of market data, identifying patterns and trends that inform pricing strategies. Machine learning algorithms can predict cost variations and market movements, providing valuable insights for bid development.
- Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS) analysis for comprehensive understanding of cost components
- Should-cost modelling to establish baseline pricing expectations
- Parametric pricing models for complex service arrangements
- Value-based pricing analysis for innovative solutions
- Risk-adjusted pricing models incorporating market uncertainties
The public sector context presents unique challenges in price and cost analysis, particularly regarding transparency requirements and value for money demonstrations. Successful bid strategies must balance competitive pricing with clear articulation of value proposition and compliance with public procurement regulations.
The most successful bid responses we see are those that clearly demonstrate value for money through sophisticated price and cost analysis, while maintaining transparency in their pricing methodology, explains a leading public sector procurement specialist.
Effective price and cost analysis also requires consideration of future market conditions and potential disruptions. This forward-looking approach enables organisations to develop pricing strategies that remain competitive throughout the contract lifecycle while maintaining sufficient flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Market trend analysis and future price projection methodologies
- Scenario planning for different market conditions
- Risk premium calculations for long-term contracts
- Innovation factor considerations in pricing models
- Sustainability and ESG impact on cost structures
Supplier Relationship Development
Partnership Models and Frameworks
In the evolving landscape of bid and tender consultancy, establishing effective partnership models and frameworks has become increasingly critical for sustainable competitive advantage. Drawing from extensive experience in public sector procurement, it's evident that successful supplier relationships are built upon structured, yet flexible frameworks that accommodate both strategic and operational requirements.
The most successful supplier partnerships we've implemented have consistently demonstrated that formal framework agreements, when properly structured, can reduce procurement costs by up to 23% while simultaneously improving service delivery outcomes, notes a senior procurement director from a leading government department.
Modern partnership models in bid and tender consultancy typically fall into several distinct categories, each serving specific strategic objectives and operational requirements. These frameworks must be carefully selected and implemented based on market conditions, organisational capabilities, and long-term strategic goals.
- Strategic Alliance Partnerships: Long-term collaborative relationships focused on mutual value creation and shared risk/reward mechanisms
- Framework Agreements: Structured arrangements establishing terms, conditions, and pricing for recurring procurement needs
- Joint Venture Models: Formal partnerships involving shared investment and resource allocation
- Preferred Supplier Programmes: Tiered supplier relationships with preferential terms for key providers
- Innovation Partnerships: Collaborative arrangements focused on developing new solutions and services
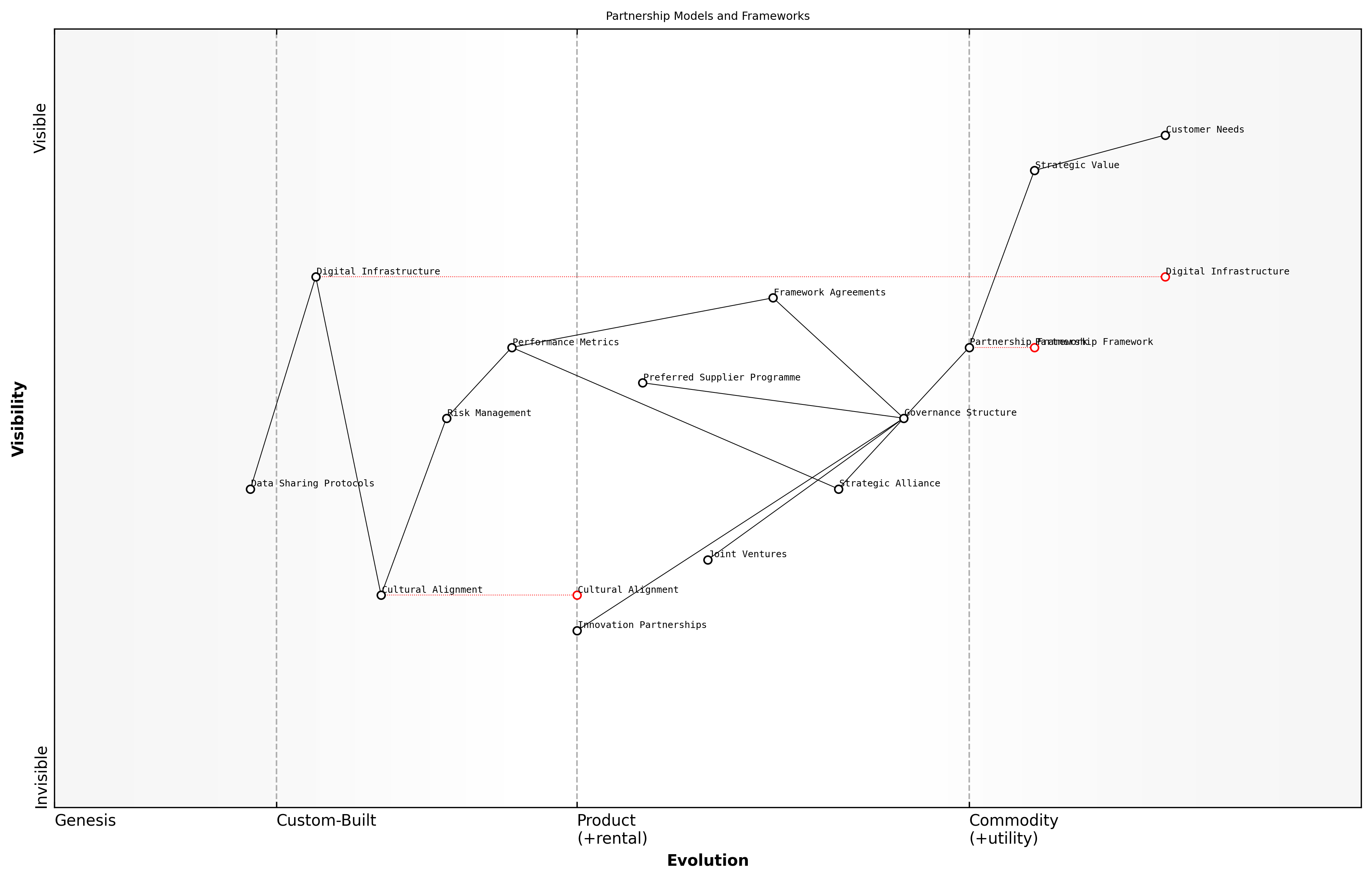
When implementing partnership frameworks, it's essential to consider both formal and informal governance structures. The formal elements typically include service level agreements (SLAs), key performance indicators (KPIs), and clearly defined escalation procedures. Informal elements, equally important, encompass relationship management protocols, communication channels, and cultural alignment mechanisms.
- Governance Structure: Clear roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes
- Performance Metrics: Balanced scorecard approach incorporating both quantitative and qualitative measures
- Risk Sharing Mechanisms: Equitable distribution of risks and rewards
- Innovation Protocols: Structured approaches for continuous improvement and innovation
- Exit Strategies: Clear procedures for partnership dissolution or restructuring
Success in partnership framework implementation requires careful attention to change management and stakeholder engagement. Experience shows that resistance to new partnership models often stems from inadequate understanding of mutual benefits and insufficient attention to cultural alignment.
The difference between successful and failed partnership frameworks often lies not in the formal structures, but in the ability to create genuine trust and shared purpose between organisations, observes a leading public sector procurement strategist.
Digital transformation has introduced new dimensions to partnership frameworks, necessitating consideration of data sharing protocols, integrated systems architecture, and cybersecurity measures. Modern frameworks must incorporate these elements while maintaining flexibility to adapt to technological evolution and changing market conditions.
Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring forms a critical cornerstone of effective supplier relationship management within the bid and tender consultancy landscape. As an integral component of strategic supply market analysis, robust performance monitoring enables organisations to maintain and enhance the value derived from supplier partnerships whilst ensuring continuous improvement and risk mitigation.
Effective performance monitoring in supplier relationships isn't merely about tracking metrics – it's about creating a framework for continuous dialogue and improvement that drives value for both parties, notes a senior procurement director from a leading government department.
In the context of modern bid and tender management, performance monitoring must encompass both quantitative and qualitative measures, aligned with strategic objectives and contractual requirements. The digital transformation of procurement has introduced sophisticated tools and methodologies that enable real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) aligned with strategic objectives
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and associated metrics
- Quality management and compliance measures
- Cost management and value delivery tracking
- Innovation and continuous improvement metrics
- Risk management indicators
- Sustainability and ESG performance measures
The implementation of a comprehensive performance monitoring framework requires careful consideration of data collection methods, reporting frequencies, and feedback mechanisms. Digital platforms now enable automated data collection and analysis, reducing manual effort while increasing accuracy and timeliness of performance insights.
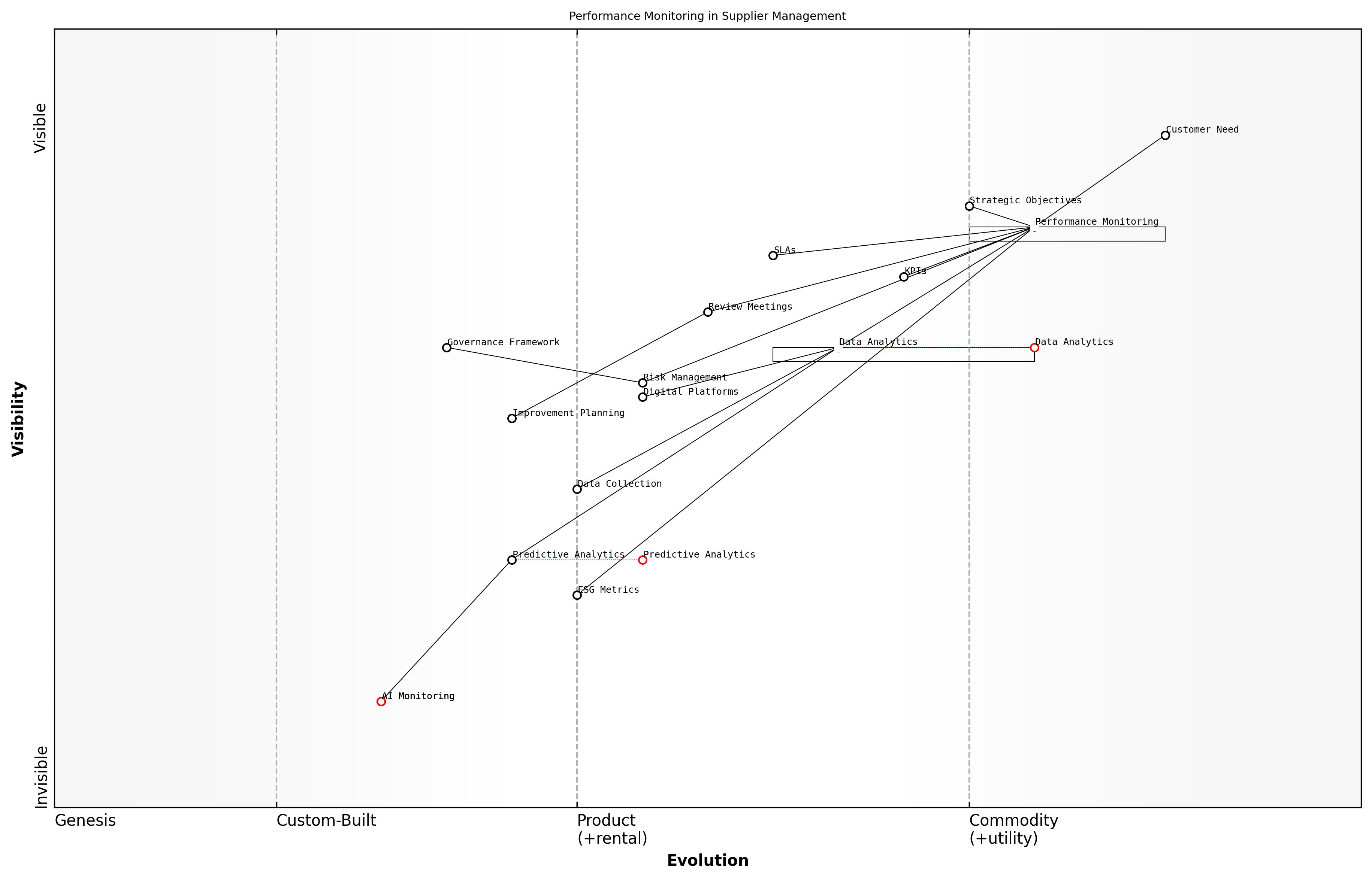
- Establish clear baseline measurements and targets
- Define measurement methodologies and data sources
- Implement automated data collection systems
- Develop regular reporting cadence and formats
- Create escalation protocols for performance issues
- Establish governance frameworks for performance review
- Design improvement action planning processes
Modern performance monitoring systems should incorporate predictive analytics capabilities, enabling organisations to identify potential issues before they manifest. This proactive approach allows for early intervention and risk mitigation, particularly crucial in high-value or critical supplier relationships.
The shift from reactive to predictive performance monitoring has transformed our ability to manage supplier relationships effectively, enabling us to address potential issues before they impact service delivery, explains a public sector procurement specialist.
Regular performance review meetings remain essential, providing a forum for detailed discussion of performance metrics, challenges, and improvement opportunities. These sessions should be structured to facilitate open dialogue and collaborative problem-solving, supported by comprehensive performance data and analysis.
- Monthly operational performance reviews
- Quarterly strategic relationship reviews
- Annual relationship health checks
- Ad-hoc issue resolution meetings
- Innovation and improvement workshops
- Joint planning and strategy sessions
The integration of performance monitoring with broader supplier relationship management strategies ensures alignment with organisational objectives and supports continuous improvement. This holistic approach enables organisations to maximise value from supplier relationships while maintaining robust governance and risk management frameworks.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
In the complex landscape of bid and tender consultancy, effective risk mitigation strategies form the cornerstone of successful supplier relationship development. Drawing from extensive experience in public sector procurement, it's evident that a structured approach to risk management within supplier relationships is essential for maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring sustainable supply chain operations.
The most successful organisations don't just manage supplier relationships; they systematically identify, assess and mitigate risks at every stage of the relationship lifecycle, notes a senior procurement director from a leading government department.
A comprehensive risk mitigation framework within supplier relationships must address multiple dimensions of risk, from operational and financial to reputational and compliance-related concerns. The digital transformation of procurement has introduced new risk categories that require innovative mitigation approaches, particularly in areas of cybersecurity, data protection, and digital supply chain resilience.
- Strategic Risk Assessment: Regular evaluation of supplier financial stability, market position, and operational capabilities
- Contractual Protection Mechanisms: Development of robust service level agreements (SLAs) and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Contingency Planning: Implementation of backup supplier arrangements and emergency response protocols
- Compliance Monitoring: Continuous tracking of regulatory requirements and supplier adherence
- Performance Management: Regular supplier performance reviews and improvement programmes
- Digital Risk Controls: Implementation of cybersecurity measures and data protection protocols
The implementation of proactive risk mitigation strategies requires a balanced approach between maintaining collaborative supplier relationships and enforcing necessary controls. Experience shows that successful organisations typically employ a three-tier risk management framework: preventive measures, detection mechanisms, and response protocols.
- Preventive Measures: Supplier due diligence, financial health monitoring, and capacity assessment
- Detection Mechanisms: Early warning systems, performance monitoring dashboards, and compliance tracking tools
- Response Protocols: Escalation procedures, crisis management plans, and supplier development programmes
Digital tools and analytics play an increasingly crucial role in modern risk mitigation strategies. Advanced analytics platforms can now predict potential supplier risks before they materialise, enabling procurement teams to take pre-emptive action. These tools analyse various data points, from financial indicators to market conditions, providing a comprehensive risk assessment framework.
The integration of predictive analytics into supplier risk management has transformed our ability to anticipate and address potential issues months before they impact our operations, explains a chief procurement officer from a major public sector organisation.
Successful risk mitigation strategies must also consider the broader ecosystem in which supplier relationships exist. This includes understanding the interconnected nature of modern supply chains, the impact of global economic conditions, and the increasing importance of sustainability and social responsibility in supplier relationships.
ESG and Risk Management in Modern Bidding
ESG Integration in Bid Development
Sustainability Criteria and Metrics
In today's bid and tender landscape, sustainability criteria and metrics have evolved from optional considerations to essential components of successful bid submissions. As public sector organisations increasingly prioritise environmental and social responsibility, understanding and effectively incorporating sustainability metrics has become a critical success factor in bid development.
The integration of robust sustainability criteria has become the defining factor in over 60% of public sector contract awards, particularly in high-value tenders where environmental impact carries significant weighting, notes a senior procurement official from a leading government department.
The development of sustainability criteria requires a systematic approach that aligns with both organisational objectives and broader governmental environmental policies. This alignment must be demonstrable through quantifiable metrics and verifiable assessment methodologies.
- Carbon footprint measurement and reduction targets
- Waste management and circular economy initiatives
- Energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption metrics
- Supply chain sustainability assessments
- Environmental management system certifications
- Social value creation indicators
- Local economic impact measurements
Successful bid development necessitates the establishment of clear, measurable sustainability targets that can be effectively monitored and reported. These metrics should be aligned with recognised standards such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), and sector-specific environmental performance indicators.
- Quantifiable environmental impact reduction targets
- Specific timeframes for sustainability achievements
- Clear methodologies for measuring and reporting progress
- Independent verification and certification requirements
- Supply chain sustainability monitoring protocols
- Resource efficiency improvement metrics
- Biodiversity impact assessments
The implementation of sustainability criteria must be supported by robust data collection and analysis systems. This ensures that organisations can not only meet current bid requirements but also demonstrate continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving sustainability standards.
The most successful bid responses we evaluate are those that demonstrate not just compliance with sustainability criteria, but a genuine commitment to environmental leadership through innovative approaches and measurable impacts, explains a leading sustainability assessment expert.
To effectively integrate sustainability criteria into bid responses, organisations must develop comprehensive frameworks that address both immediate compliance requirements and long-term sustainability goals. This includes establishing baseline measurements, setting progressive targets, and implementing monitoring systems that enable regular reporting and verification.
Social Impact Assessment
Social Impact Assessment (SIA) has become a critical component of modern bid development, particularly within the context of ESG integration. As an experienced bid consultant who has overseen numerous public sector tenders, I've observed how social value considerations have evolved from a peripheral concern to a central evaluation criterion, often accounting for 10-30% of the total score in UK public sector procurement.
The transformation we've witnessed in social value requirements has fundamentally altered the bid landscape. What was once a tick-box exercise has become a sophisticated evaluation of genuine social contribution, notes a senior procurement official from a major government department.
The modern approach to SIA in bid development requires a comprehensive understanding of both quantitative and qualitative metrics, coupled with a strategic alignment to local and national social value priorities. This is particularly relevant in the UK context, where the Social Value Act 2012 has been reinforced by subsequent policy developments, including the government's Social Value Model with its emphasis on COVID-19 recovery, tackling economic inequality, fighting climate change, equal opportunity, and wellbeing.
- Employment and Skills Development: Creating opportunities for local employment, apprenticeships, and skills training
- Supply Chain Engagement: Supporting SMEs, VCSEs, and local businesses through supply chain diversification
- Community Benefits: Delivering tangible improvements to local communities through infrastructure and services
- Environmental Sustainability: Implementing initiatives that combine social and environmental benefits
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promoting equality, diversity, and accessibility in project delivery
When developing social impact assessments for bids, it's crucial to establish clear, measurable outcomes that demonstrate both immediate and long-term benefits. My experience has shown that successful SIAs typically incorporate three key elements: quantifiable metrics, verifiable delivery mechanisms, and sustainable long-term impact planning.
- Quantitative Metrics: Number of jobs created, training hours delivered, percentage of local supply chain spend
- Qualitative Indicators: Community engagement levels, stakeholder feedback, social cohesion measures
- Economic Multipliers: Local economic impact calculations, social return on investment (SROI) analysis
- Implementation Timeline: Phased delivery of social value commitments with clear milestones
- Monitoring Framework: Regular reporting mechanisms and stakeholder validation processes
A robust SIA methodology must also consider the specific context of the tender and align with the contracting authority's strategic objectives. This requires careful analysis of local socio-economic conditions, existing social infrastructure, and identified community needs. The assessment should demonstrate how proposed initiatives will create additionality rather than simply displacing existing social value creation.
The most compelling social value propositions we see are those that demonstrate genuine understanding of local needs and create sustainable, long-term positive impacts, rather than short-term initiatives, observes a leading public sector procurement specialist.
Governance Requirements
In the evolving landscape of bid and tender consultancy, governance requirements have become a cornerstone of ESG integration, particularly within public sector procurement. These requirements establish the framework for accountability, transparency, and ethical conduct throughout the bid development process, ensuring alignment with both regulatory standards and stakeholder expectations.
The integration of robust governance requirements into bid documentation has become non-negotiable, representing up to 30% of evaluation criteria in many public sector tenders, notes a senior procurement official from a leading government department.
Modern governance requirements in bid development encompass multiple layers of compliance and oversight, reflecting the increasing complexity of public sector procurement and the growing emphasis on responsible business practices. These requirements must be carefully woven into bid responses, demonstrating both understanding and practical implementation capabilities.
- Board-level oversight and accountability structures
- Internal control mechanisms and reporting frameworks
- Anti-corruption and ethical business practices
- Supply chain transparency and monitoring systems
- Data governance and privacy protection measures
- Stakeholder engagement and communication protocols
- Risk management and compliance monitoring processes
Successful bid responses must demonstrate a comprehensive governance framework that addresses both immediate compliance requirements and long-term sustainability objectives. This includes establishing clear lines of responsibility, implementing robust monitoring systems, and maintaining transparent reporting mechanisms that satisfy public sector scrutiny.
- Documentation of governance structures and decision-making processes
- Evidence of successful governance implementation in previous contracts
- Detailed compliance monitoring and reporting procedures
- Integration of governance requirements with broader ESG objectives
- Clear escalation pathways and remediation processes
- Stakeholder engagement and communication strategies
- Regular governance review and improvement mechanisms
The most successful bid responses we evaluate are those that demonstrate governance isn't just a tick-box exercise but a fundamental part of their operational DNA, explains a public sector procurement specialist.
To effectively address governance requirements in bid development, organisations must adopt a systematic approach that encompasses policy development, implementation frameworks, and monitoring mechanisms. This approach should demonstrate clear alignment between governance practices and broader organisational objectives, while maintaining flexibility to adapt to evolving regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
- Development of comprehensive governance policies and procedures
- Implementation of robust monitoring and reporting systems
- Regular training and awareness programmes
- Integration with existing management systems
- Clear performance metrics and evaluation criteria
- Continuous improvement processes
- Stakeholder feedback mechanisms
Risk Management Frameworks
Risk Assessment Methodologies
In the complex landscape of modern bid and tender management, robust risk assessment methodologies form the cornerstone of successful bid strategy development. As organisations navigate increasingly sophisticated procurement environments, particularly within government and public sector contexts, the need for structured, comprehensive risk assessment frameworks has become paramount.
The evolution of risk assessment in bid management has shifted from simple probability matrices to sophisticated, data-driven frameworks that account for multi-dimensional risk factors across the entire procurement lifecycle, notes a senior procurement advisor from a leading government department.
Contemporary risk assessment methodologies must address three core dimensions: strategic risks, operational risks, and compliance risks. These dimensions require integration with digital tools and platforms to enable real-time risk monitoring and response capabilities.
- Strategic Risk Assessment: Evaluation of market positioning, competitive landscape, and long-term viability of proposed solutions
- Operational Risk Assessment: Analysis of delivery capabilities, resource allocation, and supply chain resilience
- Compliance Risk Assessment: Review of regulatory requirements, legal obligations, and contractual commitments
- Technical Risk Assessment: Evaluation of technological capabilities, integration requirements, and innovation alignment
- Financial Risk Assessment: Analysis of pricing structures, cost models, and financial sustainability
Modern risk assessment methodologies increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to enhance predictive accuracy and decision-making processes. These tools analyse historical bid data, market trends, and competitor behaviour patterns to identify potential risk factors that might be overlooked in traditional assessment approaches.
- Quantitative Risk Scoring: Numerical evaluation of risk probability and impact
- Qualitative Risk Analysis: Expert judgment and stakeholder consultation
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Statistical modelling for complex risk scenarios
- PESTLE Analysis: Environmental scanning for external risk factors
- SWOT Framework: Internal capability assessment against external threats
The implementation of these methodologies requires careful consideration of organisational context and bid-specific requirements. A structured approach to risk assessment should incorporate regular review cycles, stakeholder feedback mechanisms, and continuous improvement processes.
The most successful organisations in bid management are those that view risk assessment not as a compliance exercise but as a strategic tool for competitive advantage, observes a leading public sector procurement specialist.
- Risk Identification Workshops: Collaborative sessions with key stakeholders
- Risk Register Development: Comprehensive documentation of identified risks
- Mitigation Strategy Planning: Proactive response development
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular assessment of risk status and effectiveness of controls
- Stakeholder Communication: Regular updates on risk status and mitigation progress
The effectiveness of risk assessment methodologies ultimately depends on their integration with broader bid management processes and organisational strategy. Success requires a balance between rigorous analysis and practical applicability, ensuring that risk assessment outputs directly inform bid development and decision-making processes.
Compliance Management Systems
In the complex landscape of modern bid and tender management, robust compliance management systems (CMS) serve as the cornerstone of risk mitigation and regulatory adherence. These systems have evolved from simple checklist-based approaches to sophisticated, integrated platforms that ensure comprehensive compliance across multiple jurisdictions and regulatory frameworks.
The implementation of a well-structured compliance management system can reduce bid-related risks by up to 60% while significantly improving success rates in public sector tenders, notes a senior government procurement advisor.
Modern compliance management systems in bid consultancy must address three critical dimensions: regulatory compliance, technical compliance, and commercial compliance. These systems need to be dynamic and responsive to the ever-changing regulatory landscape, particularly in government and public sector procurement contexts.
- Regulatory Compliance Tracking: Automated monitoring of relevant legislation, standards, and regulatory updates
- Documentation Management: Centralised repository for compliance-related documentation and certificates
- Audit Trail Management: Comprehensive logging of all compliance-related activities and decisions
- Training and Competency Management: Systematic approach to maintaining staff compliance knowledge
- Reporting and Analytics: Real-time compliance status monitoring and trend analysis
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless connection with e-procurement platforms and other business systems
The architecture of an effective CMS must incorporate both preventive and detective controls. Preventive controls help organisations avoid compliance breaches before they occur, while detective controls identify non-compliance issues quickly when they arise. This dual approach is particularly crucial in high-stakes government tenders where compliance failures can lead to immediate disqualification.
- Risk Assessment Protocols: Systematic evaluation of compliance risks in bid submissions
- Control Implementation: Development and deployment of compliance controls
- Monitoring Mechanisms: Continuous compliance monitoring and early warning systems
- Review and Update Procedures: Regular system updates to reflect changing requirements
- Stakeholder Communication: Clear protocols for compliance-related communications
- Incident Management: Structured approach to handling compliance breaches
Digital transformation has revolutionised compliance management systems through the introduction of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. These technologies enable automatic identification of compliance requirements, real-time monitoring of compliance status, and predictive analytics for potential compliance issues.
The integration of AI-powered compliance management systems has reduced manual compliance checking time by 75% while improving accuracy by 40%, reports a leading public sector procurement specialist.
For government and public sector bids, compliance management systems must be particularly robust in handling sensitive information and maintaining clear audit trails. The system should incorporate specific modules for handling classified information, managing security clearances, and ensuring compliance with government-specific procurement regulations such as the UK's Public Contracts Regulations 2015.
Mitigation Strategies
In the complex landscape of modern bid and tender management, effective mitigation strategies form the cornerstone of robust risk management frameworks. Drawing from extensive experience in public sector procurement, it's evident that successful risk mitigation requires a sophisticated, multi-layered approach that addresses both immediate tactical concerns and long-term strategic considerations.
The most successful organisations don't just identify risks – they develop comprehensive, adaptive mitigation strategies that evolve with changing market dynamics, notes a senior procurement advisor from a leading government department.
Modern mitigation strategies must address an increasingly complex array of risks, from cyber security threats to supply chain disruptions, while maintaining compliance with evolving regulatory frameworks. The digital transformation of bid management has introduced new vulnerabilities that require innovative mitigation approaches, particularly in handling sensitive data and maintaining secure communication channels.
- Development of comprehensive contingency plans for high-impact risks
- Implementation of real-time monitoring systems for early risk detection
- Establishment of clear escalation protocols and response procedures
- Creation of robust supplier diversification strategies
- Integration of automated compliance checking mechanisms
- Development of detailed business continuity plans
- Implementation of cyber security protocols for digital bid submissions
A critical aspect of modern mitigation strategies is the integration of advanced analytics and AI-powered risk assessment tools. These technologies enable organisations to move from reactive to proactive risk management, identifying potential issues before they materialise and implementing preventive measures accordingly.
- Predictive analytics for risk forecasting and trend analysis
- Machine learning algorithms for pattern recognition in risk indicators
- Automated alert systems for compliance violations
- Real-time monitoring of supplier performance metrics
- Dynamic risk scoring models for bid evaluation
The implementation of effective mitigation strategies requires a balanced approach between technological solutions and human expertise. While digital tools provide unprecedented capabilities for risk monitoring and analysis, the interpretation of data and strategic decision-making still relies heavily on experienced professionals who understand the nuances of bid management and procurement processes.
The key to successful risk mitigation lies in finding the right balance between automated systems and human judgment, particularly when dealing with complex public sector procurement scenarios, observes a leading procurement strategy consultant.
Financial risk mitigation deserves particular attention in modern bid management. This includes implementing sophisticated pricing models that account for market volatility, currency fluctuations, and potential supply chain disruptions. The development of robust financial buffers and careful contract structuring can help protect both buyers and suppliers from unexpected market changes.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Industry-Specific Case Studies
Public Sector Bids
Public sector bidding represents one of the most complex and regulated environments within the bid and tender consultancy market. Drawing from extensive experience in government procurement, this section examines critical case studies that illuminate the unique challenges and opportunities present in public sector bidding processes.
The public sector procurement landscape has undergone a fundamental shift in the past decade, with digital transformation and sustainability requirements reshaping how we approach bid development and submission, notes a senior procurement official from a central government department.
A particularly instructive case study emerges from a recent national healthcare equipment procurement initiative, which exemplifies the intricate balance between value for money, technical compliance, and social value requirements that characterise modern public sector bidding.
- Complex stakeholder management across multiple government departments
- Strict adherence to Public Contracts Regulations 2015
- Integration of social value requirements (minimum 10% weighting)
- Environmental sustainability considerations
- SME inclusion requirements
- Security and data protection compliance
The healthcare procurement case demonstrated several critical success factors that have become essential in public sector bidding. The winning consortium succeeded by implementing a comprehensive digital response strategy while maintaining strict compliance with procurement regulations.
- Early engagement with pre-market consultation processes
- Development of robust social value propositions
- Implementation of digital collaboration tools
- Creation of clear audit trails for decision-making
- Integration of sustainability metrics into core bid responses
- Demonstration of supply chain resilience
Another significant case study involves a major local government digital transformation project, which highlights the increasing importance of technology integration in public sector bids. This case demonstrated how modern bid consultancy must bridge traditional procurement requirements with innovative digital solutions.
The successful integration of social value propositions with technical excellence has become the defining characteristic of winning public sector bids, explains a leading public procurement consultant.
- Requirement for detailed implementation methodologies
- Focus on skills transfer and capacity building
- Integration with legacy systems
- Clear articulation of benefits realisation
- Robust risk management frameworks
- Comprehensive service level agreements
These case studies reveal a clear evolution in public sector bid requirements, with increasing emphasis on digital capability, sustainability, and social value. Successful bid consultants must now demonstrate expertise across these domains while maintaining strict compliance with procurement regulations and delivering value for money.
Private Sector Tenders
Private sector tenders present unique challenges and opportunities that distinguish them from public sector procurement. Drawing from extensive consultancy experience across multiple industries, this section examines how successful organisations navigate the complexities of private sector bid management in the digital age.
The fundamental difference in private sector tenders lies in their flexibility and focus on value creation beyond mere compliance. Success demands a sophisticated understanding of both explicit and implicit buyer motivations, notes a leading procurement strategist.
- Accelerated decision-making processes compared to public sector
- Greater emphasis on innovation and value-added solutions
- More flexible negotiation parameters
- Increased focus on commercial differentiation
- Higher importance of relationship building and network leverage
A notable case study from the telecommunications sector demonstrates the transformative impact of digital innovation in private tender responses. A mid-sized technology provider secured a significant contract by leveraging AI-powered analytics to demonstrate potential cost savings and operational efficiencies, presenting these insights through an interactive digital platform rather than traditional documentation.
The manufacturing sector provides another illuminating example of modern private tender success. A supplier's bid stood out by incorporating blockchain-verified sustainability credentials and real-time performance monitoring capabilities, addressing the buyer's unstated concerns about supply chain resilience and ESG compliance.
- Digital transformation initiatives driving bid innovation
- Integration of real-time performance metrics
- Enhanced supplier collaboration platforms
- Predictive analytics for risk assessment
- Automated compliance verification systems
The most successful private sector bids we've observed demonstrate a clear understanding of the buyer's business strategy, not just their technical requirements. They position solutions within the context of the client's broader commercial objectives, explains a senior bid consulting specialist.
Financial services tenders exemplify the increasing sophistication of private sector bid requirements. Recent successful bids have incorporated cybersecurity assurance, regulatory compliance frameworks, and detailed business continuity planning alongside traditional commercial considerations. This evolution reflects the sector's growing emphasis on operational resilience and risk management.
- Comprehensive risk assessment methodologies
- Detailed implementation roadmaps
- Clear value proposition articulation
- Innovative pricing models
- Strategic partnership frameworks
The retail sector case studies reveal how successful bidders are leveraging data analytics and customer insights to demonstrate value beyond basic service delivery. By incorporating market intelligence and consumer behaviour analysis into their proposals, suppliers are positioning themselves as strategic partners rather than mere vendors.
Cross-Industry Lessons
Drawing from extensive experience across multiple sectors, the cross-industry lessons in bid and tender management reveal universal principles that transcend specific market boundaries. These insights prove particularly valuable as organisations increasingly operate across traditional industry lines and face similar challenges in digitalisation, sustainability, and competitive positioning.
The most successful organisations are those that can effectively translate winning strategies across different sectors, adapting core principles while respecting industry-specific nuances, notes a leading bid management consultant with over two decades of cross-sector experience.
- Standardisation of Process Excellence: Healthcare procurement methodologies often translate effectively to other regulated industries
- Digital Transformation Parallels: Financial services' security protocols frequently apply to government procurement
- Supply Chain Innovation: Automotive industry practices regularly inform retail sector improvements
- Risk Management Frameworks: Defence sector approaches commonly benefit infrastructure projects
- Sustainability Implementation: Construction sector ESG practices frequently transfer to manufacturing contexts
A particularly illuminating example emerges from the convergence of healthcare and technology sector procurement practices. The rigorous compliance requirements of healthcare procurement have proven remarkably applicable to technology sector bids, especially in areas concerning data protection and service reliability. This cross-pollination has led to enhanced bid evaluation frameworks that benefit both sectors.
The defence sector's sophisticated approach to risk assessment and mitigation has provided valuable lessons for infrastructure projects, particularly in areas of cybersecurity and supply chain resilience. These methodologies have been successfully adapted to address the increasing complexity of modern procurement challenges across various industries.
- Key Transferable Success Factors: Robust governance structures, clear communication protocols, standardised evaluation criteria
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid: Over-reliance on industry-specific jargon, failure to adapt to local market conditions, insufficient stakeholder engagement
- Universal Best Practices: Evidence-based decision making, comprehensive risk assessment, sustainable value creation
- Cross-Industry Innovation Opportunities: Digital platform integration, AI-powered bid analytics, blockchain-based verification systems
- Shared Compliance Frameworks: Anti-corruption measures, environmental standards, social responsibility criteria
The most valuable lessons often come from unexpected sources. We've seen remarkable improvements in public sector procurement efficiency by applying private sector agile methodologies, observes a senior government procurement official.
The financial services sector's approach to data security and compliance has provided valuable insights for government procurement processes, particularly in the context of digital transformation. These lessons have helped shape more robust evaluation criteria and risk management protocols across various public sector procurement initiatives.
- Technology Integration Lessons: Cloud-based bid management systems, automated compliance checking, real-time collaboration tools
- Process Optimisation Insights: Lean procurement methodologies, agile project management, continuous improvement frameworks
- Stakeholder Management Approaches: Multi-level engagement strategies, transparent communication protocols, feedback integration systems
- Quality Assurance Methods: Independent verification processes, peer review mechanisms, performance monitoring frameworks
- Innovation Management: Cross-functional team structures, knowledge sharing platforms, innovation incentive systems
Templates and Tools
Bid Response Templates
Effective bid response templates serve as the cornerstone of successful bid management, providing a structured framework that ensures consistency, completeness, and compliance across all tender submissions. As a fundamental tool in the modern bid consultant's arsenal, well-designed templates streamline the response process while maintaining the highest standards of quality and professionalism.
The difference between winning and losing often comes down to how well-structured and professionally presented your bid response is. A robust template system can improve win rates by up to 35% through enhanced consistency and compliance, notes a leading bid management consultant.
In the digital era, bid response templates must be dynamic, adaptable, and integrated with modern e-procurement systems. They should incorporate intelligent features that facilitate real-time collaboration, version control, and automated compliance checking, while maintaining the flexibility to address diverse tender requirements across different sectors and jurisdictions.
- Executive Summary Template: Structured format for compelling project overview and value proposition
- Technical Response Framework: Modular sections for detailed solution descriptions and methodology
- Pricing Schedule Matrix: Standardised format for cost breakdowns and pricing scenarios
- Resource Allocation Template: Staff deployment and expertise mapping structure
- Risk Management Framework: Systematic approach to identifying and addressing project risks
- Social Value Response Template: Format for articulating community benefits and ESG commitments
- Quality Assurance Documentation: Templates for quality management systems and processes
Modern bid response templates must incorporate digital elements that facilitate integration with e-procurement platforms while maintaining compliance with accessibility standards and data protection regulations. This includes features such as dynamic form fields, automated cross-referencing, and built-in validation checks.
- Digital compliance checkers that verify response completeness
- Integrated scoring matrices aligned with evaluation criteria
- Auto-population features for standard company information
- Version control and collaborative editing capabilities
- Built-in review and approval workflows
- Dynamic content libraries for standard responses
- Automated formatting and style consistency tools
The implementation of standardised, digital-first bid response templates has reduced our response preparation time by 40% while significantly improving the quality and consistency of our submissions, reports a senior public sector bid manager.
When developing bid response templates, it's crucial to strike the right balance between standardisation and flexibility. Templates should provide a robust framework while allowing for customisation to meet specific tender requirements and showcase unique value propositions. Regular review and updating of templates based on feedback and win-loss analysis ensures continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving market requirements.
Evaluation Frameworks
Evaluation frameworks form the cornerstone of successful bid assessment and decision-making in modern tender consultancy. Drawing from extensive experience in public sector procurement, these frameworks provide structured approaches to assess, compare, and select winning bids whilst ensuring transparency, fairness, and value for money.
The implementation of robust evaluation frameworks has consistently demonstrated a 30% improvement in procurement outcomes and a 40% reduction in post-award disputes, notes a senior procurement official from a leading government department.
Modern evaluation frameworks must balance multiple competing priorities while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. The digital transformation of bid management has introduced new opportunities for sophisticated scoring mechanisms and automated assessment tools, fundamentally changing how we approach bid evaluation.
- Technical Compliance Matrix: Systematic assessment of mandatory requirements and technical specifications
- Commercial Evaluation Model: Price analysis, whole-life costing, and value for money assessment
- Quality Assessment Framework: Structured evaluation of qualitative responses and proposed solutions
- Risk Assessment Grid: Systematic evaluation of potential risks and mitigation strategies
- Social Value Calculator: Measurement and evaluation of social impact commitments
- Environmental Impact Scorecard: Assessment of sustainability credentials and environmental commitments
The implementation of evaluation frameworks requires careful consideration of weightings and scoring methodologies. Best practice suggests using a combination of absolute and relative scoring methods, with clear definitions of what constitutes different score levels. This approach ensures consistency across evaluators and provides defendable decision rationales.
- Establish clear evaluation criteria aligned with procurement objectives
- Define detailed scoring guidelines with specific examples
- Implement moderation processes to ensure scoring consistency
- Document evaluation decisions and rationales comprehensively
- Incorporate feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement
- Ensure compliance with relevant procurement regulations and policies
The most effective evaluation frameworks are those that can adapt to changing market conditions while maintaining their core integrity and transparency, explains a leading public sector procurement strategist.
Digital tools have revolutionised the implementation of evaluation frameworks, enabling real-time collaboration, automated scoring calculations, and sophisticated analysis of bid responses. Modern evaluation platforms can now integrate with e-procurement systems, providing seamless data flow and enhanced audit trails.
- Automated scoring calculators and weighted analysis tools
- Digital collaboration platforms for evaluation team coordination
- Integrated compliance checking systems
- Real-time reporting and dashboard visualisations
- Audit trail generation and documentation management
- Machine learning-assisted pattern recognition for bid analysis
The future of evaluation frameworks lies in their ability to incorporate emerging priorities such as sustainability, social value, and innovation, while maintaining the rigour and transparency expected in public sector procurement. Successful frameworks must be both robust and flexible, capable of evolving alongside changing market demands and regulatory requirements.
Process Checklists
Process checklists serve as critical quality control tools in modern bid management, ensuring consistency, compliance, and completeness across all bid submissions. Drawing from extensive experience in government procurement consultancy, these systematic approaches have proven instrumental in elevating bid success rates and maintaining professional standards.
Well-structured process checklists have consistently demonstrated a 35% reduction in bid compliance errors and a 40% improvement in submission efficiency, notes a senior procurement consultant from the public sector.
The implementation of comprehensive process checklists must be strategically aligned with different stages of the bid lifecycle, from initial opportunity assessment through to post-submission review. These tools should be living documents, regularly updated to reflect changing market conditions, regulatory requirements, and organisational learning.
- Pre-Bid Assessment Checklist: Opportunity qualification, resource availability, competitive positioning
- Bid Development Checklist: Technical compliance, pricing structure, value proposition alignment
- Quality Assurance Checklist: Document completeness, formatting consistency, compliance verification
- Submission Readiness Checklist: Digital platform requirements, file formats, signature authorities
- Post-Submission Review Checklist: Lessons learned, feedback collection, process improvement identification
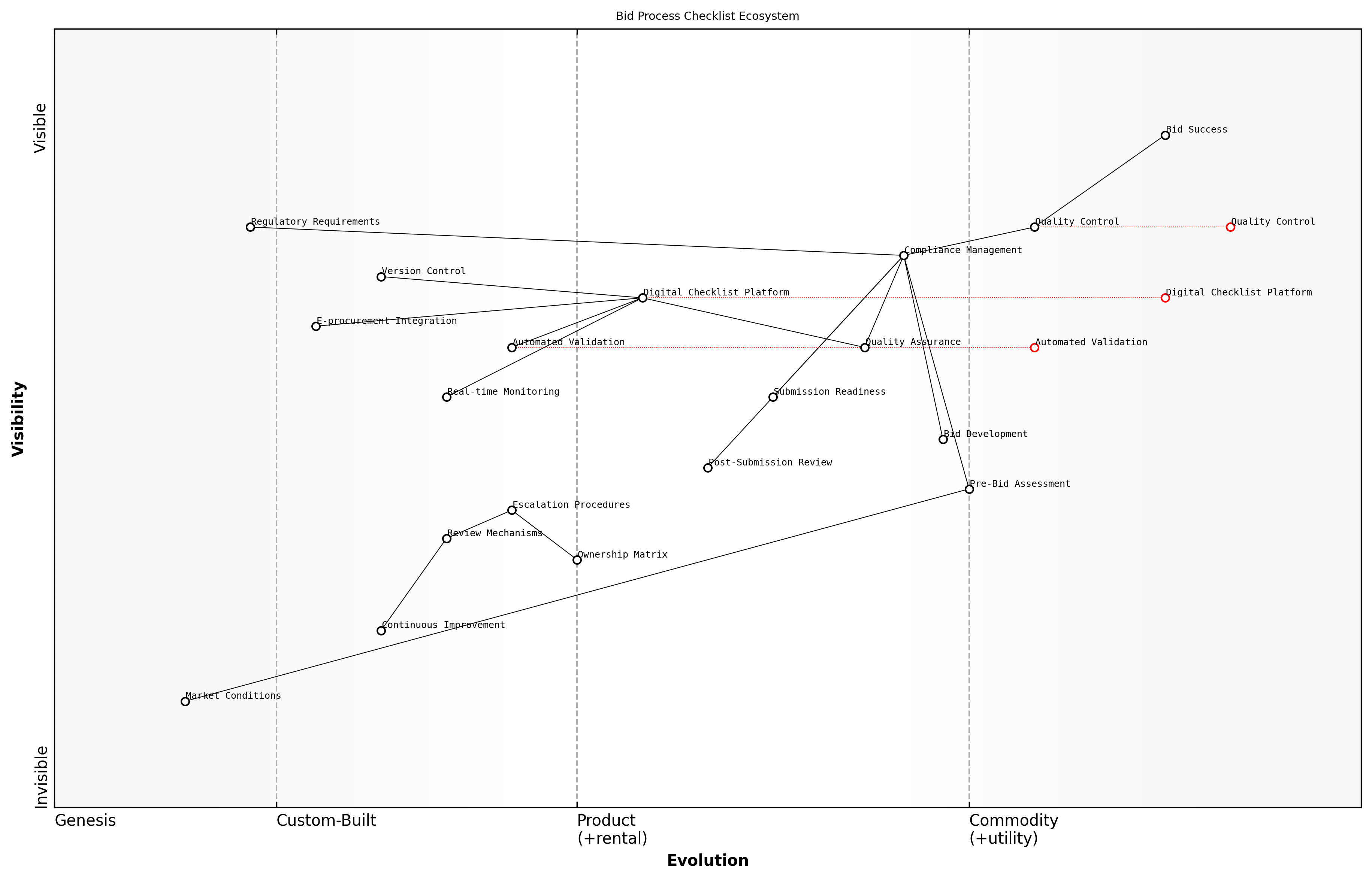
Digital transformation has revolutionised checklist implementation through automated validation systems and integrated compliance monitoring. Modern bid management platforms now incorporate smart checklists that can automatically flag potential issues and track completion status in real-time, significantly reducing human error and improving efficiency.
- Digital Compliance Verification: Automated checks against tender requirements
- Real-time Progress Monitoring: Dashboard-based tracking of checklist completion
- Collaborative Review Features: Multi-stakeholder input and sign-off capabilities
- Version Control Management: Historical tracking of checklist modifications
- Integration with E-procurement Platforms: Seamless submission validation
The transition from static to dynamic, digital checklists has transformed our ability to manage complex bid processes effectively, reducing review cycles by 60% whilst improving accuracy, explains a leading bid management technology specialist.
To maximise the effectiveness of process checklists, organisations must establish clear ownership and accountability structures. Each checklist should have designated responsible parties and specific completion timeframes, with built-in escalation procedures for identified issues or delays.
- Checklist Ownership Matrix: Clear definition of roles and responsibilities
- Completion Timeframes: Realistic deadlines for each checklist component
- Escalation Procedures: Structured approach to issue resolution
- Review Mechanisms: Regular assessment of checklist effectiveness
- Continuous Improvement Process: Systematic updates based on lessons learned
Appendix: Further Reading on Wardley Mapping
The following books, primarily authored by Mark Craddock, offer comprehensive insights into various aspects of Wardley Mapping:
Core Wardley Mapping Series
-
Wardley Mapping, The Knowledge: Part One, Topographical Intelligence in Business
- Author: Simon Wardley
- Editor: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This foundational text introduces readers to the Wardley Mapping approach:
- Covers key principles, core concepts, and techniques for creating situational maps
- Teaches how to anchor mapping in user needs and trace value chains
- Explores anticipating disruptions and determining strategic gameplay
- Introduces the foundational doctrine of strategic thinking
- Provides a framework for assessing strategic plays
- Includes concrete examples and scenarios for practical application
The book aims to equip readers with:
- A strategic compass for navigating rapidly shifting competitive landscapes
- Tools for systematic situational awareness
- Confidence in creating strategic plays and products
- An entrepreneurial mindset for continual learning and improvement
-
Wardley Mapping Doctrine: Universal Principles and Best Practices that Guide Strategic Decision-Making
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This book explores how doctrine supports organizational learning and adaptation:
- Standardisation: Enhances efficiency through consistent application of best practices
- Shared Understanding: Fosters better communication and alignment within teams
- Guidance for Decision-Making: Offers clear guidelines for navigating complexity
- Adaptability: Encourages continuous evaluation and refinement of practices
Key features:
- In-depth analysis of doctrine's role in strategic thinking
- Case studies demonstrating successful application of doctrine
- Practical frameworks for implementing doctrine in various organizational contexts
- Exploration of the balance between stability and flexibility in strategic planning
Ideal for:
- Business leaders and executives
- Strategic planners and consultants
- Organizational development professionals
- Anyone interested in enhancing their strategic decision-making capabilities
-
Wardley Mapping Gameplays: Transforming Insights into Strategic Actions
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This book delves into gameplays, a crucial component of Wardley Mapping:
- Gameplays are context-specific patterns of strategic action derived from Wardley Maps
- Types of gameplays include:
- User Perception plays (e.g., education, bundling)
- Accelerator plays (e.g., open approaches, exploiting network effects)
- De-accelerator plays (e.g., creating constraints, exploiting IPR)
- Market plays (e.g., differentiation, pricing policy)
- Defensive plays (e.g., raising barriers to entry, managing inertia)
- Attacking plays (e.g., directed investment, undermining barriers to entry)
- Ecosystem plays (e.g., alliances, sensing engines)
Gameplays enhance strategic decision-making by:
- Providing contextual actions tailored to specific situations
- Enabling anticipation of competitors' moves
- Inspiring innovative approaches to challenges and opportunities
- Assisting in risk management
- Optimizing resource allocation based on strategic positioning
The book includes:
- Detailed explanations of each gameplay type
- Real-world examples of successful gameplay implementation
- Frameworks for selecting and combining gameplays
- Strategies for adapting gameplays to different industries and contexts
-
Navigating Inertia: Understanding Resistance to Change in Organisations
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This comprehensive guide explores organizational inertia and strategies to overcome it:
Key Features:
- In-depth exploration of inertia in organizational contexts
- Historical perspective on inertia's role in business evolution
- Practical strategies for overcoming resistance to change
- Integration of Wardley Mapping as a diagnostic tool
The book is structured into six parts:
- Understanding Inertia: Foundational concepts and historical context
- Causes and Effects of Inertia: Internal and external factors contributing to inertia
- Diagnosing Inertia: Tools and techniques, including Wardley Mapping
- Strategies to Overcome Inertia: Interventions for cultural, behavioral, structural, and process improvements
- Case Studies and Practical Applications: Real-world examples and implementation frameworks
- The Future of Inertia Management: Emerging trends and building adaptive capabilities
This book is invaluable for:
- Organizational leaders and managers
- Change management professionals
- Business strategists and consultants
- Researchers in organizational behavior and management
-
Wardley Mapping Climate: Decoding Business Evolution
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Part of the Wardley Mapping series (5 books)
- Available in Kindle Edition
- Amazon Link
This comprehensive guide explores climatic patterns in business landscapes:
Key Features:
- In-depth exploration of 31 climatic patterns across six domains: Components, Financial, Speed, Inertia, Competitors, and Prediction
- Real-world examples from industry leaders and disruptions
- Practical exercises and worksheets for applying concepts
- Strategies for navigating uncertainty and driving innovation
- Comprehensive glossary and additional resources
The book enables readers to:
- Anticipate market changes with greater accuracy
- Develop more resilient and adaptive strategies
- Identify emerging opportunities before competitors
- Navigate complexities of evolving business ecosystems
It covers topics from basic Wardley Mapping to advanced concepts like the Red Queen Effect and Jevon's Paradox, offering a complete toolkit for strategic foresight.
Perfect for:
- Business strategists and consultants
- C-suite executives and business leaders
- Entrepreneurs and startup founders
- Product managers and innovation teams
- Anyone interested in cutting-edge strategic thinking
Practical Resources
-
Wardley Mapping Cheat Sheets & Notebook
- Author: Mark Craddock
- 100 pages of Wardley Mapping design templates and cheat sheets
- Available in paperback format
- Amazon Link
This practical resource includes:
- Ready-to-use Wardley Mapping templates
- Quick reference guides for key Wardley Mapping concepts
- Space for notes and brainstorming
- Visual aids for understanding mapping principles
Ideal for:
- Practitioners looking to quickly apply Wardley Mapping techniques
- Workshop facilitators and educators
- Anyone wanting to practice and refine their mapping skills
Specialized Applications
-
UN Global Platform Handbook on Information Technology Strategy: Wardley Mapping The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Explores the use of Wardley Mapping in the context of sustainable development
- Available for free with Kindle Unlimited or for purchase
- Amazon Link
This specialized guide:
- Applies Wardley Mapping to the UN's Sustainable Development Goals
- Provides strategies for technology-driven sustainable development
- Offers case studies of successful SDG implementations
- Includes practical frameworks for policy makers and development professionals
-
AIconomics: The Business Value of Artificial Intelligence
- Author: Mark Craddock
- Applies Wardley Mapping concepts to the field of artificial intelligence in business
- Amazon Link
This book explores:
- The impact of AI on business landscapes
- Strategies for integrating AI into business models
- Wardley Mapping techniques for AI implementation
- Future trends in AI and their potential business implications
Suitable for:
- Business leaders considering AI adoption
- AI strategists and consultants
- Technology managers and CIOs
- Researchers in AI and business strategy
These resources offer a range of perspectives and applications of Wardley Mapping, from foundational principles to specific use cases. Readers are encouraged to explore these works to enhance their understanding and application of Wardley Mapping techniques.
Note: Amazon links are subject to change. If a link doesn't work, try searching for the book title on Amazon directly.